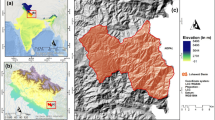
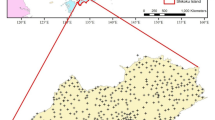
Abstract
Topographic shielding of cosmic radiation flux is a key parameter in using cosmogenic nuclides to determine surface exposure ages or erosion rates. Traditionally, this parameter is measured in the field and uncertainty and/or inconsistency may exist among different investigators. This paper provides an ArcGIS python code to determine topographic shielding factors using digital elevation models (DEMs). This code can be imported into ArcGIS as a geoprocessing tool with a user-friendly graphical interface. The DEM-derived parameters using this method were validated with field measurements in central Tian Shan. Results indicate that DEM-derived shielding factors are consistent with field-measured values. It provides a valuable tool to save fieldwork efforts and has the potential to provide consistent results for different regions in the world to facilitate the comparison of cosmogenic nuclide results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balco G (2011) Contributions and unrealized potential contributions of cosmogenic-nuclide exposure dating to glacier chronology, 1990–2010. Quaternary Science Reviews 30: 3–27, doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.11.003.
Balco G, Stone JO, Lifton NA, et al. (2008) A complete and easily accessible means of calculating surface exposure ages or erosion rates from 10Be and 26Al measurements. Quaternary Geochronology 3: 174–195, doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2007.12.001.
Bierman P, Nichols KK (2004) Rock to sediment-slope to sea with 10Be-rates of landscape change. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 32: 215–255, doi: 10.1146/ annurev.32.101802.120539.
Burrough PA, McDonell RA (1998) Principles of Geographic Information Systems. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Codilean AT (2006) Calculation of the cosmogenic nuclide production topographic shielding scaling factor for large areas using DEMs. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 31: 785–794, doi: 10.1002/esp.1336.
Desilets D, Zreda M (2003) Spatial and temporal distribution of secondary cosmic-ray nucleon intensities and applications to in situ cosmogenic dating. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 206: 21–42, doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01088-9.
Desilets D, Zreda M, Prabu T (2006) Extended scaling factors for in situ cosmogenic nuclides: New measurements at low latitude. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 246: 265–276, doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.03.051.
Dunai TJ (2000) Scaling factors for production rates of in situ produced cosmogenic nuclides: a critical reevaluation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 176: 157–169, doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00310-6.
Dunne J, Elmore D, Muzikar P (1999) Scaling factors for the rates of production of cosmogenic nuclides for geometric shielding and attenuation at depth on sloped surfaces. Geomorphology 27: 3–11, doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(98)00086-5.
Gosse JC, Phillips FM (2001) Terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides: theory and applications. Quaternary Sciences Review 20: 1475–1560, doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(00)00171-2.
Kong P, Fink D, Na CG (2009) Late Quaternary glaciation of the Tianshan, Central Asia, using cosmogenic 10Be surface exposure dating. Quaternary Research 72: 229–233, doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.06.002.
Li YK, Liu GN, Cui ZJ (2001) Glacial valley cross profile morphology, Tian Shan Mountains, China. Geomorphology 38: 153–166, doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(00)00078-7.
Li YK, Liu GN, Kong P, et al. (2011) Cosmogenic nuclide constraints on glacial chronology in the source area of the Urumqi River, Tian Shan, China. Journal of Quaternary Science 26: 297–304, doi: 10.1002/jqs.1454.
Li YK, Harbor J (2009) Cosmogenic Nuclides and Geomorphology: Theory, Limitations, and Applications. In: Ferrari DM and Guiseppi AR (eds.), Geomorphology and Plate Tectonics. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., Hauppauge, NY. pp. 1–33.
Lifton N, Bieber J, Clem J, et al.(2005) Addressing solar modulation and long-term uncertainties in scaling secondary cosmic rays for in situ cosmogenic nuclide applications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 239: 140–161, doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.07.001.
Lal D (1991) Cosmic ray labeling of erosion surfaces: in situ nuclide production rates and erosion models. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 104: 424–439, doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90220-C.
Nishiizumi K, Winterer EL, Kohl CP, et al. (1989) Cosmic ray production rates of 10Be and 26Al in quartz from glacially polished rocks. Journal of Geophysical Research 94(B12): 17907–17915, doi: 10.1029/JB094iB12p17907.
Stone JO (2000) Air pressure and cosmogenic isotope production. Journal of Geophysical Research 105(B10): 23753–23759, doi: 10.1029/2000JB900181.
Vermeesch P (2007) CosmoCalc: An Excel add-in for cosmogenic nuclide calculations. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 8: Q08003, doi:10.1029/2006GC001530.
Wittmann H, von Blanckenburg F, Kruesmann T, et al. (2007) Relation between rock uplift and denudation from cosmogenic nuclides in river sediment in the Central Alps of Switzerland. Journal of Geophysical Research 112: F04010, doi: 10.1029/2006JF000729.
Zhao JD, Zhou SZ, He YQ, et al. (2006) ESR dating of glacial tills and glaciations in the Urumqi River headwaters, Tianshan Mountains, China. Quaternary International 144: 61–67, doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.05.013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yk. Determining topographic shielding from digital elevation models for cosmogenic nuclide analysis: a GIS approach and field validation. J. Mt. Sci. 10, 355–362 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2564-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2564-1