Abstract
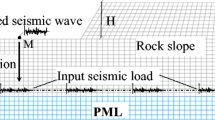
Fourier spectra and acceleration response spectra of near-field acceleration records of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake have been calculated. Relative fundamental frequencies (or predominant periods) were characterized. Then, the natural frequencies of a range of slopes with different geometric characteristics, such as height, slope ratio, and pattern, were analyzed. The seismic responses of the slopes were compared, and the variability of seismic response with the above geometric elements was found. Results show that if slope height increases, and provided that other conditions are unchanged, the natural frequency of the first mode of a double-surface slope will change as a power law. However, natural frequencies will diminish (based on a parabolic function) as the slope angle becomes large. Both the surface pattern and the number of surfaces on a slope can have a great impact on the seismic response of the slope. Moreover, within a certain range of slope heights or angles, either height or angle will also greatly influence the variability of the seismic response. The results of this research will be helpful to understanding seismic dynamic response features and explaining the ways that slope stability can be affected by earthquakes
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambraseys N. N. and Menu J. M. 1988. Earthquake-Induced Ground Displacements. Journal of Earthquake Engineering 16: 985–1006.
Bray J. D. and Travasarou T. 2007. Simplified Procedure for Estimating Earthquake-induced Deviatoric Slope Displacements. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 133(4): 381–392.
Bray J. D. and Travasarou T. 2009. Pseudostatic Coefficient for Use in Simplified Seismic Slope Stability Evaluation. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 135(9): 1336–1340.
Houston S. L., Houston W. N. and Padilla J. M. 1987. Microcomputer-aided Evaluation of Earthquake-induced Permanent Slope Deformations. Microcomputer of Civil Engineering 2(3): 207–222.
Kramer S. L. and Smith M. W. 1997. Modified Newmark Model for Seismic Displacements of Compliant Slopes. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 123(7): 635–644.
Lin J. S. and Whitman R. 1986. Earthquake Induced Displacements of Sliding Blocks. Journal of Geotechnical. Engineering 112(1): 44–59.
Rodriguez-Marek A., Bray J. D. and Abrahamson N. 2001. An Empirical Geotechnical Seismic Site Response Procedure. Earthquake Spectra 171: 65–87.
Sarma S. K. 1975. Seismic Stability of Earth Dams and Embankments. Geotechnique 25(4): 743–761.
Wartman J., Bray J. D. and Seed R. B. 2003. Inclined Plane Studies of the Newmark Sliding Block Procedure. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 129(8): 673–684.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, S., Feng, W. & Zhang, J. Analysis of the effects of slope geometry on the dynamic response of a near-field mountain from the Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Mt. Sci. 7, 353–360 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-010-2055-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-010-2055-6