Abstract
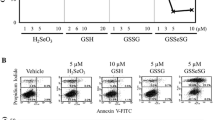
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer with limited effective treatment options. New therapeutic approaches are urgently needed to improve the prognosis of TNBC. Here we demonstrated that a redox modulator, selenocystine (SeC), significantly inhibits TNBC cell proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Through cell apoptosis assays and cell cycle distribution analyses, we have shown that the in vitro inhibitory effect of SeC on TNBC cells can be attributed to the induction of apoptosis and the S-phase arrest in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, this finding implies that SeC potentially is a novel therapeutic agent for TNBC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfarouk KO, Muddathir AK, Shayoub ME (2011) Tumor acidity as evolutionary spite. Cancers (Basel) 3:408–14
Amaral AF, Cantor KP, Silverman DT, Malats N (2010) Selenium and bladder cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:2407–15
Babaknejad N, Sayehmiri F, Sayehmiri K, Rahimifar P, Bahrami S, Delpesheh A, Hemati F, Alizadeh S (2014) The relationship between selenium levels and breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:1–7
Bosch A, Eroles P, Zaragoza R, Vina JR, Lluch A (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: molecular features, pathogenesis, treatment and current lines of research. Cancer Treat Rev 36:206–15
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW (2011) Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11:85–95
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, Ollila DW, Sartor CI, Graham ML, Perou CM (2007) The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 13:2329–34
Chen T, Wong YS (2008a) Selenocystine induces apoptosis of A375 human melanoma cells by activating ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and p53 phosphorylation. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2763–75
Chen T, Wong YS (2008b) Selenocystine induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells by modulating ERK and Akt phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem 56:10574–81
Chen T, Wong YS (2009a) Selenocystine induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 63:105–13
Chen T, Wong YS (2009b) Selenocystine induces caspase-independent apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells with involvement of p53 phosphorylation and reactive oxygen species generation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:666–76
Cleator S, Heller W, Coombes RC (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol 8:235–44
Diplock AT (1987) Trace elements in human health with special reference to selenium. Am J Clin Nutr 45:1313–22
Elias AD (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: a short review. Am J Clin Oncol 33:637–45
Fernandes A P, Gandin V (2014) Selenium compounds as therapeutic agents in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta
Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 363:1938–48
Fritz H, Kennedy D, Fergusson D, Fernandes R, Cooley K, Seely A, Sagar S, Wong R, Seely D (2011) Selenium and lung cancer: a systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS One 6, e26259
Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2004) Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer 4:891–9
Goel A, Fuerst F, Hotchkiss E, Boland CR (2006) Selenomethionine induces p53 mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 5(5):529–535
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W, Toppmeyer D (2006) Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:5652–7
Hurst R, Hooper L, Norat T, Lau R, Aune D, Greenwood DC, Vieira R, Collings R, Harvey LJ, Sterne JA, Beynon R, Savovic J, Fairweather-Tait SJ (2012) Selenium and prostate cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 96:111–22
Jiang C, Wang Z, Gunther H, Lü J (2002) Distinct effects of methylseleninic acid versus selenite on apoptosis, cell cycle, and protein kinase pathways in DU145 human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 1(12):1059–1066
Kalimuthu S, Se-Kwon K (2013) Cell survival and apoptosis signaling as therapeutic target for cancer: marine bioactive compounds. Int J Mol Sci 14(2):2334–2354
Kim JW, Dang CV (2006) Cancer's molecular sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res 66:8927–30
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME, Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y, Pietenpol JA (2011) Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest 121:2750–67
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B, Green M, Cristofanilli M, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2008) Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:1275–81
Pais R, Dumitrascu DL (2013) Do antioxidants prevent colorectal cancer? A meta-analysis. Rom J Intern Med 51:152–63
Poerschke RL, Moos PJ (2011) Thioredoxin reductase 1 knockdown enhances selenazolidine cytotoxicity in human lung cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction. Biochem Pharmacol 81:211–21
Rakha EA, Ellis IO (2009) Triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer: review. Pathology 41:40–7
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2007) Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 109:25–32
Rayman MP (2000) The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet 356:233–41
Rayman MP (2012) Selenium and human health. Lancet 379:1256–68
Roman M, Jitaru P, Barbante C (2014) Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 6:25–54
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CJ, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, Swain SM, Pisansky TM, Fehrenbacher L, Kutteh LA, Vogel VG, Visscher DW, Yothers G, Jenkins RB, Brown AM, Dakhil SR, Mamounas EP, Lingle WL, Klein PM, Ingle JN, Wolmark N (2005) Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:1673–84
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, Hess KR, Stec J, Ayers M, Wagner P, Morandi P, Fan C, Rabiul I, Ross JS, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2005) Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 11:5678–85
Shen F, W S Cai, J L Li, Z Feng, J Cao & B Xu (2015) The Association Between Serum Levels of Selenium, Copper, and Magnesium with Thyroid Cancer: a Meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res
Silver DP, Richardson AL, Eklund AC, Wang ZC, Szallasi Z, Li Q, Juul N, Leong CO, Calogrias D, Buraimoh A, Fatima A, Gelman RS, Ryan PD, Tung NM, De Nicolo A, Ganesan S, Miron A, Colin C, Sgroi DC, Ellisen LW, Winer EP, Garber JE (2010) Efficacy of neoadjuvant Cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1145–53
Singh RP, Dhanalakshmi S, Agarwal R (2002) Phytochemicals as cell cycle modulators--a less toxic approach in halting human cancers. Cell Cycle 1(3):156–161
Toogood PL (2002) Progress toward the development of agents to modulate the cell cycle. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6(4):472–478
Troester MA, Hoadley KA, Sorlie T, Herbert BS, Borresen-Dale AL, Lonning PE, Shay JW, Kaufmann WK, Perou CM (2004) Cell-type-specific responses to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer. Cancer Res 64:4218–26
Unni E, Koul D, Yung WK, Sinha R (2005) Se-methylselenocysteine inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity of mouse mammary epithelial tumor cells in vitro. Breast Cancer Res 7(5):R699–R707
Venkateswaran V, Klotz LH, Fleshner NE (2002) Selenium modulation of cell proliferation and cell cycle biomarkers in human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 62(9):2540–2545
Wallenberg M, Misra S, Wasik AM, Marzano C, Bjornstedt M, Gandin V, Fernandes AP (2014) Selenium induces a multi-targeted cell death process in addition to ROS formation. J Cell Mol Med 18:671–84
Wang Z, Hu H, Li G, Lee HJ, Jiang C, Kim SH, Lü J (2008) Methylseleninic acid inhibits microvascular endothelial G1 cell cycle progression and decreases tumor microvessel density. Int J Cancer 122(1):15–24
Wei WQ, Abnet CC, Qiao YL, Dawsey SM, Dong ZW, Sun XD, Fan JH, Gunter EW, Taylor PR, Mark SD (2004) Prospective study of serum selenium concentrations and esophageal and gastric cardia cancer, heart disease, stroke, and total death. Am J Clin Nutr 79:80–5
Zhong W, Oberley TD (2001) Redox-mediated effects of selenium on apoptosis and cell cycle in the LNCaP human prostate cancer cell line. Cancer Res 61(19):7071–7078
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Musheng Zeng for providing the human TNBC cell lines and Prof. Tianfeng Chen for providing the SeC. This research was supported by the Female Tumor Drugs Research Foundation of Guangdong Pharmaceutical Association (No. 2014D09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, M., Wu, J., Hao, J. et al. Selenocystine-induced cell apoptosis and S-phase arrest inhibit human triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 51, 1077–1084 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9937-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9937-4