Abstract
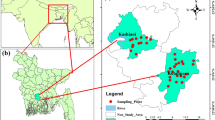
The present study investigates the hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater quality in Agastheeswaram taluk of Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, India. A total of 69 groundwater samples were collected during pre- and post-monsoon periods of 2011–2012. The groundwater quality assessment has been carried out by evaluating the physicochemical parameters such as pH, EC, TDS, HCO3 −, Cl−, SO4 2−, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ for both the seasons. Based on these parameters, groundwater has been assessed in favor of its suitability for drinking and irrigation purpose. Dominant cations for both the seasons are in the order of Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ while the dominant anions for post monsoon and pre monsoon have the trends of Cl− > HCO3 − > SO4 2− and HCO3 − > Cl− > SO4 2−, respectively. Analytical results observed from various indices reveal that the groundwater quality is fairly good in some places. Analytical results of few samples show that they are severely polluted and incidentally found to be near the coasts, estuaries and salt pans in the study area. The Gibbs plot indicates that the majority of groundwater samples fall in rock dominant region, which indicates rock water interaction in the study area. The United States salinity (USSL) diagram shows that the groundwater is free from sodium hazards but the salinity hazard varies from low to very high throughout the study area. This reveals that the groundwater is moderately suitable for agricultural activities. The observed chemical variations in pre-monsoon and post-monsoon seasons may be the effect to rock-water interactions, ion-exchange reactions, and runoff of fertilizers from the surrounding agricultural lands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghazadeh N., Nojavan M., and Mogaddam A.A. (2011) Effects of road-deicing salt (NaCl) and saline water on water quality in the Urmia area, northwest of Iran [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 5, 565–570.
Appelo C.A.J. and Postma D. (1993) Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution [M]. Rotterdam: AA Balkema.
APHA (1989) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water (19th edition) [Z]. American Public Health Association. Washington, DC.
Ballukraya P.N. and Ravi R. (1995) Hydrogeology of Madras City aquifer [J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India. 45, 87–96.
BIS (1991) Indian Standard Specification for Drinking Water [Z]. IS:10500, Bureau of Indian Standards.
CGWB (2008) Technical Report, Central Ground Water Board [R].
Eaton F.M. (1950) Significance of carbonate in irrigation waters [J]. Soil Science. 69, 123–133.
Fetter C.W. (1994) Applied Hydrogeology (Third edition) [Z]. pp.310. Macmillan College Publication, New York.
Garrels R.M. and Mackenzie F.T. (1967) Origin of the Chemical Compositions of Some Springs and Lakes (ed. Stumm W.). Equilibrium concepts in natural water systems [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 222–242.
Gibbs R.J. (1970) Mechanisms controlling world’s water chemistry [J]. Science. 170, 1088–1099.
GSI (2005) Geology and Mineral Map of Kanyakumari District (eds. Sundaram R., Ranganathan M., and Vasudevan D.) [Z]. Geological Survey of India.
Hounslow A.W. (1995) Water Quality Data—Analysis and Interpretation [C]. pp.56. Lewis publishers, USA.
Jameel A.A. and Hussain A.Z. (2012) Monitoring the quality of groundwater on the bank of Uyyakondan channel of River Cauvery at Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu—India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 183, 103–111.
Karnath K.R. (1987) Groundwater Assessment, Development and Management [C]. Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
Li Siliang, Liu Congqiang, Tao Faxiang, Lang Yunchao, and Han Guilin (2005) Carbon biogeochemistry of ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China [J]. Ground Water. 43, 494–499.
Mandel and Shiftan (1981) Ground Water Resources Academic [C]. pp.269. New York.
O’Brien J.E. and Majewski J.C. (2002) Effects of deicing salt on groundwater characteristics [J]. Environmental Letters. 8, 303–313.
Perumal S.B. and Thamarai P. (2008) Groundwater quality after Tsunami in coastal area of Kanyakumari, South Tamilnadu, India [J]. International Journal of Applied Environmental Sciences. 3, 37–55.
Piper A.M. (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis [J]. Transactions—American Geophysical Union. 25, 914–923.
Prasanna M.V., Chidambaram S., Senthil Kumar G., Ramanathan A.L., and Nainwal H.C. (2011) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater in Neyveli Basin, Cuddalore District, South India [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 4, 319–330.
PWD (2005) Groundwater Perspectives: A Profile of Kanyakumari District, Tamil Nadu [Z]. Tamil Nadu Public Works Department, India.
Raju N.J., Shukla U.K., and Ram P. (2011) Hydrogeochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Varanasi: A fast-urbanizing center in Uttar Pradesh, India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 173, 279–300.
Ramesh K. and Elango L. (2012) Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 184, 3887–3899.
Ramkumar T., Venkatramanan S., Anithamary I., and Ibrahim S.M.S. (2012) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical parameters and quality assessment of the groundwater in Kottur blocks, Tiruvarur district, Tamilnadu, India [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 6, 101–108.
Richards L.A. (1954) Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils [C]. pp.160. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 60, Washington.
Sadhana C. (1994) Water pollution from mass bathing in River Mandakini during Chitrakoot Deepawali mela 1993 [J]. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection. 14, 758–765.
Sami K. (1992) Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa [J]. Journal of Hydrology. 139, 27–48.
Sawyer C.N., Mccarty P.L., and Parkin G.F. (2003) Chemistry for Environmental Engineering and Science. (5th edition). [M]. pp.752. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Schoeller H. (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigations and Development [M]. pp.54–83. UNESCO, Paris.
Srinivasamoorthy K., Nanthakumar C., Vasanthavigar M., Vijayaraghavan K., Rajivgandhi R., Chidambaram S., Anandhan P., Manivannan R., and Vasudevan S. (2011) Groundwater quality assessment from a hard rock terrain, Salem District of Tamilnadu, India [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 4, 91–102.
Srinivasamoorthy K., Vasanthavigar M., Vijayaraghavan K., Sarathidasan R., and Gopinath S. (2013) Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region of Cuddalore District, Tamilnadu, India: Implication for quality assessment [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 6, 441–454.
Stallard R.F. and Edmond J.M. (1983) Geochemistry of the Amazon River. The influence of the geology and weathering environment on dissolved load [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres. 88, 9671–9688.
Subba Rao N. (2008) Factors controlling the salinity in groundwaters from a part of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 138, 327–341.
Subramani T., Elango L., and Damodarasamy R. (2005) Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Chithar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India [J]. Environmental Geology. 47, 1099–1110.
Subramanian A. (2011) Ground water quality assessment of Nagercoil Town [J]. Journal of Environment and Earth Science. 1.
Latha S. and Rao N. (2012) An integrated approach to assess the quality of groundwater in a coastal aquifer of Andhra Pradesh, India [J]. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences. 66, 2143–2169
Jacob C.T., Azariah J., and Roy A.G.V. (1999) Impact of textile industries on River Noyyal and riverine groundwater quality of Tirupur, India [J]. Pollution Research. 18, 359–368.
Todd D.K. (1980) Groundwater Hydrology (2nd edition) [M]. Wiley, New York.
Tyagi S.K., Datta P.S., and Pruthi N.K. (2009) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater and its suitability in the intensive agricultural area of Muzaffarnagar District, Uttar Pradesh, India [J]. Environmental Geology. 56, 901–912.
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2000) Classification of Natural Ponds and Lakes [Z]. Department of the Interior, Washington DC.
USRSL (US Regional Salinity Laboratory) (1954) Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils [Z]. pp.1–160.
Vasanthavigar M., Srinivasamoorthy K., Vijayaragavan K., Rajiv Ganthi R., Chidambaram S., Anandhan P., Manivannan R., and Vasudevan S. (2010) Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar Sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 171, 595–609.
WHO (1997) Guideline for Drinking Water Quality (Recommendations) [Z]. (Vol. 1, 2nd ed). Geneva.
Wilcox L.V. (1955) Classification and Use of Irrigation waters. USDA, Circular 969, Washington DC, USA.
Zhu Gaofeng, Su Yonghong, Huang Chunlin, Qi Feng, and Liu Zhiguang (2010) Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences. 60, 139–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, Y., Hudson, O.D., Stanley, R.A. et al. Quality assessment and hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in Agastheeswaram taluk, Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, India. Chin. J. Geochem. 33, 221–235 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0681-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0681-3