Abstract
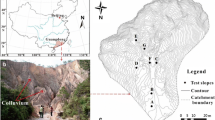
Studies on rain-runoff process in the peripheral mountainous area of the Sichuan Basin, which is regarded as a key ecological shelter, will contribute to flood control and environmental protection for the Upper Yangtze River Basin. In two typical catchments—the Fujiang River Catchment and the Wujiang River Catchment, rainfall simulations have been conducted to study the rain-runoff processes of yellow soil and limestone soil in three types of land use—forestland, farmland and grassland. Results showed that (1) within the same rainfall process, overland flow occurs first on farmland, then on grassland, and finally on forestland; (2) soil surface coverage has a great impact on the occurrence and amount of overland flow. The runoff amount can increase 2–4 times after the coverage is removed; (3) the infiltration before the occurrence of overland flow will decrease because of higher gravel contents of soil, but it takes no effect on infiltration once overland flow becomes stable; (4) the runoff coefficient of the limestone soil forestland is greater than that of the yellow soil forest land, but less than that of the farmland; (5) three empirical infiltration models, including Horton’ model, Kostiakov’ model, and modified Kostiakov’ model, were compared by using the observed results under rainfall simulation. The results showed that the Kostiakov’ model performed better than both the Horton’ model and modified Kostiakov model. According to the results of this research, the Kostiakov’s model can be used to simulate rainfall infiltration when water erosion is modeled in the peripheral mountainous area of the Sichuan Basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams A.D. and Parsons A.J. (1991) Relation between infiltration and stone cover on a semi-arid hillslope, southern Arizona [J]. Journal of Hydrology. 122, 49–59.
Chahinian N., Roger Moussa, Patrick Andrieux, and Marc Voltz (2004) Comparison of infiltration models to simulate flood events on a field scale [J]. Journal of Hydrology. 306, 191–214.
Chen Qibo, Cun Yukang, Liu Zhiqing, Wang Keqing, and Wang Liming (2005) Study on runoff and sediment production on slope land of western plateau of Yunnan Province [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation. 12, 71–73 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Guojie (1998) Ecological rehabilitation and development strategy in the peripheral mountain region of western Sichuan Basin—A case study in Tianquan, Baoxing and Maoxian counties [J]. Resources Science. 20, 34–40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Clausnitzer V., Hopmans J.W., and Starr J.L. (1998) Parameter uncertainty analysis of common infiltration models [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 62, 1477–1487.
Fu Suhua (2005) Effect of soil containing rock fragments on infiltration [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation. 19, 171–175 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Guilin and Liu Congqiang (2001) Hydrogeochemistry of the Wujiang River water in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry. 20, 240–248.
Horton R.I. (1938) The interpretation and application of runoff plot experiments with reference to soil erosion problems [J]. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings. 3, 340–349.
Kostiakov A.N. (1932) On the Dynamics of the Coefficient of Water-percolation in Soils and on the Necessity for Studying it from a Dynamic Point of View for Purpose of Amelioration [R]. pp. 17–21. Trans. Int. Congr. Soil Sci.
Li Hong, Deng Liangji, Zhang Sirong, and Wu Jintao (2005) Characteristics and mechanism of LUCC and countermeasures in the mountain regions around the western Sichuan Basin—A case study of Tianquan County in Ya’an [J]. Soils. 37, 169–175 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mbagwu J.S.C. (1995) Testing the goodness of fit of infiltration models for highly permeable soils under different tropical soil management systems [J]. Soil & Tillage Research. 34, 199–205.
Poesen J., Ingelmo-Sanchez F., and Mucher H. (1990) The hydrological response of soil surface to rainfall as affected by cover and position of rock fragments in the top layer [J]. Earth Surf. Processes Landforms. 15, 653–671.
Surendra Kumar Mishra, Tyagi J.V., and Vijay P. Singh (2003) Comparison of infiltration models [J]. Hydrol. Process. 17, 2629–2652.
Smith R.E. (1972) The infiltration envelope results from a theoretical infiltrometer [J]. Journal of Hydrology. 17, 12–21.
Tang Xiaochun and Xie Shiyou (1994) The exploration on the causes of geotectonic to form the regularity of distribution of the mountain calamity landforms surrounding Sichuan basin [J]. Journal of water and soil conservation. 8, 76–84.
Wang Huifang and Shao Ming’an (2006) Experimental study on water infiltration of soil containing rock fragments [J]. Advances in Water Science. 17, 604–609 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiaoyan, Wang Yixun, Li Tingfang, He Wei, Hu Qiuju, and Zhang Hongfen (2002) Characteristics of non-point source pollution in the watershed of the Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry. 21, 89–95.
Wang Yunqi, Wang Yujie, Zhu Jingzhao, and Qi Shi (2005) Responses of slope runoff generation to rainstorm with different land use types in Jinyun mountain in Chongqing City [J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation. 13, 9–26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wilcox B.P. and Forest M.K. (1988) Factors influencing interrill erosion from semi-arid slopes in New Mexico [J]. Journal of Range Management. 42, 66–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bin, F., Yu-kuan, W., Yi, R. et al. Study on rain-runoff process in the peripheral mountainous area of the Sichuan Basin. Chin. J. Geochem. 27, 183–188 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-008-0183-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-008-0183-2