Abstract
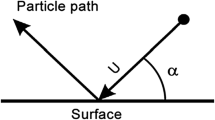
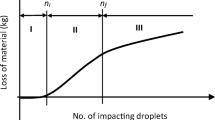
Sand erosion is a phenomenon where solid particles impinging to a wall cause serious mechanical damages to the wall surface. This phenomenon is a typical gas-particle two-phase turbulent flow and a multi-physics problem where the flow field, particle trajectory and wall deformation interact with each other. On the other hand, aircraft engines operating in a particulate environment are subjected to the performance and lifetime deterioration due to sand erosion. Especially, the compressor of the aircraft engines is severely damaged. The flow fields of the compressor have strongly three dimensional and unsteady natures. In order to estimate the deterioration due to sand erosion, the sand erosion simulation for a compressor is required under the consideration of the rotor-stator interaction. In the present study, we apply our three dimensional sand erosion prediction code to a single stage axial flow compressor. We numerically investigate the change of the flow field, the particle trajectories, and the eroded wall shape in the compressor, to clarify the effects of sand erosion in the compressor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finnie, I.: Erosion of surfaces by solid particles, Wear, vol.3, pp.87–103, (1960).
Bitter, J. G. A.: A study of erosion phenomena part I, Wear, vol.6, pp.5–21, (1963).
Bitter, J. G. A.: A study of erosion phenomena part II, Wear, vol.6, pp. 169–190, (1963).
Neilson, J. H. and Gilchrist, A.: Erosion by a stream of solid particle, Wear, vol.11, pp.111–122, (1968).
Neilson, J. H. and Gilchrist, A.: An experimental investigation into aspects of erosion in rocket motor nozzles, Wear, vol.11, pp.123–143, (1968).
Balan, C. and Tabakoff, W.: Axial Flow Compressor Performance Deterioration, AIAA-84-1208, (1984).
Kuki, J., Toda, K., Yamamoto, M.: Development of Numerical Code to Predict Three-Dimensional Sand Erosion Phenomena, FEDSM2003-45017, Proc. ASME FEDSM’03 4TH ASME_JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference, Honolulu, (2003).
Miyama, T., Nakayama, T., Kitamura, O. and Yamamoto, M.: Numerical Prediction of Sand Erosion along Curved Passages, Proc. Third World Conference in Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics, 27, pp.53–60, (1996).
Kuki, J., Toda, K., Yamamoto, M.: Numerical Simulation of Sand Erosion Phenomena in a Particle Separator, Key Engineering Materials, 243–244, pp. 565–570, (2003).
Suzuki, M., Toda, K. and Yamamoto, M., Numerical Simulation of Sand Erosion Phenomena on Turbine Blade Surface, Proc. WCCM VI in conjunction with APCOM’04, Beijing, (2004).
Emery, J. C., Herring, L. J., Erwin, J. R. and Felix, A. R.: Systematic Two-Dimensional Cascade Tests of NACA 65-Series Compressor Blades at Low Speeds, NACA Report 1368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, M., Inaba, K. & Yamamoto, M. Numerical simulation of sand erosion phenomena in rotor/stator interaction of compressor. J. Therm. Sci. 17, 125–133 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-008-0125-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-008-0125-7