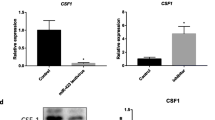
Abstract
Previous studies have reported that microRNA-764-3p (miR-764-3p) is one of the most up-regulated microRNAs (miRNAs) in TGF-β1-stimulated mouse ovarian granulosa cells. However, little is known about the roles and mechanisms of miR-764-3p in granulosa cell function during follicular development. In this study, we found that overexpression of miR-764-3p inhibited 17β-estradiol (E2) synthesis of granulosa cells through directly targeting steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1). MiR-764-3p inhibited SF-1 by affecting its messenger RNA (mRNA) stability, which subsequently suppressed the expression levels of Cyp19a1 gene (aromatase, a downstream target of SF-1). In addition, SF-1 was involved in regulation of miR-764-3p-mediated Cyp19a1 expression in granulosa cells which contributed, at least partially, to the effects of miR-764-3p on granulosa cell E2 release. These results suggest that miR-764-3p functions to decrease steroidogenesis by targeting SF-1, at least in part, through inactivation of Cyp19a1. Taken together, our data provide mechanistic insights into the roles of miR-764-3p on E2 synthesis. Understanding of potential miRNAs affecting estrogen synthesis will help to diagnose and treat steroid-related diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adashi EY, Hsueh AJ (1982) Estrogens augment the stimulation of ovarian aromatase activity by follicle-stimulating hormone in cultured rat granulosa cells. J Biol Chem 257(11):6077–6083
Ahn HW et al (2010) Micron transcriptome in the newborn mouse ovaries determined by massive parallel sequencing. Mol Hum Reprod 16(7):463–471
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006):350–355
Barnett KR et al (2006) Ovarian follicle development and transgenic mouse models. Hum Reprod Update 12(5):537–555
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233
Buaas FW et al (2012) In vivo evidence for the crucial role of SF1 in steroid-producing cells of the testis, ovary and adrenal gland. Development 139(24):4561–4570
Cocquet J et al (2005) Sense and antisense Foxl2 transcripts in mouse. Genomics 85(5):531–541
Dai A et al (2013) MicroRNA-133b stimulates ovarian estradiol synthesis by targeting Foxl2. FEBS Lett 587(15):2474–2482
Drummond AE (2006) The role of steroids in follicular growth. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 4:16
Edson MA, Nagaraja AK, Matzuk MM (2009) The mammalian ovary from genesis to revelation. Endocr Rev 30(6):624–712
Endo M et al (2013) Estradiol supports in vitro development of bovine early antral follicles. Reproduction 145(1):85–96
Fortune JE (2003) The early stages of follicular development: activation of primordial follicles and growth of preantral follicles. Anim Reprod Sci 78(3–4):135–163
Garzo VG, Dorrington JH (1984) Aromatase activity in human granulosa cells during follicular development and the modulation by follicle-stimulating hormone and insulin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 148(5):657–662
Griffiths-Jones S et al (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D140–D144
Hirshfield AN (1991) Development of follicles in the mammalian ovary. Int Rev Cytol 124:43–101
Hrabia A, Ha Y, Shimada K (2004) Expression of estrogen receptor alpha mRNA in theca and granulosa layers of the ovary in relation to follicular growth in quail. Folia Biol (Krakow) 52(3–4):191–195
Ingraham HA et al (1994) The nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor 1 acts at multiple levels of the reproductive axis. Genes Dev 8(19):2302–2312
Jenkins C et al (1993) Exon-specific northern analysis and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) reveal that the proximal promoter II (PII) is responsible for aromatase cytochrome P450 (CYP19) expression in human ovary. Mol Cell Endocrinol 97(1–2):R1–R6
Knight PG, Glister C (2006) TGF-beta superfamily members and ovarian follicle development. Reproduction 132(2):191–206
Krek A et al (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37(5):495–500
Lan HC et al (2007) Cyclic AMP stimulates SF-1-dependent CYP11A1 expression through homeodomaininteracting protein kinase 3-mediated Jun N-terminal kinase and c-Jun phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 27(6):2027–2036
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120(1):15–20
Liang N et al (2011) Steroidogenic factor-1 is required for TGF-beta3-mediated 17beta-estradiol synthesis in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology 152(8):3213–3225
Liang M et al (2013) Transcriptional cooperation between p53 and NF-kappaB p65 regulates microRNA-224 transcription in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 370(1–2):119–129
Lourenco D et al (2009) Mutations in NR5A1 associated with ovarian insufficiency. N Engl J Med 360(12):1200–1210
Luo X, Ikeda Y, Parker KL (1994) A cell-specific nuclear receptor is essential for adrenal and gonadal development and sexual differentiation. Cell 77(4):481–490
Matsumura T et al (2013) Human glutathione S-transferase A (GSTA) family genes are regulated by steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) and are involved in steroidogenesis. FASEB J 27(8):3198–3208
McGee EA, Hsueh AJ (2000) Initial and cyclic recruitment of ovarian follicles. Endocr Rev 21(2):200–214
Morohashi K et al (1992) A common trans-acting factor, Ad4-binding protein, to the promoters of steroidogenic P- 450s. J Biol Chem 267(25):17913–17919
Nagaraja AK et al (2008) Deletion of Dicer in somatic cells of the female reproductive tract causes sterility. Mol Endocrinol 22(10):2336–2352
Otsuka M et al (2008) Impaired microRNA processing causes corpus luteum insufficiency and infertility in mice. J Clin Invest 118(5):1944–1954
Parker KL, Schimmer BP (1997) Steroidogenic factor 1: a key determinant of endocrine development and function. Endocr Rev 18(3):361–377
Parker KL et al (2002) Steroidogenic factor 1: an essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog Horm Res 57:19–36
Rice DA et al (1991) A shared promoter element regulates the expression of three steroidogenic enzymes. Mol Endocrinol 5(10):1552–1561
Robker RL, Richards JS (1998) Hormone-induced proliferation and differentiation of granulosa cells: a coordinated balance of the cell cycle regulators cyclin D2 and p27Kip1. Mol Endocrinol 12(7):924–940
Salilew-Wondim D et al (2014) The expression pattern of microRNAs in granulosa cells of subordinate and dominant follicles during the early luteal phase of the bovine estrous cycle. PLoS One 9(9):e106795
Sasson R et al (2003) Novel genes modulated by FSH in normal and immortalized FSH-responsive cells: new insights into the mechanism of FSH action. FASEB J 17(10):1256–1266
Shen L et al (2013) MicroRNA23a and microRNA23b deregulation derepresses SF-1 and upregulates estrogen signaling in ovarian endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(4):1575–1582
Sun K, Lai EC (2013) Adult-specific functions of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet 14(8):535–548
Takasawa K et al (2014) FOXL2 transcriptionally represses Sf1 expression by antagonizing WT1 during ovarian development in mice. FASEB J 28(5):2020–2028
Tam OH et al (2008) Pseudogene-derived small interfering RNAs regulate gene expression in mouse oocytes. Nature 453(7194):534–538
Tasaki H et al (2013) Estradiol has a major role in antrum formation of porcine preantral follicles cultured in vitro. Theriogenology 79(5):809–814
Troppmann B et al (2014) Micron miR-513a-3p acts as a co-regulator of luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor gene expression in human granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 390(1–2):65–72
Vanderhyden BC, Macdonald EA (1998) Mouse oocytes regulate granulosa cell steroidogenesis throughout follicular development. Biol Reprod 59(6):1296–1301
Xia HF et al (2014) Micron expression and regulation in the uterus during embryo implantation in rat. FEBS J 281(7):1872–1891
Xu S et al (2011) Micro-RNA378 (miR-378) regulates ovarian estradiol production by targeting aromatase. Endocrinology 152(10):3941–3951
Xue Q et al (2014) Methylation of a novel CpG island of intron 1 is associated with steroidogenic factor 1 expression in endometriotic stromal cells. Reprod Sci 21(3):395–400
Yao G et al (2010) Micron-224 is involved in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated mouse granulosa cell proliferation and granulosa cell function by targeting Smad4. Mol Endocrinol 24(3):540–551
Yao G et al (2014) Micron-224 is involved in the regulation of mouse cumulus expansion by targeting Ptx3. Mol Cell Endocrinol 382(1):244–253
Yin M et al (2012) Transactivation of microRNA-383 by steroidogenic factor-1 promotes estradiol release from mouse ovarian granulosa cells by targeting RBMS1. Mol Endocrinol 26(7):1129–1143
Zamore PD, Haley B (2005) Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science 309(5740):1519–1524
Zhang H et al (2014) microRNA 376a regulates follicle assembly by targeting Pcna in fetal and neonatal mouse ovaries. Reproduction 148(1):43–54
Zhao Z et al (2012) Circulating microRNA miR-323-3p as a biomarker of ectopic pregnancy. Clin Chem 58(5):896–905
Funding
This work was supported by the following grants: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81100399); Chongqing Yuzhong District Natural Science Foundation of China (20150117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure summary
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Authors’ contribution
Ll.W. performed cell extraction, RNA extraction, gene expression, Western blotting, and drafted the manuscript. C.L. performed cell proliferation and estradiol analysis. R.L. performed cell culture. Yl.D. and Yx.T. performed plasmid construction and data analysis. C.T. revised the manuscript. Hb.Q. designed experiments and wrote this manuscript. All of the authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supplemental Figure S1. The efficacy of SF-1 siRNAs was evaluated by Western blotting after 48 h transfection with either si-NC or si-SF-1. Supplemental Table S1. List of primer pairs for real-time PCR. Supplemental Table S2. List of primer pairs for construction of vectors. (DOCX 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Li, C., Li, R. et al. MicroRNA-764-3p regulates 17β-estradiol synthesis of mouse ovarian granulosa cells by targeting steroidogenic factor-1. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 365–373 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9977-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9977-9