Summary
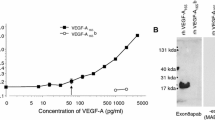
VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) overproduction has been identified as a major factor underlying pathological angiogenesis in vivo, including such conditions as psoriasis, macular degeneration, and tumor proliferation. Endothelial cell tyrosine kinase receptors, KDR and Flt-1, have been implicated in VEGF responses including cellular migration, proliferation, and modulation of vascular permeability. Therefore, agents that limit VEGF-cellular interaction are likely therapeutic candidates for VEGF-mediated disease states (particularly agents blocking activity of VEGF165, the most frequently occurring VEGF isoform). To that end, a nuclease-resistant, VEGF165-specific aptamer NX1838 (2′-fluoropyrimidine, RNA-based oligonucleotide/40-kDa-PEG) was developed. We have assessed NX1838 inhibition of a variety of cellular events associated with VEGF, including cellular binding, signal transduction, calcium mobilization, and induction of cellular proliferation. Our data indicate that NX1838 inhibits binding of VEGF to HUVECs (human umbilical vein endothelial cells) and dose-dependently prevents VEGF-mediated phosphorylation of KDR and PLCγ, calcium flux, and ultimately VEGF-induced cell proliferation. NX1838-inhibition of VEGF-mediated cellular events was comparable to that observed with anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, but was ineffective as an inhibitor of VEGF121-induced HUVEC proliferation. These findings, coupled with nuclease stability of the molecule, suggest that NX1838 may provide therapeutic utility in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, M. J. Inositol triphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature (Lond) 361:315–325; 1993.
Brown, L. F.; Detmar, M.; Claffey, K.; Nagy, J. A.; Feng, D.; Dvorak, A. M.; Dvorak, H. F. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a multifunctional angiogenic cytokine. Exper. Suppl. (Basel) 79:233–269; 1997.
Claffey, K. P.; Robinson, G. S. Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by melanoma cells increases tumor growth, angiogenesis, and experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 56:172–181; 1996.
Claffey, K. P.; Wilkison, W. O.; Spiegelman, B. M. Vascular endothelial growth factor: regulation by cell differentiation and activated second messenger pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 267:16317–16321; 1992.
Clauss, M.; Gerlach, M.; Gerlach, H.; Brett, J.; Wang, F.; Familletti, P. C.; Pan, Y. C.; Olander, J. V.; Connolly, D. T.; Stern, D. Vascular permeability factor: a tumor-derived polypeptide that induces endothelial cell and monocyte procoagulant activity, and promotes monocyte migration. J. Exp. Med. 172:1535–1545; 1990.
Clauss, M.; Weich, H.; Breier, G.; Knies, U.; Rockl, W.; Waltenberger, J.; Risau, W. The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flt-1 mediates biological activities. Implications for a functional role of placenta growth factor in monocyte activation and chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 271:17629–17634; 1996.
Conn, G.; Soderman, D. D.; Shaeffer, M.-T.; Wile, M.; Hatcher, V. B.; Thomas, K. A. Amino acid and cDNA sequences of a vascular endothelial cell mitogen from a rat glioma-derived cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:1323–1327; 1990.
D’Angelo, G.; Lee, H.; Weiner, R. I. cAmp-dependent protein kinase inhibits the mitogenic action of vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor in capillary endothelial cells by blocking Raf activation. J. Cell. Biochem. 67:353–366; 1997.
D’Angelo, G.; Struman, I.; Martial, J.; Weiner, R. I. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in capillary endothelial cells is inhibited by the antiangiogenic factor 16-kDa N-terminal fragment of prolactin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:6374–6378; 1995.
deVries, C.; Escobendo, J. A.; Ueno, H.; Houck, K.; Ferrara, N.; Williams, L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science (Wash DC) 255:989–991; 1992.
Eriksson, A.; Rorsman, C.; Ernlund, A.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Heldin, C. H. Ligand-induced homo- and hetero-dimerization of platelet-derived growth factor alpha- and beta-receptors in intact cells. Growth Factors 6:1–14; 1992.
Ferrara, N.; Houck, K. A.; Jakeman, L. B.; Winer, J.; Leung, D. W. The vascular endothelial growth factor family of polypeptides. J. Cell. Biochem. 47:211–218; 1991.
Fukumura, D.; Xavier, R.; Sugiura, T.; Chen, Y.; Park, E. C.; Lu, N.; Selig, M.; Nielsen, G.; Taksir, T.; Jain, R. K.; Seed, B. Tumor induction of VEGF promoter activity in stromal cells. Cell 94:715–725; 1998.
Gitay-Goren, H.; Soker, S.; Vlodavsky, I.; Neufeld, G. The binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptors is dependent on cell surface-associated heparin-like molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 267:6093–6098; 1992.
Green, L. S.; Jellinek, D.; Bell, C.; Beebe, L. A.; Feistner, B. D.; Gill, S. C.; Jucker, F. M.; Janjic, N. Nuclease-resistant nucleic acid ligands to vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Chem. Biol. 2:683–695; 1995.
Heldin, C.-H. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell 80:213–223; 1995.
Hill, C. S.; Treisman, R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell 80:199–211; 1995.
Jellinek, D.; Green, L. S.; Bell, C.; Janjic, N. Inhibition of receptor binding by high-affinity RNA ligands to vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochemistry 33:10450–10456; 1994.
Kanakaraj, P.; Raj, S.; Khan, S. A.; Bishayee, S. Ligand-induced interaction between alpha- and beta-type platelet-derived growth factor (PEGF) receptors: role of receptor heterodimers in kinase activation. Biochemistry 30:1761–1767; 1991.
Kanner, S. B.; Grosmaire, L. S.; Ledbetter, J. A.; Damle, N. K. Beta 2-integrin LFA-1 signaling through phospholipase C-gamma 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7099–7103; 1993.
Kendall, R. L. and Thomas, K. A. Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor activity by an endogenously encoded soluble receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:10705–10709; 1993.
Keyt, B. A.; Berleau, L. T.; Nguyen, H. V.; Chen, H.; Heinsohn, H.; Vandlen, R.; Ferrara, N. The carboxyl-terminal domain (111–165) of vascular endothelial growth factor is critical for its mitogenic potency. J. Biol. Chem. 271:7788–7795; 1996.
Koch, A. E.; Harlow, L. A.; Haines, G. K.; Amento, E. P.; Unemori, E. N.; Wong, W. L.; Pope, R. M.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. A cytokine modulating endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 152:4149–4156; 1994.
Leung, D. W.; Cachianes, G.; Guang, W. J.; Goeddel, D. V.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science (Wash DC) 246:1306–1309; 1989.
Millauer, B.; Wizigman-Voos, S.; Schnurch, H.; Martinez, R.; Moller, N. P. H.; Risau, W.; Ullrich, A. High affinity VEGF binding and developmental expression suggest Flk-1 as a major regulator of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell 72:835–846; 1993.
Motulsky, H. Intuitive biostatistics. New York: Oxford University Press; 1995.
Nemerson, Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 71:1–8; 1988.
Omura, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Ostman, A.; Heldin, C. H. Identification of a 190-kDa vascular endothelial growth factor 165 cell surface binding protein on a human glioma cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 272:23317–23322; 1997.
Park, J. E.; Keller, G. A.; Ferrara, N. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms: differential deposition into the subepithelial extracellular matrix and bioactivity of extracellular matrix-bound VEGF. Mol. Biol. Cell. 4:1317–1326; 1993.
Plate, K. H.; Breier, G.; Weich, H. A.; Risau, W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature (Lond) 359:845–848; 1992.
Ruckman, J.; Green, L. S.; Beeson, J.; Waugh, S.; Gillette, W. L.; Henninger, D. D.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Janjic, N. 2′-Fluoropyrimidine RNA-based aptamers to the 165-amino acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165). Inhibition of receptor binding and VEGF-induced vascular permeability through interactions requiring the exon 7-encoded domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273:20556–20567; 1998.
Schlessinger, J. Direct binding and activation of receptor tyrosine kinases by collagen. Cell 91:869–872; 1997.
Senger, D. R.; Claffey, K. P.; Benes, J. E.; Perruzzi, C. A.; Sergiou, A. P.; Detmar, M. Angiogenesis promoted by vascular endothelial growth factor: regulation through alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 integrins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:13612–13617; 1997.
Senger, D. R.; Galli, S. J.; Dvorak, A. M.; Perruzzi, C. A.; Harvey, V. S.; Dvorak, H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science (Wash DC) 219:983–985; 1983.
Sioussat, T.; Dvorak, H. F.; Brock, T. A.; Senger, D. R. Inhibition of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) with antipeptide antibodies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 301:15–20; 1993.
Soker, S.; Fidder, H.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Characterization of novel vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors on tumor cells that bind VEGF165 via its exon 7-encoded domain. J. Biol. Chem. 271:5761–5767; 1996.
Soker, S.; Gollamudi-Payne, S.; Fidder, H.; Charmahelli, H.; Klagsbrun, M. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced endothelial cell proliferation by a peptide corresponding to the exon 7-encoded domain of VEGF165. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31582–31588; 1997.
Soker, S.; Takashima, S.; Miao, H. Q.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 92:735–745; 1998.
Strawn, L. M.; McMahon, G.; App, H.; Schreck, R.; Kuchler, W. R.; Longhi, M. P.; Hui, T. H.; Tang, C.; Levitzki, A.; Gazit, A.; Chen, I.; Keri, G.; Orfi, L.; Risau, W.; Flamme, I.; Ullrich, A.; Hirth, K. P.; Shawver, L. K. Flk-1 as a target for tumor growth inhibition. Cancer Res. 56:3540–3545; 1996.
Takahashi, T.; Shibuya, M. The 230 kDa mature form of KDR/Flk-1 (VEGF receptor-2) activates the PLC-gamma pathway and partially induces mitotic signals in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene 14:2079–2089; 1997.
Terman, B. I.; Dougher-Vermazen, M. Biological properties of VEGF/VPF receptors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 15:159–163; 1996.
Terman, B. I.; Dougher-Vermazen, M.; Carrion, M. E.; Dimitrov, D.; Armellino, D. C.; Gospodarowicz, D.; Bohlen, P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 187:1579–1586; 1992.
Tuerk, C. and Gold, L.; Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands. Science (Wash DC) 249:505–510; 1990.
Vaisman, N.; Gospodarowicz, D.; Neufeld, G. Characterization of the receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 265:19461–19466; 1990.
Waltenberger, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Siegbahn, A.; Shibuya, M.; Heldin, C.-H. Different signal transduction properties of KDR and Flt1, two receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 269:26988–26995; 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, C., Lynam, E., Landfair, D.J. et al. Oligonucleotide NX1838 inhibits VEGF165-mediated cellular responses in vitro . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 35, 533–542 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-999-0064-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-999-0064-y