Abstract
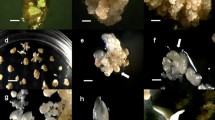
Embryogenic suspensor mass (ESM) was established from immature seeds of Fraser fir. The initiation frequency of ESM was dependent on genotype, collection time, medium, and plant growth regulators (PGR) used. The ESM initiation potential was higher with seeds collected in late June (clone 16-273, 4.7%) or early July (clone 16-45, 2.2%) and decreased as the zygotic embryos matured. Excised proembryo stage of zygotic embryos was most appropriate to initiation of ESM. Most of the ESM arose from the seeds that were at the proembryo stage. From the four different culture media we compared, seven ESM lines were obtained: two lines from Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 4.4 μM benzyladenine (BA), one from Schenk and Hildebrandt (SH) medium with 4.5 μM thidiazuron (TDZ), and four from SH with 4.4 μM 6-benzyladenine. However, only one ESM line from clone 16-273 (June 24, SH+TDZ) could be proliferated in subsequent culture. Different concentrations of l-glutamine and casein hydrolysate (CH) in the medium were also compared for their effect on ESM proliferation. The highest proliferation rate (1.16-fold) was obtained from SH medium supplemented with 250 mg/L CH and 3.42 mM l-glutamine. In contrast, the lowest rate was noted when 1,000 mg/L CH plus 3.42 mM l-glutamine (0.17-fold) was added to the medium. As for somatic embryo maturation, the highest number of mature precotyledonary (100.1/g−1 FW ESM) or cotyledonary (64.3/g−1 FW ESM) somatic embryos was obtained on a medium containing 20 or 80 μM abscisic acid, 10% polyethyleneglycol, 4% maltose, and 0.3% gellan gum. For germination of the somatic embryos, the cotyledonary somatic embryos derived from maturation medium were transferred on half-strength Litvay medium containing 0.3% gellan gum. The somatic plantlets were recovered from the germination medium and transferred to soils.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durzan D. J.; Gupta P. K. Somatic embryogenesis in Duglas-fir cell suspension cultures. Plant Sci. 52: 229–235; 1987. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(87)90056-2.
Find J.; Grace L.; Krogstrup P. Effect of anti-auxins on maturation of embryogenic tissue cultures of Nordmanns fir (Abies nordmanniana). Physiol. Plant. 116: 231–237; 2002. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1160213.x.
Find J. I.; Floto F.; Krogstrup P.; Dahl Mollern J.; NØrgaard J. V.; Kristensen M. M. H. Cryopreservation of an embryogenic suspension culture of Picea sitchensis and subsequent plant regeneration. Scand. J. For. Res. 8: 156–162; 1993.
Hakman I.; Fowke L. C.; von Arnold S.; Eriksson T. The development of somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos of Picea abies (Norway spruce). Plant Sci. 38: 53–59; 1985. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(85)90079-2.
Harry I. S.; Thorpe T. A. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from mature zygotic embryos of red spruce. Bot. Gaz. 152: 446–452; 1991. doi:10.1086/337905.
Hineslet L. E.; Blazich F. A. Vegetative propagation of Abies fraseri by stem cuttings. HortSci. 15: 96–97; 1985.
Hristoforoglu, K.; Grahsl, A.; Schmidt, J. Somatic embryogenesis from mature embryos of Abies alba. Poster at Conifer Biotechnology Working Group Meeting, Raleigh, North Carolina, April 23–28; 1992.
Hristoforoglu K.; Schmidt J.; Bolhar-Nordenkampf H. Development and germination of Abies alba somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 40: 277–284; 1995. doi:10.1007/BF00048134.
Gebhardt, K. Somatic embryogenesis in silver fir (Abies alba). Poster at Conifer Biotechnology Working Group 6th Meeting, North Carolina, April 23–28; 1992.
Guevin T. G.; Kirby E. G. Induction of embryogenesis in cultured mature zygotic embryos of Abies fraseri (Pursh) Poir. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 49: 219–222; 1997. doi:10.1023/A:1005747026269.
Guevin T. G.; Micah V.; Kirby E. G. Somatic embryogenesis in cultured mature zygotic embryos of Abies balsamea. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 37: 205–208; 1994. doi:10.1007/BF00043618.
Kirby E. G.; Leustek T.; Lee M. S. Nitrogen nutrition. In: Bonga J. M.; Durzan D. J. (eds) General principles and biotechnology. Cell and tissue culture in forestry, vol. 1. Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 67–88; 1987.
Khlifi S.; Tremblay F. M. Maturation of black spruce somatic embryos. I. Effect of l-glutamine on the number and germinability of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 41: 23–32; 1995. doi:10.1007/BF00124083.
Krogstrup P.; Erikson E. N.; Moller J. D.; Roulund H. Somatic embryogenesis in Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.). Plant Cell Rep. 7: 594–597; 1988. doi:10.1007/BF00272766.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497; 1962. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x.
NØrgaard J. V. Somatic embryo maturation and plant regeneration in Abies nordmanniana LK. Plant Sci. 124: 211–221; 1997. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(97)04614-1.
NØrgaard, J. V.; Baldursson, S.; Krogstrup, P. Somatic embryogenesis in Abies nordmanniana. Induction and maturation of somatic embryos. Poster at Conifer Biotechnology Working Group 6th Meeting, North Carolina, April 23–28; 1992.
NØrgaard J. V.; Krogstrup P. Cytokinin induced somatic embryogenesis from immature embryos of Abies nordmanniana LK. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 509–513; 1991.
NØrgaard, J. V.; Krogstrup, P. Somatic embryogenesis in Abies spp. In: Jain S.; Gupta P.; Newton R. (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 3. Kluwer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp 341–355; 1995.
Park Y. S. Implementation of conifer somatic embryogenesis in clonal forestry: technical requirements and deployment considerations. Ann. For. Sci. 59: 651–656; 2002. doi:10.1051/forest:2002051.
Rajbhandari N.; Stomp A. Embryogenic callus induction in Fraser fir. HortSci. 32: 737–738; 1997.
Ramarosandratana A.; Harvengt L.; Bouvet A.; Calvaryrac R.; Paques M. Effects of carbohydrate source, polyethylene glycol, and gellan gum concentration of embryonal-suspensor mass (ESM) proliferation and maturation of maritime pine somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol., Plant 37: 29–34; 2001. doi:10.1007/s11627-001-0006-1.
Roberts D. R. Abscisic acid and mannitol promote early development, maturation and storage protein accumulation in somatic embryos of interior spruce. Physiol. Plant. 83: 247–254; 1991. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1991.tb02149.x.
Salaj, T.; Salaj, J. Somatic embryo formation on mature Abies alba × Abies cephalonica zygotic embryo explants. Biol. Plant. 47: 7–11; 2003/4.
Salajova T.; Jasik J.; Kormuták A.; Salaj J.; Hakman I. Embryogenic culture initiation and somatic embryo development in hybrid firs (Abies alba × Abies cephalonica, and Abies alba × Abies numidica). Plant Cell Rep. 15: 527–530; 1996.
Schenk R. V.; Hildebrandt A. C. Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50: 199–204; 1972. doi:10.1139/b72-026.
Schuller A.; Kirchner-NEβ R.; Reuther G. Interaction of plant growth regulators and organic C and N components in the formation and maturation of Abies alba somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 60: 23–31; 2000. doi:10.1023/A:1006429428170.
von Arnold S. Improved efficiency of somatic embryogenesis in mature embryos of Picea abies (L.) Karst. J. Plant Physiol. 128: 233–244; 1987.
Vooková B.; Kormuták A. Effect of sucrose concentration, charcoal, and indole-3-butyric acid on germination of Abies numidica somatic embryos. Biol. Plant. 44: 181–184; 2001. doi:10.1023/A:1010278704613.
Vooková B.; Kormuták A. Plantlet generation in Abies cilicica Carr. and Abies cilicica × Abies nordmanniana hybrid via somatic embryogenesis. Turk. J. Bot. 27: 71–76; 2003.
Vooková B.; Matusova R.; Kormuták A. Secondary somatic embryogenesis in Abies numidica. Biol. Plant. 46: 513–517; 2003. doi:10.1023/A:1024899124774.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Michigan Agricultural Experimentation Station GREEEN Project grant to K.-H.H. (grant no. GR03-015). The authors are grateful to the North Carolina Division of Forest Resources for providing the immature seeds used for this investigation. We also gratefully acknowledge the efforts of Avery County Extension Agent, Jerry Moody, in making the weekly cone collections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.W., Newton, R., Frampton, J. et al. Embryogenic tissue initiation and somatic embryogenesis in Fraser fir (Abies fraseir [Pursh] Poir.). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 45, 400–406 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9169-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9169-3