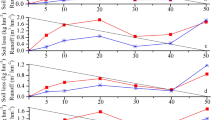
Abstract
Slope eco-restoration has always received extensive attention as a positive way to reverse ecosystem deterioration derived from human interventions. A simplified framework is proposed to undertake a quantitative evaluation of the engineering disturbed slope eco-restoration success in the alpine region, southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The Dagu hydropower project that disturbs the local ecosystem to some certain was selected as the study area. Since August 2018, six types of slope (soil, rock, soil-rock, spoil, construction site, hardened) were served as the demonstration test for the slope eco-restoration with two years monitoring in the study area. Meanwhile, the topography, erosion, soil quality, and vegetation were selected as assessment indicators of the methodology. Finally, combined with the weighting method and the expert panel, the slope eco-restoration quality index (SERQI) was established and applied in the six slopes. The results suggested that the frost-resistant ecological substrate performed well in alpine region, and the SERQI value is in accordance with the actual monitoring level with spoil slope>soil slope>construction site slope>soil-rock slope>rock slope>hardened slope. The proposed framework could support slope eco-restoration practitioners for making a more objective and quantitative evaluation easily for the postimplementation restoration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASF Data Research (2020) Synthetic Aperture Radar data. https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/?tdsourcetag=spctim_aiomsg&flightDirs (Accessed on 2020-09-10)
Bochet E, García-Fayos P (2004) Factors Controlling Vegetation Establishment and Water Erosion on Motorway Slopes in Valencia, Spain. Restor Ecol 12(2): 166–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1061-2971.2004.0325.x.
Beier P, Hansen LJ, Helbrecht L, Behar D (2017) A how-to guide for coproduction of actionable science. Conserv Lett 10(3): 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12300.
Campbell D, Bergeron J (2012) Natural revegetation of winter roads on peatlands in the Hudson Bay lowland, Canada. Arct Antarct Alp Res 44: 155–163. https://doi.org/10.1657/1938-4246-44.2.155
Comín FA, Miranda B, Sorando R, et al. (2018) Prioritizing sites for ecological restoration based on ecosystem services. J Appl Ecol 55(3): 1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13061.
Carabassa V, Ortiz O, Alcañiz JM (2019) RESTOQUARRY: Indicators for self-evaluation of ecological restoration in open-pit mines. Ecol Indic 102: 437–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.001.
Chen JA, Wang JF, Yu J, et al. (2017) Eco-environmental characteristics of reservoirs in southwest China and their research prospects. Earth Env 45(2): 115–125. https://doi.org/10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2017.02.001.
Dale VH, Beyeler SC (2001) Challenges in the development and use of ecological indicators. Ecol Indic 1(1): 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-160X(01)00003-6.
Deltoro V, Jimenez J, Vilan XM (2012). Bases para el manejo y control de Arundo donax L. (Caña común). Coleccion Manuales Tecnicos de Biodiversidad, 4. Conselleria d’Infraestructures, Territori i Medi Ambient. Generalitat Valenciana. Valencia.
Gonzalez-Ollauri A, Mickovski SB (2017) Shallow landslides as drivers for slope ecosystem evolution and biophysical diversity. Landslides 14:1699–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0822-y.
Gao JZ, Zhou MT, Xu WN, et al. (2020) The evolution of structure properties of vegetation concrete under freeze-thaw cycles. Int J Elec Eng Educ 0(0): 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020720920930363.
Gatica-Saavedra P, Echeverría C, Nelson CR (2017) Ecological indicators for assessing ecological success of forest restoration: a world review. Restor Ecol 25(6): 850–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.12586.
Hagen D, Evju M (2013) Using short-term monitoring data to achieve goals in a large-scale restoration. Ecol Soc 18(3): 29. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05769-180329.
Higgs ES (1997). What is good ecological restoration? Conserv Biol 11:3381348. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.1997.95311.x.
Huang L, Shao QQ, Liu JY, Lu QS (2018) Improving ecological conservation and restoration through payment for ecosystem services in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecosyst Serv 31(PA): 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.04.005.
Huang RQ (2002) Discussion on the main engineering geological problems in hydropower development in southwestern China and their research strategies. J Geol Hazards Environ Preserv 13(1): 1–5. (In Chinese)
Huang XF, Wang LX, Gong L, et al. (2020) Soil fertility characteristics and evaluation of paddy field and dry land in Jianhe County. Southwest China J Agr Sci 33(7): 1510–1516.
Hobbs RJ, Norton DA (1996) Towards a conceptual framework for restoration ecology. Restor Ecol 4(2): 93–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-100X.1996.tb00112.x.
Heink U, Kowarik I (2010) What are indicators? On the definition of indicators in ecology and environmental planning. Ecol Indic 10(3): 585–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.09.009.
Immerzeel WW, Ludovicus PH, Bierkens MF (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328(5984): 1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188.
Le HD, Smith C, Herbohn J, Harrison S (2012) More than just trees: assessing reforestation success in tropical developing countries. J Rural Stud 28:5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2011.07.006.
Li XJ, Zhang J, Xu LY (2015) An evaluation of ecological losses from hydropower development in Tibet. Ecol Eng 76: 178–185.
Li ZW, Wang ZY, Yu GA, et al. (2015) Effects on Slope Stability of the Yarlung Tsangbu Grand Canyon under Future Hydropower Development. Mt Res 33(3): 331–338. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000042.
Liu L, Niu QK, Heng JX, et al. (2019) Transition Characteristics of the Dry-Wet Regime and Vegetation Dynamic Responses over the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens 11(10): 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101254.
Liu MX (2013) Plant community composition and nitrogen-phosphorus stoichiometry along a slope aspect gradients in a alpine meadow.Lanzhou Univ. (In Chinese)
Maccherini S, Bacaro G, Marignani M (2018) Beneficial effects of restoration practices can be thwarted by climate extremes. Sci Total Environ 626: 851–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.117.
Nilsson C, Aradottir AL, Hagen D, et al. (2016) Evaluating the process of ecological restoration. Ecol Soc 21(1):41. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-08289-210141.
National Energy Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for eco-restoration of vegetation concrete on steep slope of hydropower projects: NB/T 35082-2016. (Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2016).
Orsi F, Geneletti D, Newton AC (2011) Towards a common set of criteria and indicators to identify forest restoration priorities: An expert panel-based approach. Ecol Indic 11(2): 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.06.001.
Prach K, Durigan G, Fennessy S, et al. (2019) A primer on choosing goals and indicators to evaluate ecological restoration success. Restor Ecol 27(5): 917–923. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.13011.
Roces-Díaz JV, Vayreda J, Banqué-Casanovas M, et al. (2018) Assessing the distribution of forest ecosystem services in a highly populated Mediterranean region. Ecol Ind 93, 986–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.076.
Rivera D, Mejías V, Jáuregui BM, et al. (2014) Spreading Topsoil Encourages Ecological Restoration on Embankments: Soil Fertility, Microbial Activity and Vegetation Cover. PLOS ONE 9(7): e101413. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101413.
Seabrook L, McAlpine CA, Bowen ME (2011) Restore, repair or reinvent: options for sustainable landscapes in a changing climate. Landscape Urban Plan 100(4):407–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2011.02.015.
SER (Society for Ecological Restoration) (2004) Society for ecological restoration international’s primer of ecological restoration (available from http://www.ser.org/resources/resources-detail-view/ser-internationalprimer-on-ecological-restoration).
Sun XM, Peng BR (2014) Evaluating ecological restoration success in China: a review of the literature. Environ Sci Manage 39(7): 153–157. (In Chinese)
Teng Y, Zhan J, Agyemang FB, Sun Y (2020) The effects of degradation on alpine grassland resilience: a study based on meta-analysis data. Glob Ecol Conserv, 24, e01336.
Wilker J, Rusche K, Benning A, et al. (2016) Applying ecosystem benefit valuation to inform quarry restoration planning. Ecosyst Serv 20: 44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.06.003.
Williams BK (2011) Adaptive management of natural resources-framework and issues. J Environ Manage 92: 1346–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.10.041.
Wortley L, Hero JM, Howes M (2013) Evaluating ecological restoration success: a review of the literature. Restor Ecol 21: 537–543. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.12028.
Wang C (2017) Research conception of ecological protection and restoration of high dams and large reservoirs construction and hydropower cascade development in southwestern China. Adv Eng Sci 49(1): 19–26. https://doi.org/10.15961/j.jsuese.2017.01.003.
Xu F, Jia YW, Penng H, et al. (2018) Temperature and precipitation trends and their links with elevation in the Hengduan Mountain region, China. Clim Res 75: 163–1880. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr01516.
Xin Q (2017) Research on fast ecological restoration technology of high and steep rocky slope of highway. GREEN ENERGY AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT I: Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Energy and Sustainable Development (GESD 2017) 1864(1): 020127.
Xue R, Yang Q, Miao FH, et al. (2018) Slope aspect influences plant biomass, soil properties and microbial composition in alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 18(1): 1–12. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162018005000101
Xu WN, Xia ZY, Zhou MT, et al. (2012) The vegetation concrete eco-restoration technology theory and practice. China Water & Power Press, Beijing. (In Chinese)
Xu WN, Xia D, Zhao BQ, et al. (2017) Research on vegetation ecological restoration technology in disturbed areas of hydropower projects. Science Press, Beijing. (In Chinese)
Yang Y, Yang JY, Zhao TN, et al. (2016) Ecological restoration of highway slope by covering with straw-mat and seeding with grass-legume mixture. Ecol Eng 90: 68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.052.
Yang YS, Xu WN, Liu DX, Xia ZY (2018) Evaluation and Eco-regulation of Eco-restoration Engineering on Slopes of Hydropower Projects. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 17(1): 131–138.
Zhao BQ, Xia ZY, Xu WN, et al. (2017) Review on research of slope eco-restoration technique for engineering disturbed area. Water Resour Hydropower Eng 48(2): 130–137. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2017.02.022.
Zedler JB, Callaway JC (2000) Evaluating the progress of engineered tidal wetlands. Ecol Eng 15: 211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(00)00077-X.
Zhan JH (2007) Comparative study on yield and other characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) at different altitude. Master thesis, Northwest A&F Univ, Shanxi Province, China. (In Chinese)
Zhang L, Wang JM, Bai ZK, Lv CJ (2015) Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena 128: 44–53.
Zhen L, Du BZ, Wei YJ, et al. (2018) Assessing the effects of ecological restoration approaches in the alpine rangelands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ Res Lett 13(9): 095005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aada51.
Zhou MT, Xu WN, Hu H, et al. (2016) A kind of frost-resistant ecological substrate for slope protection. China Patent Number: CN103510488B. (In Chiness)
Zeng QB (2015) The analysis of left bank dam abutment slope stability of DG hydropower station. Master degree thesis, Chengdu Univ of Technol. (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
Financially supported by the Key Laboratory of Mountain Hazards and Earth Surface Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KLMHESP-20-02), the Key Programs of Science and Technology Research Plan, Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. D20201205), China Huadian Corporation Research Foundation (Grant No. 12IJD201800018), and National Key Research and Development Project (2017YFC0504902-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Xd., Gao, Jz., Zhou, Mt. et al. Evaluating the success of engineering disturbed slope eco-restoration in the alpine region, southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 18, 2820–2832 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6502-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6502-8