Summary
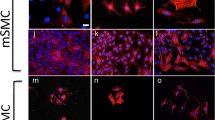
Transcriptional regulation of smooth muscle cell (SMC) differentiation is a rapidly growing area of interest that has relevance for understanding intimal disease. Despite the wealth of data accumulating in vitro, however, no study has compared the cell-specific marker profile, transfectability, promoter activity, and growth characteristics among several SMC culture systems. Accordingly, we performed a comprehensive analysis of the marker profile, growth properties, transfectability, and SMC promoter activity in four rat SMC lines (A7r5, adult and pup aortic, and PAC1). Despite alterations in chromosomal number and structure, A7r5, adult aortic, and PAC1 cells express all SMC markers studied including SM α-actin, SM calponin, SM22, tropoelastin, and to a lesser extent, SM myosin heavy chain (SMMHC). In contrast, pup aortic cells express very low or undetectable levels of all the above markers except tropoelastin. Adult aortic, pup, and PAC1 cells display similar growth curves and levels of proto-oncogene transcripts, whereas those in the A7r5 line are comparatively less. All cell lines studied except pup cells show expression of SMC differentiation genes during active growth, indicating that growth and differentiation are not mutually exclusive in cultured smooth muscle. Transfection studies reveal dramatic differences in DNA uptake and SMC-restricted promoter activity between cell lines. Collectively, these results provide detailed information relating to SMC molecular biology in culture that should facilitate the selection of a cell line for studying the transcriptional regulatory mechanisms underlying SMC differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belknap, J. K.; Grieshaber, N. A.; Schwartz, P. E., et al. Tropoelastin gene expression in individual vascular smooth muscle cells: relationship to DNA synthesis during vascular development and after arterial injury. Circ. Res. 78:388–394; 1996.
Bochaton-Piallat, M. L.; Gabbiani, F.; Ropraz, P., et al. Cultured aortic smooth muscle cells from newborn and adult rats show distinct cytoskeletal features. Differentiation 49:175–185; 1992.
Byron, K. L. Vasopressin stimulates Ca2+ spiking activity in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of phospholipase A2. Circ. Res. 78:813–820; 1996.
Campbell, G. R.; Chamley-Campbell, J. H. Smooth muscle phenotypic modulation: role in atherogenesis. Med. Hypotheses 7:729–735; 1981.
Chamley-Campbell, J.; Campbell, G. R.; Ross, R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol. Rev. 59:1–61; 1979.
Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156–159; 1987.
Cook, C. L.; Weiser, M. C. M.; Schwartz, P. E., et al. Developmentally timed expression of an embryonic growth phenotype in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 74:189–196; 1994.
de Lucca, E. J.; Dhaliwal, M. K.; Furlong, C. L., et al. A high resolution G-banding idiogram of rattus norvegicus chromosomes. Cytobios 62:153–160; 1990.
Ehler, E.; Jat, P. S.; Noble, M. D., et al. Vascular smooth muscle cells of H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mice: characterization of cell lines with distinct properties. Circulation 92:3289–3296; 1995.
Firulli, A. B.; Miano, J. M.; Bi, W., et al. Myocyte enhancer binding factor-2 expression and activity in vascular smooth muscle cells: association with the activated phenotype. Circ. Res. 78:196–204; 1996.
Fritz, K. E.; Jarmolych, J.; Daoud, A. S. Association of DNA synthesis and apparent dedifferentiation of aortic smooth muscle cells in vitro. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 12:354–362; 1970.
Gotwals, P. J.; Chi-Rosso, G.; Lindner, V., et al. The α1β1 integrin is expressed during neointimal formation in rat arteries and mediates collagen matrix reorganization. J. Clin. Invest. 97:2469–2477; 1996.
Herring, B. P.; Smith, A. F. Telokin expression is mediated by a smooth muscle cell-specific promoter. Am. J. Physiol. 270:C1656-C1665; 1996.
Holifield, B.; Helgason, T.; Jemelka, S., et al. Differentiated vascular myocytes: are they involved in neointimal formation? J. Clin. Invest. 97:814–825; 1995.
Huang, S.; Simonson, M. S.; Dunn, M. J. Manidipine inhibits endothelin-1-induced [Ca2+]1 signaling but potentiates endothelin’s effect on c-fos and c-jun induction in vascular smooth muscle and glomerular mesangial cells. Am. Heart J. 125:589–597; 1993.
Kimes, B. W.; Brandt, B. L. Characterization of two putative smooth muscle cell lines from rat thoracic aorta. Exp. Cell Res. 98:349–366; 1976.
Kokubu, T.; Pollak, O. J. In vitro cultures of aortic cells of untreated and of cholesterol-fed rabbits. J. Atherosclerosis Res. 1:229–239; 1961.
Lemire, J. M.; Covin, C. W.; White, S., et al. Characterization of cloned aortic smooth muscle cells from young rats. Am. J. Pathol. 144:1068–1081; 1994.
Li, L.; Miano, J. M.; Cserjesi, P., et al. SM22α, a marker of adult smooth muscle, is expressed in multiple myogenic lineages during embryogenesis. Circ. Res. 78:188–195; 1996.
Li, L.; Miano, J. M.; Mercer, B., et al. Expression of the SM22α promoter in transgenic mice provides evidence for distinct transcriptional regulatory programs in vascular and visceral smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 132:849–859; 1996.
Longtine, J. A.; Pinkus, G. S.; Fujiwara, K., et al. Immunohistochemical localization of smooth muscle myosin in normal human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33:179–184; 1985.
Majesky, M. W.; Benditt, E. P.; Schwartz, S. M. Expression and developmental control of platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and B-chain/Sis genes in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:1524–1528; 1988.
Majesky, M. W.; Giachelli, C. M.; Reidy, M. A., et al. Rat carotid neointimal smooth muscle cells reexpress a developmentally regulated mRNA phenotype during repair of arterial injury. Circ. Res. 71:759–768; 1992.
Miano, J. M.; Cserjesi, P.; Ligon, K. L., et al. Smooth muscle myosin heavy chain exclusively marks the smooth muscle lineage during mouse embryogenesis. Circ. Res. 75:803–812; 1994.
Miano, J. M.; Olson, E. N. Expression of the smooth muscle cell calponin gene marks the early cardiac and smooth muscle cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 271:7095–7103; 1996.
Miano, J. M.; Tota, R. R.; Vlasic, N., et al. Early proto-oncogene expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells following endothelial removal. Am. J. Pathol. 137:761–765; 1990.
Miano, J. M.; Vlasic, N.; Tota, R. R., et al. Localization of Fos and Jun proteins in rat aortic smooth muscle cells after vascular injury. Am. J. Pathol. 142:715–724; 1993.
Moessler, H.; Mericskay, M.; Li, Z., et al. The SM22 promoter directs tissue-specific expression in arterial but not in venous or visceral smooth muscle cells in transgenic mice. Development 122:2415–2425; 1996.
Moss, N. S.; Benditt, E. Spontaneous and experimentally induced arterial lesions I. An ultrastructural survey of the normal chicken aorta. Lab. Invest. 22:166–183; 1970.
Nachtigal, M.; Nagpal, M. L.; Greenspan, P., et al. Characterization of a continuous smooth muscle cell line derived from rabbit aorta. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:892–898; 1989.
Orlandi, A.; Ehrlich, H. P.; Ropraz, P., et al. Rat aortic smooth muscle cells isolated from different layers and at different times after endothelial denudation show distinct biological features in vitro. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14:982–989; 1994.
Owens, G. K. Regulation of differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Physiol. Rev. 75:487–517; 1995.
Perez-Reyes, N.; Halbert, C. L.; Smith, P. P., et al. Immortalization of primary human smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1224–1228; 1992.
Reilly, C. Rat vascular smooth muscle cells immortalized with SV40 large T antigen possess defined smooth muscle cell characteristics including growth inhibition by heparin. J. Cell. Physiol. 142:342–357; 1990.
Rosenquist, T. H.; Beall, A. C. Elastogenic cells in the developing cardiovascular system: smooth muscle, nonmuscle, and cardiac neural crest. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 588:106–119; 1990.
Rothman, A.; Kulik, T. J.; Taubman, M. B., et al. Development and characterization of a cloned rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell line that maintains differentiated properties through multiple subcultures. Circ. Res. 86:1977–1986; 1992.
Rothman, A.; Wolner, B.; Button, D., et al. Immediate-early gene expression in response to hypertrophic and proliferative stimuli in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269:6399–6404; 1994.
Samaha, F. F.; Ip, H. S.; Morrisey, E. E., et al. Developmental pattern of expression and genomic organization of the calponin-h1 gene: a contractile smooth muscle cell marker. J. Biol. Chem. 271:395–403; 1996.
Schwartz, S. M.; deBlois, D.; O’Brien, E. R. M. The intima: soil for atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circ. Res. 77:445–465; 1995.
Seifert, R. A.; Schwartz, S. M.; Bowen-Pope, D. F. Developmentally regulated production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules. Nature 311:669–671; 1984.
Solway, J.; Seltzer, J.; Samaha, F. F., et al. Structure and expression of a smooth muscle cell-specific gene, SM22α. J. Biol. Chem. 270:13460–13469; 1995.
Thyberg, J.; Blomgren, K.; Hedin, U., et al. Phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells during the formation of neointimal thickenings in the rat carotid artery after balloon injury: an electron-microscopic and stereological study. Cell Tissue Res. 281:421–433; 1995.
Thyberg, J.; Palmberg, L.; Nilsson, J., et al. Phenotype modulation in primary cultures of arterial smooth muscle cells: on the role of platelet-derived growth factor. Differentiation 25:156–167; 1983.
Walker, L. N.; Bowen-Pope, D. F.; Ross, R., et al. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules by cultured arterial smooth muscle cells accompanies proliferation after arterial injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:7311–7315; 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firulli, A.B., Han, D., Kelly-Roloff, L. et al. A comparative molecular analysis of four rat smooth muscle cell lines. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 34, 217–226 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-998-0127-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-998-0127-5