Abstract
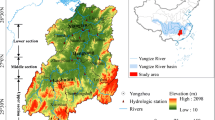
Based on annual runoff data collected from several hydrological stations in the Nen River Basin from 1956 to 2004, the cumulative filter method, Mann-Kendall method and Morlet wavelet analysis were used to analyze variations in the characteristics and factors influencing runoff. Specifically, the general characteristics list as: The distribution of runoff was found to be uneven within a year, and the annual variation showed an overall decreasing trend. The abrupt change points of runoff were found to be in the early 1960s, middle 1980s and late 1990s. Multiple time scales analysis revealed three time-scale cycles, a long-term cycle of about 20–35 years with a scale center of 25 years, another cycle of about 8–15 years with a scale center of 11 years and a short-term cycle of about 5 years. Based on the Morlet wavelet transform coefficients figure of the 25-year time scale, it is preliminarily estimated that the Nen River Basin will enter a high flow period in 2013. The results obtained using various methods were consistent with each other. The physical causes of the results were also analyzed to confirm their accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen RS, Kang E, Yang JP, et al. (2002) Variation tendency in the 50-year annual meteorological and hydrological series of Hexi region of Gansu Province. Journal of Lanzhou University (Nature Sciences) 38(2): 163–170. (In Chinese)
Li HY, Wu YN, Li XB (2012) Mountain effect and differences in storm floods between northern and southern sources of the Songhua River Basin. Journal of Mountain Science 9(3):431–440. Doi: 10.1007/s11629-009-2178-9.
Li HY, Wang YX, Li XB (2011) Mechanism and forecasting methods for severe droughts and floods in Songhua River Basin in China. Chinese Geographical Science 21(5): 531–542. Doi:10.1007/s11769-011-0492-y.
Li ZL, Xu ZX, Gong TL (2008) Characteristics of runoff variation in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Geographical Research 27(2): 353–361. (In Chinese)
Liu J, Yao ZJ, Chen CY (2007) Evolution trend and causation analysis of the runoff evolution in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Journal of Natural Resources 22(3): 471–477. (In Chinese)
Miao R (2007) Principles of Hydrology. Waterpower Press, Beijing, China. pp3 (In Chinese)
Mu XM, Song XY, Gao P et al. (2011) The multiple-time scales features of runoff and sediment discharge in Harbin. Journal of Natural Resources 26(1): 135–144. (In Chinese)
Shi XH, Qin NS, Wang QC, et al. (2007) Analysis on runoff variation characteristics and influencing factors in the upper Yellow River. Journal of Desert Research 27(4): 690–697. (In Chinese)
Sun YG, Bai RH (2005) Main Meteorological Disaster in Songhua River and Nen River. Meteorological Press. Beijing, China 7–8. (In Chinese)
Wang JD. (2003). Hydrologic Statistics. Waterpower Press, Beijing, China. pp 140. (In Chinese)
Wang WS, Ding J, Li YQ (2005) Hydrological Wavelet Analysis. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing,China. pp 4–8. (In Chinese)
Wang YZ, Peng MX (1993) The relationship between runoff variation of the Yellow River and solar activity. Journal of Shandong Meteorology 13(2): 6–10. (In Chinese)
Wang ZL, Chen XH, Yang T (2010) Runoff variation and its impacting factors in the Dongjiang River Basin during 1956–2005. Journal of Nature Resources 25(8): 1365–1374 (In Chinese)
Wei FY. (2007) Statistical Diagnosis and Forecasting Technique of Modern Climate. Meteorological Press, Beijing, China pp63–66. (In Chinese)
Wu Y, Cheng WM, Ren LL, et al. (2006) Analysis on the characteristics of annual runoff in Hotan catchment. Journal of Natural Resources 21(3): 375–381. (In Chinese)
Xu DX (2008) Runoff variation and it’s impacting factor in Nenjiang River during 1956–2006. Master Degree Thesis of the Chinese Academy of Science 28–35. (In Chinese)
Xu DX, Zhang GX, Feng XQ (2009) Discussion on multiple time scales of runoff variation in the Nenjiang River Basin. Resources Science 31(9): 1592–1598. (In Chinese)
Zhang GX, Xu DX, Yin XR (2008) Memoir of the First Conference on Water in Cold Region 182–190.
Zhao XH, Huang Q (2004) Analysis of influencing factors of runoff variation. Process in Natural Science 14(6): 700–704. (In Chinese)
Zhu YL, Chen J, Chen GC (2011) Runoff variation and its impacting factors in the headwaters of the Yangtze River in recent 32 years. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute 28(6): 1–9. (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Hy., Wang, Yx., Jia, Ln. et al. Runoff characteristics of the Nen River Basin and its cause. J. Mt. Sci. 11, 110–118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2332-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2332-7