Abstract
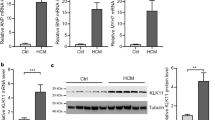
Cardiac hypertrophy plays a major role in heart failure and is related to patient morbidity and mortality. Calcium overloading is a main risk for cardiac hypertrophy, and Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) has been found that it could not only regulate intracellular Na+ levels but also control the intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) level through Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (NCX). Recent studies have reported that klotho could affect [Ca2+]i level. In this study, we aimed at exploring the role of klotho in improving isoproterenol-induced hypertrophic response of H9C2 cells. The H9C2 cells were randomly divided into control and isoproterenol (ISO) (10 μM) groups. Klotho protein (10 μg/ml) or NKAα2 siRNA was used to determine the changes in isoproterenol-induced hypertrophic response. The alterations of [Ca2+]i level were measured by spectrofluorometry. Our results showed that H9C2 cells which were treated with isoproterenol presented a higher level of [Ca2+]i and hypertrophic gene expression at 24 and 48 h compared with the control group. Moreover, the expressions of NKAα1 and NKAα2 were both increased in control and ISO groups after treating with klotho protein; meanwhile, the NKA activity was increased and NCX activity was decreased after treatment. Consistently, the [Ca2+]i level and hypertrophic gene expression were decreased in ISO group after klotho protein treatment. However, these effects were both prevented by transfecting with NKAα2 siRNA. In conclusion, these findings demonstrated that klotho inhibits isoproterenol-induced hypertrophic response in H9C2 cells by activating NKA and inhibiting the reverse mode of NCX and this effect may be associated with the upregulation of NKAα2 expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askoxylakis V, Thieke C, Pleger ST, Most P, Tanner J, Lindel K, Katus HA, Debus J, Bischof M (2010) Long-term survival of cancer patients compared to heart failure and stroke: a systematic review. BMC Cancer 10(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-105
Bos R, Mougenot N, Findji L, Mediani O, Vanhoutte PM, Lechat P (2005) Inhibition of catecholamine-induced cardiac fibrosis by an aldosterone antagonist. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 45(1):8–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200501000-00003
Braunwald E (2013) Heart failure. JACC Heart failure 1(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchf.2012.10.002
Burchfield JS, Xie M, Hill JA (2013) Pathological ventricular remodeling: mechanisms: part 1 of 2. Circulation 128(4):388–400. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001878
Correll RN, Eder P, Burr AR, Despa S, Davis J, Bers DM, Molkentin JD (2014) Overexpression of the Na+/K+ ATPase alpha2 but not alpha1 isoform attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Circ Res 114(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302293
Dai H, Jia G, Liu X, Liu Z, Wang H (2014) Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy via suppressing Ca(2)(+)-mediated calcineurin/NFATc3 and CaMKII signaling cascades. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38(1):263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.008
Despa S, Lingrel JB, Bers DM (2012) Na(+)/K)+)-ATPase alpha2-isoform preferentially modulates Ca2(+) transients and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+) release in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 95(4):480–486. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvs213
Frey N, Katus HA, Olson EN, Hill JA (2004) Hypertrophy of the heart: a new therapeutic target? Circulation 109(13):1580–1589. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000120390.68287.BB
Fuller W, Parmar V, Eaton P, Bell JR, Shattock MJ (2003) Cardiac ischemia causes inhibition of the Na/K ATPase by a labile cytosolic compound whose production is linked to oxidant stress. Cardiovasc Res 57(4):1044–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(02)00810-6
Ikushima M, Rakugi H, Ishikawa K, Maekawa Y, Yamamoto K, Ohta J, Chihara Y, Kida I, Ogihara T (2006) Anti-apoptotic and anti-senescence effects of Klotho on vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339(3):827–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.094
Imura A, Tsuji Y, Murata M, Maeda R, Kubota K, Iwano A, Obuse C, Togashi K, Tominaga M, Kita N, Tomiyama K, Iijima J, Nabeshima Y, Fujioka M, Asato R, Tanaka S, Kojima K, Ito J, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N, Ito T, Nishio T, Uchiyama T, Fujimori T (2007) Alpha-Klotho as a regulator of calcium homeostasis. Science 316(5831):1615–1618. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1135901
James PF, Grupp IL, Grupp G, Woo AL, Askew GR, Croyle ML, Walsh RA, Lingrel JB (1999) Identification of a specific role for the Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 isoform as a regulator of calcium in the heart. Mol Cell 3:555–563
Jia Z, Wei L, Liu Q, Zhu Z, Yang J, Yang X, Gan S, Chen W, Zhang L (2015) Impact of transfection with recombinant adenovirus vector-mediated Klotho gene on myocardial remodeling in a rat model of heart failure. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 43(3):219–226
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nagai R, Nabeshima YI (1997) Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390(6655):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/36285
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Nandi A, Gurnani P, McGuinness OP, Chikuda H, Yamaguchi M, Kawaguchi H, Shimomura I, Takayama Y, Herz J, Kahn CR, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309(5742):1829–1833. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112766
Kusaba T, Okigaki M, Matui A, Murakami M, Ishikawa K, Kimura T, Sonomura K, Adachi Y, Shibuya M, Shirayama T, Tanda S, Hatta T, Sasaki S, Mori Y, Matsubara H (2010) Klotho is associated with VEGF receptor-2 and the transient receptor potential canonical-1 Ca2+ channel to maintain endothelial integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(45):19308–19313. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008544107
Ohara T, Sussman KE, Draznin B (1991) Effect of diabetes on cytosolic free Ca2+ and Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase in rat aorta. Diabetes 40(11):1560–1563. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.40.11.1560
Razzaque MS (2008) Klotho and Na+,K+-ATPase activity: solving the calcium metabolism dilemma? Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:459–461
Satoh H, Ginsburg KS, Qing K, Terada H, Hayashi H, Bers DM (2000) KB-R7943 block of Ca(2+) influx via Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange does not alter twitches or glycoside inotropy but prevents Ca(2+) overload in rat ventricular myocytes. Circulation 101(12):1441–1446. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.12.1441
Schafer C, Ladilov Y, Inserte J, Schafer M, Haffner S, Garcia-Dorado D, Piper HM (2001) Role of the reverse mode of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Cardiovasc Res 51(2):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00282-6
Schiattarella GG, Hill JA (2015) Inhibition of hypertrophy is a good therapeutic strategy in ventricular pressure overload. Circulation 131(16):1435–1447. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.013894
Song S, Si LY (2015) Klotho ameliorated isoproterenol-induced pathological changes in cardiomyocytes via the regulation of oxidative stress. Life Sci 135:118–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.024
Song S, Gao P, Xiao H, Xu Y, Si LY (2013) Klotho suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice with stress-induced cardiac injury via downregulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS One 8(12):e82968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082968
Swift F, Tovsrud N, Sjaastad I, Sejersted OM, Niggli E, Egger M (2010) Functional coupling of alpha(2)-isoform Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase and Ca(2+) extrusion through the Na(+)/Ca(2+)-exchanger in cardiomyocytes. Cell Calcium 48(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2010.06.006
Watkins SJ, Borthwick GM, Arthur HM (2011) The H9C2 cell line and primary neonatal cardiomyocyte cells show similar hypertrophic responses in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47(2):125–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-010-9368-1
Xu KY, Zhu W, Chen L, DeFilippi C, Zhang J, Xiao RP (2011) Mechanistic distinction between activation and inhibition of (Na(+)+K(+))-ATPase-mediated Ca2+ influx in cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406:200–203
Xu H, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wei J, Sun L, Zhang J (2012) Effect of distinct sources of Ca(2+) on cardiac hypertrophy in cardiomyocytes. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 237(3):271–278. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2011.011273
Zhang R, Khoo MS, Wu Y, Yang Y, Grueter CE, Ni G, Price EE Jr, Thiel W, Guatimosim S, Song LS, Madu EC, Shah AN, Vishnivetskaya TA, Atkinson JB, Gurevich VV, Salama G, Lederer WJ, Colbran RJ, Anderson ME (2005) Calmodulin kinase II inhibition protects against structural heart disease. Nat Med 11(43):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1215
Funding
This study was supported by grant numbers 81400299 and 81370446 from the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, G., Shen, Y., Gao, P. et al. Klotho attenuates isoproterenol-induced hypertrophic response in H9C2 cells by activating Na+/K+-ATPase and inhibiting the reverse mode of Na+/Ca2+-exchanger. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 54, 250–256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-017-0215-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-017-0215-5