Abstract
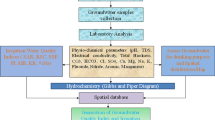
The aim of this work is to evaluate the hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of the lower Benue Through in Nigeria as well as to evaluate the variation in groundwater chemistry data and the suitability of the groundwater for drinking and other domestic purposes. This was based on chemical analyses of 44 water samples from existing wells and boreholes in the study area. From the statistical analysis (wide ranges, median and standard deviation), it is obvious that there are significant variations in the quality/composition of groundwater in the period of sampling. The calculated SAR, Na% and RSC values indicated that the water is of excellent to good quality and is suitable for irrigation. Na and HCO3 are dominant with respect to the chemical composition of the groundwater. On the basis of water chemistry, hydrochemical indices and factor analysis the dominant controls or processes affecting the distribution of geochemical variables in the study area have been shown to be water/rock interaction which is mainly controlled by carbonate and silicate dissolution as well as anthropogenic influence to a lesser extent. Additional processes include cation exchange reactions and reverse ion exchange to a minor extent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benkhelil J. (1982) Benue Trough and Benue Chain [J]. Geol. Mag. 119, 155–168.
Berner E.K. and Berner R.A (1987) The Global Water Cycle [M]. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
Burke K.C., Dessauvagie T.F.J., and Whiteman A.J. (1970) Geological history of Benue valley and the adjacent areas. In African Geology (eds. Dessauvagie T.F.J. and Whiteman A.J.) [M]. pp.187–206. Ibadan Univ. Press, Ibadan.
Cerling T.E., Pederson B.L., and Damm K.L.V. (1989) Sodium-calcium ion exchange in the weathering of shales: Implications for global weathering budgets [J]. Geology. 17, 552–554.
Custodio F. (1983) Hydrogeoquimica. In Hidrologia Subterrainca (Section 10) (eds. Custodio E. and Llamas M.R.). [M]. Barcelona, Spain.
Davis J.C. (1986) Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology. Wiley, New York.
Dessauvagie T.F.J. (1975) Explanatory notes to the geological map of Nigeria [J]. Nig. Jour. of Min. Geo. 19, 11–28.
Datta P.S. and Tyagi S.K. (1996) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in Delhi area: Chemical weathering, process and groundwater flow regime [J]. Jour. Geol. Soc. India. 47, 179–189.
Edet A.E. and Ekpo B.O. (2008) Hydrogeochemistry of a fractured aquifer in the Ogoja/Obudu area of southeastern Nigeria [J]. Adelana. 12, 391–403.
Ekwere S.J. and Ukpong E.E. (1994) Geochemistry of saline groundwater in Ogoja, Cross River State, Nigeria [J]. Jour. of Min. and Geol. 29, 277–282.
Ekwueme B.N. and Kroner A. (2006) Single zircon ages of Nigerian gneisses and granulites in the Obudu Plateau: Timing of granulite-facies metamorphism southeastern Nigeria [J]. Jour. of Afri. Ear. Sci. 44, 459–469.
Ettazarini S. (2005) Processes of water-rock interaction in the Turonian aquifer of Oum Er-Rabia Basin, Morocco [J]. Environ. Geol. 49, 293–299.
Fisher R.S. and Mullican W.F.I (1997) Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulphate and sodium-chloride beneath the Northern Chihuahuan desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas [J]. USA Hydrogeol Jour. 10, 455–474
Garcia M.G., Hidalgo M.D.V., and Blesa M.A. (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of Trucman province, Argentina [J]. Hygrolgeo J. 9, 597–610.
Grant N.L. (1971) South Atlantic, Benue Trough and Gulf of Guinea Cretaceous triple Junction [J]. Geol. Soc. of Amer. Bull. 28, 2295–2298.
Hem J.D. (1985) Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water [R]. pp.2254. United States Geological Survey (USGS) Water Supply Paper.
Hoque M. and Nwajide C.S. (1984) Tectono-sedimentological evolution of an intratonic basin (aulacogen): The case of the Benue Trough of Nigeria [J]. Jour. of Min. Geol. 21, 19–26
Kumar M., Ramanathan A., Rao S.O., and Kumar B. (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India [J]. Environ. Geol. 50, 1025–1039.
Matthess G. and Harvey J.C. (1982) The Properties of Groundwater [M]. Wiley, New York.
Mbipom E.W., Okon-Umoren O.E., and Umoh J.U. (1990) Geophysical investigation of salt ponds in Okpoma area southeastern Nigeria [J]. Jour. of Min. Geol. 26, 285–290.
Michard G., Pearson Jr.F.J., and Gautschi A. (1996) Chemical evolution of waters during long term interactions with granitic rocks in northern Switzerland [J]. Appl. Geochem. 11, 757–774
Morell I., Pulido-Bosch A., and Fernandez Rubio R. (1986) 19th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting [C]. pp.61–72. Delft.
Nigerian Standard for Drinking Water Quality (2007) Standards Organization of Nigeria [S]. pp.37. Abuja Nigeria.
Nwachukwu J.L. (1985) Petroleum prospect of Benue Trough Nigeria [J]. AAPG. 69, 601–609. Nigerian standard for drinking water quality (2007), ICS 13.060.20:1–30.
Obiora S.C. and Umeji A.C. (1995) Alkaline intrusive and Extrusive Rocks west of Anyim River, southeastern Benue Trough [J]. Jour. of Min. Geol. 31, 9–19.
Offodile M.E. (1976) A hydrogeochemical interpretation of the middle Benue of Nigeria and Abakaliki brine fields [J]. Jour. Min. Geol. Nig. 13, 73–88.
Ofoegbu C.O. (1984) An aeromagnetic study of part of the Benue Trough of Nigeria [J]. Geol. Runds. 73, 1007–1018.
Palmer C.D. and Fish W. (1991) Physiochemical processes:Inorganic contaminants. In USEPA Seminar Publication on Site Characterization for Subsurface Remediation [M]. EPA/625/4-91/026: 179–192.
Panapoulos G., Lambrakis N., Tsolis-Katagas P., and Papoulis D. (2004) Cation exchange processes and human activities in unconfined aquifer [J]. Environ. Geol. 46, 542–552.
Petters S.W. (1978) Stratigraphic evolution of the Benue Trough and its implications for the Upper Cretaceous Paleogeography of West Africa [J]. Jour. of Geol. 86, 311–322.
Petters S.W. and Ekweozor C.M. (1982) Petroleum Geology of Benue Trough and southeastern Chad basin, Nigeria [J]. AAPG Bull. 66, 1141–1149.
Rabemanana V., Violette S., Marsity G. de, Robin H., Deffontaines B., Andreux P., Bensimon M., and Parriaux A. (2005) Origin of The high variability of water mineral content in the Bedrock aquifers of southern Madagascar [J]. Jour. Hydrol. 310, 143–156.
Richards L.A. (1954) Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkalis Soils [M].US Department of Agricultural Handbook, (60), 160.
Rose S. (2000) Comparative major ion geochemistry of piedmont streams in the Atlanta Georgia region: Possible effects of urbanization [J]. Environ. Geol. 42, 102–113.
Singh A.K., Mondal G.C., Singh P.K., Singh S., Singh T.B., and Terway B.K. (2005) Hydrochemistry of reservoirs of Damodar River basin, India: Weathering processes Water quality assessment [J]. Environ. Geol. 48, 1014–1028.
Tijani M.N., Loehnert E.P., and Uma K.O. (1996) Origin of saline groundwater in the Ogoja area, lower Benue trough, Nigeria [J]. Jour. of Afri. Earth Sci. 23, 237–252.
Tijani M.N. (2004) Evaluation of saline waters and brines in the Benue trough, Nigeria [J]. Appl. Geochem. 19, 1355–1365.
Tonetto E.M. and Bonotto D.M. (2005) Hydrochemical relationships in groundwater from central Sao Paulo state, Brazil [J]. Environ. Geol. 47, 942–955.
Uma K.O. and Lohnert E.P. (1992) Research on the saline groundwater in the Benue Trough, Nigeria: Preliminary results and projections [J]. Zbl Geol. Palaeont. Teil: Heft. 11, 2751–2756.
Uma K.O., Onuoha K.M., and Egboka B.C.E. (1990) Hydrochemical facies, groundwater flow pattern and origin of saline waters in parts of the western flank of the Cross River basin, Nigeria. In The Benue Trough, Structure and Evolution (ed. Ofoegbu C.O.) [M]. pp.115–134. Braunsweig Vieweg.
WHO (1993) Guideline for drinking water quality [J]. World Health Organisation Recommendations. 118, Genera.
Zhang J., Huang W.W., Letolle R., and Jusserand C. (1995) Major Element chemistry of the Huanghe (Yellow River), China: Weathering processes and chemical fluxes [J]. J. Hydrol. 168, 173–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nganje, T.N., Adamu, C.I., Ugbaja, A.N. et al. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of the lower Benue Trough, Nigeria. Chin. J. Geochem. 29, 398–406 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-010-0472-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-010-0472-4