Abstract
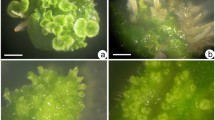
Embelia ribes, an important vulnerable medicinal liana, was regenerated through organogenesis and embryogenesis using leaf explants. Leaf explants produced organogenic calluses on MS medium supplemented with 1.0 mg l−1 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D) and 0.5 mg l−1 6-benzylaminopurine. Shoot regeneration was obtained from organogenic calluses on MS medium containing different concentrations of thidiazuron (TDZ) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). The frequency of shoot bud organogenesis was highest (23.9 shoots/explant) in MS medium containing 0.5 mg l−1 TDZ and 0.1 mg l−1 IAA. The best result for induction of embryogenic callus was noticed in the combination of 2.0 mg l−1 TDZ and 0.5 mg l−1 2,4-D. This callus, maintained in the same medium, showed the highest differentiation of embryos (56.5%) after 6 wk of culture. Embryos were transferred to MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of TDZ, and this facilitated conversion of embryos into plants. After 6 wk of subculture, MS medium with 0.05 mg l−1 TDZ favored the highest percentage (52.2%) embryo conversion. As per the present protocol, 52.2% of the embryos underwent conversion, and a mean number of 29.5 shoots per culture was obtained. Shoots developed from both types of calluses were rooted on half-strength MS basal medium supplemented with 1.0 mg l−1 indole-3-butyric acid. HPLC-UV assay demonstrated the highest embelin content (5.33% w/w) in the embryogenic callus cultures. Embelin was isolated from embryogenic callus and was identified using IR and 1H NMR studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammirato P. V. Embryogenesis. In: Evans D. A.; Sharp W. R.; Ammirato P. V.; Yamada Y. (eds) Hand book of plant culture, vol 1. Macmillan, New York, pp 82–123; 1983.
Anonymous. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India. Part I vol II Ministry of Health and Family welfare. Government of India, New Delhi, pp 123–124; 1990.
Anonymous. The Wealth of India—raw materials. First SupplSer 3 National Institute of Science Communication. CSIR India, New Delhi, pp 74–75; 2002.
Chitra M.; Shyamala Devi C. S.; Sukumar E. Protective action of embelin against lipid peroxidation in tumour-bearing rats. Fitoterapia 65: 317–321; 1994a.
Chitra M.; Sukumar E.; Suja V.; Shyamala Devi C. S. Antitumour, anti-inflammatory and analgesic property of embelin, a plant product. Chemotherapy 40: 109–113; 1994b.
Danquah M.; Li F.; Duke C.; Miller D.; Mahato R. Micellar delivery of bicalutamide and embelin for treating prostate cancer. PharmaceuticalResearch 26(9): 2081–2092; 2009.
Dharmendra S.; Ruchi S.; Pahup S.; Radhey G. S. Effects of embelin on lipid peroxidation and free radical scavenging activity against liver damage in rats. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology 105(4): 243–248; 2009.
Feher A.; Pasternak T. P.; Duditis D. Transition of somatic cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 74: 201–228; 2003.
Flick C. E.; Evans D. A.; Sharp W. R. Organogenesis. In: Evans D. A.; Sharp W. R.; Ammirato P. V.; Yamada Y. (eds) Hand book of plant culture, vol 1. Macmillan, New York, pp 13–81; 1983.
Gary A. T.; Brent H. M. Establishing a micropropagation system for American ginseng (Panaxquinquefolium). Hortscience 21: 232–236; 1986.
Gastaldo P.; Carli S.; Profumo P. Somatic embryogenesis from stem explants of Aesculushippostanum. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 39: 97–99; 1994.
Ignacimuthu S.; Arockiasamy S.; Antonysamy M.; Ravichandran P. Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from mature leaf explants of Eryngiumfoetidum, a condiment. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 56: 131–137; 1999.
Jain M. S., Saxena P. K. (eds) Methods in molecular biology, protocols for in vitro cultures and secondary metabolite analysis of aromatic and medicinal plants, vol 547. Humana Press, New York; 2009.
Jeyaseelan M.; Rao M. V. Biochemical studies of embryogenic and non embryogenic callus of Cardiospermumhalicacabum L. Ind J Exp Bio 43: 555–560; 2005.
Krishna V.; Shankarmurthy K.; Maruthi K. R.; Nagaraja Y. P.; Rahiman B. A. Somatic embryogenesis and regeneration of plantlets from leaf callus culture of Embelia ribes. J Tropical Med Plants 5(1): 44–46; 2004.
Kumara Swamy H. M.; Krishna V.; Shankaramurthy K.; Rahiman B. A.; Manikani K. L.; Mahadevan K. M.; Harish B. G.; Raja Naika H. Wound healing activity of embelin isolated from the ethanol extract of leaves of Embelia ribes Burm. J Ethanopharmacol 109(3): 529–534; 2007.
Mulabagal V.; Tsay S. H. Plant cell cultures—an alternative and efficient source for the production of biologically important secondary metabolites. Inter J ApplSci 2: 29–48; 2004.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497; 1962.
Murthy B. N. S.; Murch S. J.; Saxena P. K. Thidiazuron: a potent regulator of in vitro plant morphogenesis. In Vitro Cell DevBiol Plant 34: 267–275; 1998.
Ozcan S.; Barghchi M.; Firek S.; Draper J. Efficient adventitious shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis in pea. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 34: 271–277; 1993.
Raghu A. V.; Geetha S. P.; Martin G.; Balachandran I.; Ravindran P. N. Direct organogenesis from leaf explants of Embelia ribes Burm. f.—a vulnerable medicinal plant. J Forest Res 11: 57–60; 2006.
Rajashekaran P. E. Biodiversity of threatened species of medicinal plants in India. In: Hosette B. B.; Venkateshwarulu M. (eds) Trends in wildlife Biodiversity Conservation and Management vol 2. Daya Publishing House, India, pp 104–125; 2001.
Rao S. R.; Ravishankar G. A. Plant cell cultures: chemical factories of secondary metabolites. Biotechnology Advances 20(2): 101–153; 2002.
Ravikumar K.; Ved D. K. Hundred red listed medicinal plants of conservation concern in Southern India. 1st ed. Foundation for Revitalization of Local Health Traditions (FRLHT), India, pp 45–47; 2000.
Reinert J. Aspects of organisation organogenesis and embryogenesis. In: Street S. E. (ed) Plant Tissue and Cell culture. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, pp 338–355; 1973.
Rodriguez A. P. M.; Wetzstein H. Y. A morphological and histological comparison of the initiation and development of pecan (Caryaillinoinensis) somatic embryogenic cultures induced with napththaleneacetic acid or 2,4-diclorophenoxyacetic acid. Protoplasma 204: 71–83; 1998.
Shankarmurthy K.; Krishna V.; Maruthi K. R.; Nagaraja Y. P.; Rahiman B. A. High frequency plant regeneration from callus cultures of Embelia ribes Burm. A threatened medicinal plant. Plant Cell Biotech Mol Bio 5(3&4): 115–120; 2004.
Siegelin M. D.; Gaiser T.; Siegelin Y. The XIAP inhibitor embelin enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in malignant glioma cells by down-regulation of the short isoform of FLIP. Neurochemistry International 55(6): 423–430; 2009.
Sivarajan V. V.; Balachandran I. Ayurvedic drugs and their plant sources. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, India, pp 267–269; 1994.
Sudhakar Raja S.; Unnikrishnan K. P.; Ravindran P. N.; Balalachandran I. Determination of embelin in Embelia ribes and Embelia tsjeriam-cottam by HPLC. Ind J Pharm Sci 4: 734–736; 2005.
Tawfik A. A.; Noga G. Cumin regeneration from seedling derived embryogenic callus in response to amended kinetin. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 69: 35–40; 2002.
Vinutha B.; Prashanth D.; Salma K.; Sreeja S. L.; Pratiti D.; Padmaja R.; Radhika S.; Amith A.; Vankateshwarly K.; Deepak M. Screening of selected Indian medicinal plants for Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. J Ethanopharm 109(2): 359–363; 2007.
Yancheva S. D.; Golubowicz S.; Fisher E. S.; Lev-Yadun M. A. Auxin type and timing of application determine the activation of the developmental program during in vitro organogenesis in apple. Plant Sci 165: 299–309; 2003.
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. P. S. Udayan, Senior Scientist, Botany Division, Centre for Medicinal Plants Research for collection and identifying the plant species. The help rendered by Dr. S. Ravi, Senior Scientist, Phytochemistry division, Centre for Medicinal Plants Research, for spectral analysis of the compound is also acknowledged. We are also thankful to Hashim K. M., Phytochemistry division, Centre for Medicinal Plants Research for helpful discussions and comments. Authors are also thankful to the authorities of Arya Vaidya Sala (AVS), Kottakkal for providing facilities and Sir Dorabji Tata Trust, Mumbai for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: J. Canhoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghu, A.V., Unnikrishnan, K., Geetha, S.P. et al. Plant regeneration and production of embelin from organogenic and embryogenic callus cultures of Embelia ribes Burm. f.—a vulnerable medicinal plant. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 47, 506–515 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-011-9365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-011-9365-4