Abstract
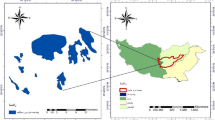
Water scarcity is a challenge in many arid and semi-arid regions; this may lead to a series of environmental problems and could be stressed even further by the effects from climate change. This study focused on the water resource management in Shanshan County, an inland arid region located in northwestern China with a long history of groundwater overexploitation. A model of the supply and demand system in the study area from 2006 to 2030, including effects from global climate change, was developed using a system dynamics (SD) modeling tool. This SD model was used to 1) explore the best water-resource management options by testing system responses under various scenarios and 2) identify the principal factors affecting the responses, aiming for a balance of the groundwater system and sustainable socio-economic development. Three causes were identified as primarily responsible for water issues in Shanshan: low water-use efficiency, low water reuse, and increase in industrial water demand. To address these causes, a combined scenario was designed and simulated, which was able to keep the water deficiency under 5% by 2030. The model provided some insights into the dynamic interrelations that generate system behavior and the key factors in the system that govern water demand and supply. The model as well as the study results may be useful in water resources management in Shanshan and may be applied, with appropriate modifications, to other regions facing similar water management challenges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablikim A, Zhou JW (2014) Surface discharge characteristics of the Turpan Basin, Xinjiang. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 36(3): 717–723. (In Chinese) DOI: 10.7522/j.issn. 1000-0240.2014.0086
Abulikemu A (2012) Investigation and analysis on present situation of water resources and basic situation of irrigation and water conservancy constructions in Piqan County. In WIT Transactions on Engineering Sciences 80: 419–424. DOI: 10.2495/AIE120471
Ahmad S, Simonovic SP (2000) System dynamics modeling of reservoir operations for flood management. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 14(3): 190–198. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(2000)14:3(190)
Ahmad S, Simonovic SP (2004) Spatial system dynamics: a new approach for simulation of water resources systems. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 18(4): 331–340. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(2004)18:4(331)
Ahmad S, Simonovic SP (2006) An intelligent decision support system for management of floods. Water Resources Management 20(3): 391–410. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-006- 0326-3
Barnett TP, Adams JC, Lettenmaier DP (2005) Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snowdominated regions. Nature 438: 303–309. DOI: 10.1038/ nature04141
Bruelheide H, Jandt U, Gries D, et al. (2003) Vegetation changes in a river oasis on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert in China between 1956 and 2000. Phytocoenologia 33(4): 801–818. DOI: 10.1127/0340-269X/ 2003/0033-0801
Carrier C, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2016) Long-range precipitation forecast using paleoclimate reconstructions in the western United States. Journal of Mountain Science 13(4): 614–632. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-014-3360-2
Chen C, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2015) Exploring Water Management Strategies in Inland Arid Area Using Dynamic Simulation Model, ASCE World Environmental & Water Resources Congress, 1009–1018. DOI: 10.1061/9780784479162.098
Chen P (2010) Study on Water Supply and Water-saving Potential in Turpan-Hami Oilfield. Master thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China. (In Chinese)
Chen Y, Takeuchi K, Xu C, et al. (2006) Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China. Hydrological Processes 20(10): 2207–2216. DOI: 10.1002/hyp.6200
Choubin B, Sigaroodi SK, Malekian A, et al. (2014) Drought forecasting in a semi-arid watershed using climate signals: a neuro-fuzzy modeling approach. Journal of Mountain Science 11(5): 1593–1605. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-014-3020-6
Dawadi S, Ahmad S (2012) Changing climatic conditions in the Colorado River Basin: implications for water resources management. Journal of Hydrology 430: 127–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.010
Dawadi S, Ahmad S (2013) Evaluating the impact of demandside management on water resources under changing climatic conditions and increasing population. Journal of Environmental Management 114: 261–275. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.015
Fang S, Pei H, Liu Z, et al. (2010) Water Resources Assessment and Regional Virtual Water Potential in the Turpan Basin, China. Water Resources Management 24(13): 3321–3332. DOI:10.1007/s11269-010-9608-x Food and Agriculture Organization of United States (FAO) (2013) Water Scarcity (Available online at: http://www.fao. org/nr/water/topics_scarcity.html, accessed on 06 December 2015)
Ford A (1999) Modeling the Environment: an Introduction to System Dynamics Modeling of Environmental Systems. Washington, DC., Island Press. pp 401.
Frederick KD, Major DC, Eugene ZS (1997) Climate change and water resources. Climatic Change 37(1): 7–23. DOI: 10.1023/ A:1005336924908
Gao Y, Liu C (1997) Research on simulated optimal decision making for a regional water resources system. International Journal of Water Resources Development 13(1): 123–134. DOI: 10.1080/07900629749971
Gleick PH (1998) Water in crisis: paths to sustainable water use. Ecological Applications 8(3): 571–579. DOI: 10.1890/1051- 0761(1998)008
Gleick PH (2003) Global freshwater resources: soft-path solutions for the 21st century. Science 302(5650): 1524–1528. DOI: 10.1126/science.1089967
Gleick PH (2010) Roadmap for sustainable water resources in southwestern North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107 (50): 21300–21305. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005473107
Gupta HV, Sorooshian S, Yapo PO (1999) Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 4(2): 135–143. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699 (1999)4:2(135)
He B, Zhang Y (2003) Issues in water resources demand and supply in arid Xinjiang, China. Proceedings of SPIE, the international society for optical engineering (0277-786X) 4890(1): 285. DOI: 10.1117/12.466760
Hering JG, Ingold KM (2012) Water Resources Management: What Should Be Integrated? Science 336(6086): 1234–1235. DOI: 10.1126/science.1218230
Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research (IWHR) (2011) Shanshan Water Rights Transference Program.
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. p 996.
IPCC (2014) Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva, Switzerland, IPCC. p 151.
Jiang Y, Zhou C, Cheng W (2007) Streamflow trends and hydrological response to climatic change in Tarim headwater basin. Journal of Geographical Sciences 17(1): 51–61. DOI: 10.1007/s11442-007-0051-8
Jones JA, Vardanian T, Hakopian C (2009) Threats to Global Water Security. Springer Science & Business Media, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Kalra A, Ahmad S (2011) Evaluating changes and estimating seasonal precipitation for the Colorado River Basin using a stochastic nonparametric disaggregation technique. Water Resources Research 47: W05555. DOI: 10.1029/2010WR 009118
Kalra A, Ahmad S (2012) Estimating annual precipitation for the Colorado River Basin using oceanic-atmospheric oscillations. Water Resources Research 48(6): W06527. DOI: 10.1029/2011WR010667
Kalra A, Ahmad S, Nayak A (2013) Increasing streamflow forecast lead time for snowmelt driven catchment based on large scale climate pattern. Advances in Water Resources 53: 150–162. DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.11.003
Konikow LF, Kendy E (2005) Groundwater depletion: A global problem. Hydrogeology Journal 13: 317–320. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-004-0411-8
Langsdale S, Beall A, Carmichael J, et al. (2007) An exploration of water resources futures under climate change using system dynamics modeling. Integrated Assessment 7(1): 51–79.
Langsdale S, Beall A, Carmichael J, et al. (2009) Exploring the implications of climate change on water resources through participatory modeling: case study of the Okanagan Basin, British Columbia. J Water Resources Planning Management 135(5): 373–381. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2009)135: 5(373)
Leal Neto AC, Legey LFL, Gonzalez-Araya MC, et al. (2006) A system dynamics model for the environmental management of the Sepetiba Bay watershed, Brazil. Environmental Management 38(5):879–888. DOI: 10.1007/s00267-005- 0211-5
Leaver JD, Unsworth CP (2006) System dynamics modeling of spring behaviour in the Orakeikorako geothermal field, New Zealand. Geothermics 36(2): 101–114. DOI: 10.1016/ j.geothermics.2006.08.001
Li H (2010) The Countermeasure Discussion about the Water Resources Development and Utilization Problems of Turpan Region. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences/Xinjiang Nongye Kexue 47(12): 2522–2525. (In Chinese)
Madani K, Mariño MA (2009) System dynamics analysis for managing Iran’s Zayandeh-Rud river basin. Water Resources Management 23(11): 2163–2187. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-008- 9376-z
Mirchi A, Madani K, WatkinsZ Jr, et al. (2012) Synthesis of system dynamics tools for holistic conceptualization of water resources problems. Water Resources Management 26:2421–2442. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-012-0024-2
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, et al. (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE 50(3):885–900. DOI: 10.13031/2013.23153
Moriasi DN, Gitau MW, Pai N, et al. (2015) Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Transactions of the ASABE. 58(6): 1763–85. DOI: 10.13031/trans.58.10715
Nagasawa T, Yamamoto T, Jalaldin A (2006) Problems of the irrigation system in the Turpan Basin of China. Sustainable Irrigation Management, Technologies and Policies 1: 37–44. DOI: 10.2495/SI060051
Nash J, Sutcliffe J (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part I. A discussion of principles. Journal of Hydrology 10(3):282–290. DOI: 10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Peng DZ, Xu ZX (2010) Simulating the Impact of Climate change on streamflow in the Tarim River basin by using a modified semi-distributed monthly water balance model. Hydrological Processes 216: 209–216. DOI: 10.1002/hyp.7485
Raneesh KY (2014) Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources. Earth Science & Climatic Change 5(3):1–5. DOI: 10.4172/2157-7617.1000185
Rusuli Y, Li L, Ahmad S, et al. (2015) Dynamics model to simulate water and salt balance of Bosten Lake in Xinjiang, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 74(3): 2499–2510. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-015-4257-2
Sagarika S, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2014) Evaluating the effect of persistence on long-term trends and analyzing step changes in streamflows of the continental United States. Journal of Hydrology 517: 36–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.002
Sagarika S, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2015a) Interconnection between oceanic-atmospheric indices and variability in the US streamflow. Journal of Hydrology 525: 724–736. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.04.020
Sagarika S, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2015b) Pacific Ocean and SST and Z500 climate variability and western U.S. seasonal streamflow. International Journal of Climatology 36: 1515–1533. DOI: 10.1002/joc.4442
Schreider SY, Jakeman AJ, Pittoc AB, et al. (1996) Climatic Change 34(3): 513–546. DOI: 10.1007/BF00139304
Shrestha E, Ahmad S, Johnson W, et al. (2011) Carbon footprint of water conveyance versus desalination as alternatives to expand water supply. Desalination 280(1): 33–43. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.062
Shrestha E, Ahmad S, Johnson W, et al. (2012) The carbon footprint of water management policy options. Energy Policy 42: 201–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.enpol.2011.11.074
Simonovic SP, Fahmy H (1999) A new modeling approach for water resources policy analysis, Water Resources Research 35 (1): 295–304. DOI: 10.1029/1998WR900023
Simonovic SP, Li L (2003) Methodology for Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Large-Scale Flood Protection System. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 129(10): 361–371. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2003)129:5(361)
Stave KA (2003) A system dynamics model to facilitate public understanding of water management options in Las Vegas, Nevada. Environmental Management 67(4): 303–313. DOI: 10.1016/S0301-4797(02)00205-0
Sterman JD (2000) Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. McGraw-Hill, NY, USA.
Tamaddun K, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2016) Identification of Streamflow Changes across the Continental United States Using Variable Record Lengths. Hydrology 3(2): 24. DOI: 10.3390/hydrology3020024
Tangirala AK, Teegavarapu RSV, Ormsbee L (2003) Modeling adaptive water quality management strategies using system dynamics simulation. Environmental Informatics Archives 1: 245–253. (Available online at: http://www.iseis.org/eia/ contents.asp?sn=1, accessed on 06 December 2015)
Tidwell VC, Passell HD, Conrad SH, et al. (2004) System dynamics modeling for community-based water planning: application to the Middle Rio Grande. Aquatic Sciences 66: 357–372. DOI: 10.1007/s00027-004-0722-9 Turpan sixth national population census, the main data bulletin, 2011. (Available online at: http://tjj.tlf.gov.cn/info/1398/ 70391.htm, accessed on 06 December 2015)
Venkatesan AK, Ahmad S, Johnson W, et al. (2011a) Salinity reduction and energy conservation in direct and indirect potable water reuse. Desalination 272(1-3): 120–127. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.007
Venkatesan AK, Ahmad S, Johnson W, et al. (2011b) System dynamics model to forecast salinity load to the Colorado River due to urbanization within the Las Vegas Valley. Science of The Total Environment 409: 2616–2625. DOI: 10.1016/ j.scitotenv. 2011.03.018
Wang XJ, Zhang JY, Shamsuddin S, et al. (2012) Water resources management strategy for adaptation to droughts in China. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change 17(8): 923–937. DOI: 10.1007/s11027-011-9352-4
Wang ZZ, Cheng L, Wang YT, et al. (2014) A multi-reservoir ecological operation model based on subdivision application of reservoir storage capacities. Advances in Water Science 25(3): 435–443. (In Chinese) DOI: 1001-6791(2004)03-0435-09
Winz I, Brierley G, Trowsdale S (2009) The Use of System Dynamics Simulation in Water Resources Management. Water Resources Management 23(7): 1301–1323. DOI: 10.1007/s11 269-008-9328-7
Wu G, Li L, Ahmad S, et al. (2013) A dynamic model for vulnerability assessment of regional water resources in arid areas: a case study of Bayingolin, China. Water Resources Management 27(8): 3085–3101. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-013-0334-z
Yeh W (1985) Reservoir management and operations models: a state-of-the-art review. Water Resources Research 21(12): 1797–1818. DOI: 10.1029/WR021i012p01797
Zhang F, Ahmad S, Zhang H, et al. (2016) Simulating low and high streamflow driven by snowmelt in an insufficiently gauged Alpine Basin. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment 30(1): 59–75. DOI: 10.1007/s00477-015- 1028-2
Zhang F, Li LH, Ahmad S, et al. (2014) Using path analysis to identify the influence of climatic factors on spring peak flow dominated by snowmelt in an alpine watershed. Journal of Mountain Science 11(4): 990–1000. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-013-2789-z
Acknowledgments
This study is based on some of the data prepared for the project, Development of Shanshan Water Rights Transference System, by China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research (IWHR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6119-9485
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9903-9321
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3878-2346
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6613-2642
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Ahmad, S., Kalra, A. et al. A dynamic model for exploring water-resource management scenarios in an inland arid area: Shanshan County, Northwestern China. J. Mt. Sci. 14, 1039–1057 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4210-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4210-1