Abstract
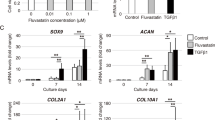
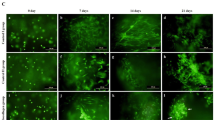
Recent studies have demonstrated that insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-I) modulates bone mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation independent of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling in vitro. However, it is unclear whether IGF-I can solely modulate human adipose-derived mesenchymal cell (hAMC) chondrogenic differentiation, or whether it has additive effects with TGF-β1 to induce chondrogenic differentiation in vitro and development of mature cartilage in vivo. We investigated the effect of IGF-I on the induction of hAMC chondrogenic differentiation in the presence or absence of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) in vitro, and chondrogenesis of the induced hAMC in vivo. The results showed that IGF-I alone induced collagen type II, aggrecan, and Sox9 mRNA expression and collagen type II and aggrecan proteins expressions in hAMCs. Notably, there was greater mRNA expression of collagen type II, aggrecan and Sox9, and greater protein expression of collagen type II and aggrecan following TGF-β1 + IGF-I treatment, compared to either TGF-β1 or IGF-I-treated hAMCs. These results were confirmed in cartilage tissues derived from induced hAMCs. These findings indicate that IGF-I alone has the ability to induce chondrogenic differentiation and has additive effects with TGF-β1 to induce chondrogenic differentiation in vitro and in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baddoo M, Hill K, Wilkinson R, Gaupp D, Hughes C, Kopen GC, Phinney DG (2003) Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from murine bone marrow by negative selection. J Cell Biochem 89:1235–1249
Blunk T, Sieminski AL, Gooch KJ, Courter DL, Hollander AP, Nahir AM, Langer R, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Freed LE (2002) Differential effects of growth factors on tissue-engineered cartilage. Tissue Eng 8:73–84
Bogdanova-Jantniece A, Berzins U, Kozlovska T (2014) Growth properties and pluriopotency marker expression of spontaneously formed three-dimensional aggregates of human adipose-derived stem cells. Int J Stem Cells 7:143–152
Bonnevie ED, Puetzer JL, Bonassar LJ (2014) Enhanced boundary lubrication properties of engineered menisci by lubricin localization with insulin-like growth factor I treatment. J Biomech 47(9):2183–2188
Brzoska M, Geiger H, Gauer S, Baer P (2005) Epithelial differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:142–150
Chiou M, Xu Y, Longaker MT (2006) Mitogenic and chondrogenic effects of fibroblast growth factor-2 in adipose-derived mesenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343:644–652
Correia SI, Pereira H, Silva-Correia J, Van Dijk CN, Espregueira-Mendes J, Oliveira JM, Reis RL (2014) Current concepts: tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications in the ankle joint. J R Soc Interface 11:20130784
De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, Alfonso Z, Zuk PA, Zhu M, Dragoo JL, Ashjian P, Thomas B, Benhaim P, Chen I, Fraser J, Hedrick MH (2003) Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs 174:101–109
Deng Y, Cao H, Cu F, Xu D, Lei Y, Tan Y, Magdalou J, Wang H, Chen L (2013) Nicotine-induced retardation of chondrogenesis through down-regulation of IGF-1 signaling pathway to inhibit matrix synthesis of growth plate chondrocytes in fetal rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 269:25–33
Denko CW, Boja B, Moskowitz RW (1990) Growth promoting peptides in osteoarthritis: insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1, growth hormone. J Rheumatol 17:1217–1221
Derynck R, Zhang YE (2003) Smad-dependent and smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 425:577–584
Fortier LA, Mohammed HO, Lust G, Nixon AJ (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances cell-based repair of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol 84:276–288
Fukumoto T, Sperling JW, Sanyal A, Fitzsimmons JS, Reinholz GG, Conover CA, O’Driscoll SW (2003) Combined effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 on periosteal mesenchymal cells during chondrogenesis in vitro. Osteoarthr Cartil 11:55–64
Gao S, Zhao P, Lin C, Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Yang D, Wang X, Xu H, Zhou F, Cao L, Zhou W, Ning K, Chen X, Xu J (2014) Differentiation of human-adipose derived stem cells into neuron-like cells which are compatible with photocurable three-dimensional scaffolds. Tissue Eng A 20:1271–1284
Goude MC, McDevitt TC, Temenoff JS (2014) Chondroitin sulfate microparticles modulate transforming growth factor-β1-indcuced chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cell spheroids. Cells Tissues Organs 199:117–130
Hendriks J, Riesle J, van Blitterswijk CA (2007) Co-culture in cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 1:170–178
Hennig T, Lorenz H, Thiel A, Goetzke K, Dickhut A, Geiger F, Richter W (2007) Reduced chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue derived stromal cells correlates with an altered TGFbeta receptor and BMP profile and is overcome by BMP-6. J Cell Physiol 211:682–691
Indrawattana N, Chen G, Tadokoro M, Shann LH, Ohgushi H, Tateishi T, Tanaka J, Bunyaratvej A (2004) Growth factor combination for chondrogenic induction from human mesenchymal stem cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:914–919
Kim HJ, Im GI (2009) Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: greater doses of growth factor are necessary. J Orthop Res 27:612–619
Kingham PJ, Kalbermatten DF, Mahay D, Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M, Terenghi G (2007) Adipose-derived stem cells differentiate into a Schwann cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol 207:267–274
Li J, Zhao Q, Wang E, Zhang C, Wang G, Yuan Q (2012) Dynamic compression of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells transfected with insulin-like growth factor 1 in chitosan/gelatin scaffolds induces chondrogenesis and matrix biosynthesis. J Cell Physiol 227:2003–2012
Lin Y, Luo E, Chen X, Liu L, Qiao J, Yan Z, Li Z, Tang W, Zheng X, Tian W (2005) Molecular and cellular characterization during chondrogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in vitro and cartilage formation in vivo. J Cell Mol Med 9:929–939
Longobardi L, O’Rear L, Aakula S, Johnstone B, Shimer K, Chytil A, Horton WA, Moses HL, Spagnoli A (2006) Effect of IGF-I in the chondrogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the presence or absence of TGF-beta signaling. J Bone Miner Res 21:626–636
Madry H, Padera R, Seidel J, Langer R, Freed LE, Trippel SB, Vunjak-Novakovic G (2002) Gene transfer of a human insulin-like growth factor I cDNA enhances tissue engineering of cartilage. Hum Gene Ther 13:1621–1630
Madry H, Kaul G, Zurakowski D, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Cucchiarini M (2013) Cartilage constructs engineered from chondrocytes overexpressing IGF-I improve the repair of osteochondral defects in a rabbit model. Eur Cell Mater 25:229–247
Martel-Pelletier J, Di BJA, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP (1998) IGF/IGFBP axis in cartilage and bone in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Inflamm Res 47:90–100
Merceron C, Portron S, Masson M, Lesoeur J, Fellah BH, Gauthier O, Geffroy O, Weiss P, Guicheux J, Vinatier C (2011) The effect of two- and three-dimensional cell culture on the chondrogenic potential of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells after subcutaneous transplantation with an injectable hydrogel. Cell Transplant 20:1575–1588
Middleton JF, Tyler JA (1992) Upregulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in the lesions of osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis 51:440–447
Milne M, Quail JM, Baran DT (1998) Dexamethasone stimulates osteogenic differentiation in vertebral and femoral bone marrow cell cultures: comparison of IGF-I gene expression. J Cell Biochem 71:382–391
Nixon AJ, Lillich JT, Burton-Wurster N, Lust G, Mohammed HO (1998) Differentiated cellular function in fetal chondrocytes cultured with insulin-like growth factor-I and transforming growth factor-beta. J Orthop Res 16:531–541
Oh CD, Chun JS (2003) Signaling mechanisms leading to the regulation of differentiation and apoptosis of articular chondrocytes by insulin-like growth factor-1. J Biol Chem 278:36563–36571
Olney RC, Tsuchiya K, Wilson DM, Mohtai M, Maloney WJ, Schurman DJ, Smith RL (1996) Chondrocytes from osteoarthritic cartilage have increased expression of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and -5, but not IGF-II or IGFBP-4. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1096–1103
Pelton RW, Saxena B, Jones M, Moses HL, Gold LI (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2, and TGF beta 3 in the mouse embryo: expression patterns suggest multiple roles during embryonic development. J Cell Biol 115:1091–1105
Sakimura K, Matsumoto T, Miyamoto C, Osaki M, Shindo H (2006) Effects of insulin-like growth factor I on transforming growth factor beta1 induced chondrogenesis of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in a polyglycolic acid scaffold. Cells Tissues Organs 183:55–61
Schouten JS, Van den Ouweland FA, Valkenburg HA, Lamberts SW (1993) Insulin-like growth factor-1: a prognostic factor of knee osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol 32:274–280
Sowa Y, Imura T, Numajiri T, Takeda K, Mabuchi Y, Matsuzaki Y, Nishino K (2013) Adipose stromal cells contain phenotypically distinct adipogenic progenitors derived from neural crest. PLoS One 8:e84206
Takagi M, Umetsu Y, Fujiwara M, Wakitani S (2007) High inoculation cell density could accelerate the differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to chondrocyte cells. J Biosci Bioeng 103:98–100
Worster AA, Brower-Toland BD, Fortier LA, Bent SJ, Williams J, Nixon AJ (2001) Chondrocytic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells sequentially exposed to transforming growth factor-beta1 in monolayer and insulin-like growth factor-I in a three-dimensional matrix. J Orthop Res 19:738–749
Yi C, Ma C, Xie Z, Zhang G, Song W, Zhou X, Cao Y (2013) Down-regulation of programmed cell death 5 by insulin-like growth factor 1 in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int Orthop 37:937–943
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P, Hedrick MH (2002) Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4279–4295
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the scientific research fund of the Bureau of Public Health of Jiangsu province (no. H201254) and the Huai’an Technology Support Program (social development) funded projects (no. HAS2013046).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Quan Zhou and Baojun Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Li, B., Zhao, J. et al. IGF-I induces adipose derived mesenchymal cell chondrogenic differentiation in vitro and enhances chondrogenesis in vivo. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 356–364 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9969-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9969-9