Abstract
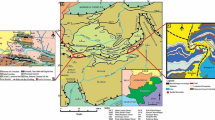
The black shale samples collected from two Neogene formations in the Klias Peninsula area, West Sabah, have been assessed and characterized in details by gas chromatography, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and a variety of organic geochemical parameters. The aims of this study are to describe the characteristics of organic matter of these sediments in terms of source/type of the organic matter, assess its thermal maturity and paleoenvironment of deposition, based primarily on biomarker distributions. The results of both formations do not reveal significant differences within the rock extracts. The gas chromatograms of the saturated hydrocarbon fractions of the Setap Shale and the Belait formations displayed monomodal n-alkane distributions and nearly identical regular sterane compositions with a predominance of C27 regular steranes. These are consistent with open marine depositional environments dominated by marine biological matter. Another related feature of these rock extracts is the presence of a high relative abundance of gammacerane, indicating anoxic marine hypersaline source depositional environment. The relatively high abundance of common land plant-derived biomarkers, such as bicadinanes and oleananes, is a clear indication of a major terrigenous input to the source of the extractable organic matter. The predominance of oleanane biomarkers in both formations is indicative of angiospermis input and Tertiary source rocks. The high C29/C30 hopane ratios, moderate development of C33–C35 hopanes, high abundance of tricyclic terpanes and a slight predominance of C27 regular sterane over C28 and C29 steranes are characteristic features tending to suggest a significant marine influence on these source rocks, thereby suggesting a mixed source input. The 22S/(22S+22R)C32 hopane ratio has reached equilibrium, and this is supported by the high maturity level as indicated by the 22S/22SC31–33 extended hopane ratios and 20S/(20S+20R)C29 regular steranes ratios.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams C.G. and Kirk H.J.C. (1962) The Madai-Binturong Limestone Member of the Chert- Spilite Formations, North Borneo [J]. Geological Magazine. 44, 289–303.
Alexander C., Masaru S., Amane W., and Kuniaki T. (1997) Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary oils derived from siliceous sources in Japan, Russia and U.S.A [J]. Organic Geochemistry. 27, 523–536.
Aquino Neto F.R., Trendel J.M., Restle A., Connon J., and Albrecht P.A. (1983) Occurence and formation of tricyclic and teteracyclic terpanes in sediments and petroleums. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry (eds. Bjoroy M. et al., 1981) [M]. pp.659–667. Wiley, Chichester.
Basir Jasin and Sanudin Tahir (1988) Barremian Radiolarian from Chert-Spilite Formation, Kudat, Sabah [J]. Sains Malaysiana. 17, 67–79.
Basir Jasin (1992) Significance of radiolarian chert from the Chert—Spilite Formation, Telupid, Sabah [J]. Bulletin of the geological Society of Malaysia. 31, 67–84.
Bray E.E. and Evans E.D. (1961) Distribution of n-paraffins as a clue to recognition of source beds [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 22, 2–15.
Brooks J. and Smith W.J. (1969) The diagenesis of plant lipids during the formation of coal petroleum and natural gascolification and the formation of oils and gas in the Gippsland basin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 33, 1183–1194.
Brooks J.D., Gould K., and Smith J.W. (1969) Isoprenoid hydrocarbons in oil and petroleum [J]. Nature. 222, 257–259.
Clayton J.L. (1993) Composition of crude oils generated from coals and organic matter in shale. In Hydrocarbons from Coal AAPG Studies in Geology (eds. Low B.E. and Rice D.D.) [M]. 38, 85–198.
Connan J. and Cassou A.M. (1980) Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 44, 1–23.
Cooper B.S. (1990) Practical Petroleum Geochemistry [M]. Roberston Scientific Publications, London.
Didyk C.B.M., Simoneit B.R.T., Brassell S.C., and Eglinton G. (1978) Organic geochemical indicators of paleoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation [J]. Nature. 272, 216–222.
Douglas A.G. and Williams P.F.V (1981) Kimmeridge oil shale. A study of organic maturation. In Organic Maturation Studies and Fossil Fule Exploration (ed. Brooks J.) [M]. pp.255–269. Academic Press Inc., London.
Duan Y. and Ma L.H. (2001) Lipid geochemistry in a sediment core from Ruoergai Marsh deposit (Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China) [J]. Organic Geochemistry. 32, 1429–1442.
Duan Y., Wang Z.P., Zhang H., Zhang X.B., Qian Y.R., and Zheng G.D. (2006) Biomarker geochemistry of crude oils from Qaidam basin, northwestern China [J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology. 29, 175–188.
Duan Y. (2000) Organic geochemistry of recent marine sediment from Nansha Sea, China [J]. Organic Geochemistry. 2/3, 159–167.
Ekweozor C.M., Okogun J.I., Ekong D.E.U., and Maxwell J.R. (1979) Preliminary organic geochemical studies of samples from the Niger Delta (Nigeria). I. Analyses of crude oils for triterpanes [J]. Chemical Geology. 27, 11–29.
Gonzalez-vila F.J. (1995) Alkane biomakers geochemical significance and application in oil shale geochemistry. In Composition, Geochemistry and Conversions of Oil Shales (ed. Snape C.) [M]. pp.51–68. Kluwer Academic Publishes, Dordrecht.
Han J. and Calvin M. (1969) Hydrocarbon distribution of algae and bacteria, and microbial activity in sediments [J]. Process National Academy of Sciences (USA). 64, 436–443.
Lee C.P. (1977) The Geology of Labuan Island, Sabah, East Malysia [M]. BSc. Thesis. University of Malaya.
Leong K.M. (1999) Geological setting of Sabah. In The Petroleum Geology and Resources of Malaysia (ed. Petronas ) [M]. pp.675–497. Petroleum National Berhad (PETRONAS).
Lijmbach G.W.M. (1975) On the Origin of Petroleum [M]. pp.357–369. Proc. 9th World Petrol. Cong. 2.
Mackenzie A.S. (1984) Application of biological markers in petroleum geochemistry. In Advances in Petroleum Geochemistry (eds. Brooks J. and Welte ) [M]. pp.115–214. Academic Press, London, UK.
Mackenzie A.S., Patience R.L., Maxwell J.R., Vandebroucke M., and Durand B. (1980) Molecular parameters of maturation in the Toarcian shales, Paris, France: I. Changes in configurations of acyclic isoprenoid alkanes, steranes and triterpanes [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 44, 1709–1721.
Mazlan B., Madon H.J., Leong K.M., and Azlina A. (1999) Sabah Basin. In The Petroleum Geology and Resources of Malaysia (ed. Petronas ) [M]. Pp.675–497. Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Mello M.R., Telnaes N., Gaglianone P.C., Chicaralli M.J., Brassell S.C., and Maxwell J.R. (1988) Organic geochemical characterization of depositional paleeoenvironment of source rocks and oils in Brazilian marginal basins. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1987 (eds. Maltavelli L. and Novell C.) [M]. pp.31–45. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Moldowan J.M. (1988) State of the art in biological marker research. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1987 (eds. Mattorelli L. and Novelli L.) [M]. pp. 31–45. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Moldowan J.M., Dahl J., Huizinga B., and Fago F. (1994) The molecular fossil record of oleanane and it’s relation to angiosperms [J]. Science. 265, 768–771.
Moldowan J.M., Seifert W.K., and Gallegos E.J. (1985) Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks [J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin. 69, 1255–1268.
Moldowan J.M., Sundararaman P., and Schoell M. (1986) Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the Lower Toarcian of S.W. Germany [J]. Organic Geochemistry. 10, 915–926.
Palacas J.G., Anders D.E., and King J.D. (1984) South Florida basin-prime example of carbonate source rocks of petroleum. In Petroleum Geochemistry and Source Rock Potential of Carbonate Rocks AAPG (ed. Palaces J.G.) [M]. Studies in Geology. 18, 71–96.
Peters K.E. and Moldowan M.J. (1991) Effects of source, thermal maturity, and biodegradation on the distribution and isomerization of homohopanes in petroleum [J]. Organic Geochemistry. 17, 47–61.
Peters K.E. and Moldowan M.J. (1993) The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments [M]. pp.363. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
Peters K.E., Fraser T.H., Amris W., Rustanto B., and Hermanto E. (1999) Geochemistry of crude oils from eastern Indonesia [J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin. 83, 1927–1942.
Peters K.E. (1986) Guidelines for evaluating petroleum source rock using programmed pyrolysis [J]. American Petroleum Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin. 70, 318–329.
Philp R.P., Fan P., Lewis C.A., Li J., Zhu H., and Wang H. (1991) Geochemical characteristics of oils from Chaidamu, Shanganning and Jianghan basins, China [J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Science. 5, 351–358.
Philp R.P. (1994) Geochemical characteristics of oil derived predominantly from terrigenous source materials. In Coal and Coal-bearing Strata as Oil Prone Source Rocks? (eds. Scott A.C. and Fleet A.J.) (Geol. Soc. Special Publication) [M]. The Geological Society, London. 77, 71–91.
Philp R.P. and Gilbert T.D. (1986) Biomarkers distributions in Australian oils predominantly derived from terrigenous source material. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1985 (eds. Leythaeuser D. and Rulkötter J.) [M]. pp.73–84. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Powell T.G and Makriday D.M. (1973) Relationships between ratio of pristine to phytane, rude oil composition and geological environments in Australia [J]. Nature. 243, 37–39.
Seifert K. and Moldowan J.M. (1978) Application of steranes, terpanes and monoaromatics to the maturation, migration and source of crude oils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 42, 77–95.
Sinninghe Damste J.S., Kening F., and Koopmans M.P. (1995) Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 59, 1895–1990.
Tan D.N.K and Lamy J.M. (1990) Tectonic evolution of the NW Sabah continental margin since the late Eocene [J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia. 27, 241–260.
Tissot B. and Welte D.H. (1984) Petroleum Formation and Occurance (2nd) [M]. Springer-Verlage, New York.
Volkman J.K., Farrington J.W., Gasgosian R.B., and Wakeham S.G. (1981) Lipid composition of coastal marine sediments from the Peru upwelling region. In Advance in Organic Geochemistry (eds. Bjorøy M. et al.)[M]. pp.228–240. Wiley, New York.
Wilson R.A.M. (1964) The Geology and Mineral Resource of the Labuan and Padas Valley Area, Sabah, Malaysia [M]. Geological Survey Borneo Region, Malaysia, Memoir. 17, 150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgan, A.M., Ali, C.A. An assessment of paleodepositional environment and maturity of organic matter in sediments of the Setap Shale and Belait formations in West Sabah, East Malaysia by organic geochemical methods. Chin. J. Geochem. 29, 42–52 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-010-0042-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-010-0042-9