Abstract
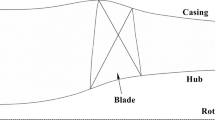
An experimental investigation on the unsteady tip flow field of a transonic compressor rotor has been performed. The casing-mounted high frequency response pressure transducers were arranged along both the blade chord and the blade pitch. The chord-wise ones were used to indicate both the ensemble averaged and time varying flow structure of the tip region of the rotor at different operating points under 95% design speed and 60% design speed. The pitch-wise circumferential transducers were mainly used to analyze the unsteadiness frequency of the tip leakage flow in the rotor frame at the near stall condition. The contours of casing wall pressure show that there were two clear low pressure regions in blade passages, one along the chord direction, caused by the leakage flow and the other along the tangential direction, maybe caused by the forward swept leading edge. Both low pressure regions were originated from the leading edge and formed a scissor-like flow pattern. At 95% design speed condition, the shock wave interacted with the low pressure region and made the flow field unsteady. With the mass flow reduced, the two low pressure regions gradually contracted to the leading edge and then a spike disturbance emerged.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Hoying, C. S. Tan, Huu Duc Vo, and E. M. Greitzer, “Role of Blade Passage Flow Structures in Axial Compressor Rotating Stall Inception”, ASME Journal of Turbomachinery, Vol.121, pp. 735–742, 1999.
Huu Duc Vo, C. S. Tan and E. M. Greitzer, 2008, “Criteria for Spike Initiated Rotating Stall”, ASME Journal of Turbomachinery, Vol.130, pp. 11–23.
Mailach, R., Sauer, H., and Vogeler, K., 2001, “The Periodical Interaction of the Tip leakage Flow in the Blade Rows of Axial Compressor”, ASME Paper 2001-GT-0299
Zhang, H. W., Deng, X. Y., Lin, F., Chen, J. Y., Huang, W. G., 2005, “Unsteady Tip leakage Flow in an Isolated Axial Compressor rotor”, Journal of Thermal Science, Sep. 2005, 14(3).
Tong, Z. T., Lin, F., Chen, J. Y., Nie, C. Q., 2007, “The Self-Induced Unsteadiness of Tip Leakage Vortex and its Effect on Compressor Stall Inception”, ASME Paper GT2007-27010.
J.X. Zhang, F. Lin, J.Y. Chen and C.Q. Nie, “The flow mechanism of how distorted flows deteriorate stability of an axial compressor” ASME Paper No. GT2007-27628
Yamada, K., Furukawa, M., Inoue, M., Funazaki, K., 2004, “Unsteady Three-Dimensional Flow Phenomena due to Breakdown of Tip Leakage Vortex in a Transonic Axial Compressor Rotor”, ASME Paper GT2004-53745.
Hah, C., Rabe, D. C., Wadia, A. R., 2004, “Role of Tip-Leakage Vortices and Passage Shock in Stall Inception in a Swept Transonic Compressor Rotor”, ASME Paper GT2004-53867.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, C., Zhang, H. et al. A study of the unsteady tip flow field of a transonic compressor. J. Therm. Sci. 20, 1–5 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-011-0426-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-011-0426-0