Abstract
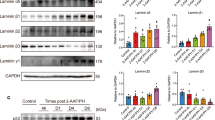
The origin of the myofibroblast, the primary effector cell of liver fibrosis, is still elusive. Here, we report that fluorescence-activated cell sorting purified E-cad + rhesus monkey liver epithelial progenitor cells (mLEPCs) may serve as a potential source for liver myofibroblasts. Adult mLEPCs colonies were cultured in medium containing 2 ng/ml transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) to induce differentiation. Phenotypic changes of cells were analyzed by morphological observation, immunostaining, and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). After cultured with TGF-β and FBS, some cells in adult mLEPCs colonies converted to fibroblasts-like cells. Immunostaining showed that fibroblasts-like cells had acquired the expression of mesenchymal cell marker vimentin but lost the expression of epithelial cell marker CK8. Fibroblasts-like cells were maintained in culture for up to 40 passages. RT-PCR analysis revealed that fibroblasts-like cells had acquired the expression of mesenchymal genes (snail, PAI-1, and collagen I) and lost the expression of epithelial specific genes (E-cad, ZO-1, CK18, and occludin). In addition, more than 60% of fibroblasts-like cells expressed myofibroblastic-related proteins such as αSMA, vimentin, and N-cad, which were not presented in mLEPCs. Furthermore, increased cell motility was also detected in these fibroblasts-like cells by time-lapse video observation. Our results demonstrate that hepatic epithelial progenitor cells, mLEPCs, transform to myofibroblast-like cells via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. This finding will facilitate understanding of the origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batlle E.; Sancho E.; Franci C.; Dominguez D.; Monfar M.; Baulida J.; Garcia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2: 84–89; 2000.
Bissell D. M.; Roulot D.; George J. Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology 34: 859–867; 2001.
Cano A.; Perez-Moreno M. A.; Rodrigo I.; Locascio A.; Blanco M. J.; del Barrio M. G.; Portillo F.; Nieto M. A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2: 76–83; 2000.
Cassiman D.; Libbrecht L.; Desmet V.; Denef C.; Roskams T. Hepatic stellate cell/myofibroblast subpopulations in fibrotic human and rat livers. J. Hepatol. 36: 200–209; 2002.
Clark J. B.; Rice L.; Sadiq T.; Brittain E.; Song L.; Wang J.; Gerber D. A. Hepatic progenitor cell resistance to TGF-beta1’s proliferative and apoptotic effects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329: 337–344; 2005.
Fausto N. Liver regeneration. J. Hepatol. 32: 19–31; 2000.
Forbes S. J.; Russo F. P.; Rey V.; Burra P.; Rugge M.; Wright N. A.; Alison M. R. A significant proportion of myofibroblasts are of bone marrow origin in human liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 126: 955–963; 2004.
Hinz B.; Phan S. H.; Thannickal V. J.; Galli A.; Bochaton-Piallat M. L.; Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am. J. Pathol. 170: 1807–1816; 2007.
Ji S.; Jin L.; Guo X.; Ji W. Culture of newborn monkey liver epithelial progenitor cells in chemical defined serum-free medium. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 46: 693–701; 2010.
Jiao J.; Friedman S. L.; Aloman C. Hepatic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 25: 223–229; 2009.
Jin L.; Ji S.; Tang X.; Guo X.; Lu Y.; Chen H.; Deng H.; Zhou Q.; Ji W. Isolation and characterization of liver epithelial progenitor cells from normal adult rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Cell Res. 19: 268–270; 2009.
Kakinuma S.; Ohta H.; Kamiya A.; Yamazaki Y.; Oikawa T.; Okada K.; Nakauchi H. Analyses of cell surface molecules on hepatic stem/progenitor cells in mouse fetal liver. J. Hepatol. 51: 127–138; 2009.
Knittel T.; Kobold D.; Piscaglia F.; Saile B.; Neubauer K.; Mehde M.; Timpl R.; Ramadori G. Localization of liver myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells in normal and diseased rat livers: distinct roles of (myo-)fibroblast subpopulations in hepatic tissue repair. Histochem. Cell Biol. 112: 387–401; 1999.
Kon J.; Ooe H.; Oshima H.; Kikkawa Y.; Mitaka T. Expression of CD44 in rat hepatic progenitor cells. J. Hepatol. 45: 90–98; 2006.
Lee J. M.; Dedhar S.; Kalluri R.; Thompson E. W. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol. 172: 973–981; 2006.
Leu J. I.; Crissey M. A.; Taub R. Massive hepatic apoptosis associated with TGF-beta1 activation after Fas ligand treatment of IGF binding protein-1-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 111: 129–139; 2003.
Libbrecht L.; Roskams T. Hepatic progenitor cells in human liver diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13: 389–396; 2002.
Liu Y. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15: 1–12; 2004.
Nguyen L. N.; Furuya M. H.; Wolfraim L. A.; Nguyen A. P.; Holdren M. S.; Campbell J. S.; Knight B.; Yeoh G. C.; Fausto N.; Parks W. T. Transforming growth factor-beta differentially regulates oval cell and hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatology 45: 31–41; 2007.
Nierhoff D.; Ogawa A.; Oertel M.; Chen Y. Q.; Shafritz D. A. Purification and characterization of mouse fetal liver epithelial cells with high in vivo repopulation capacity. Hepatology 42: 130–139; 2005.
Nitou M.; Sugiyama Y.; Ishikawa K.; Shiojiri N. Purification of fetal mouse hepatoblasts by magnetic beads coated with monoclonal anti-e-cadherin antibodies and their in vitro culture. Exp. Cell Res. 279: 330–343; 2002.
Novo E.; di Bonzo L. V.; Cannito S.; Colombatto S.; Parola M. Hepatic myofibroblasts: a heterogeneous population of multifunctional cells in liver fibrogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41: 2089–2093; 2009.
Omenetti A.; Porrello A.; Jung Y.; Yang L.; Popov Y.; Choi S. S.; Witek R. P.; Alpini G.; Venter J.; Vandongen H. M.; Syn W. K.; Baroni G. S.; Benedetti A.; Schuppan D.; Diehl A. M. Hedgehog signaling regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during biliary fibrosis in rodents and humans. J. Clin. Invest. 118: 3331–3342; 2008.
Parola M.; Marra F.; Pinzani M. Myofibroblast—like cells and liver fibrogenesis: emerging concepts in a rapidly moving scenario. Mol. Aspects Med. 29: 58–66; 2008.
Rastaldi M. P.; Ferrario F.; Giardino L.; Dell’Antonio G.; Grillo C.; Grillo P.; Strutz F.; Muller G. A.; Colasanti G.; D’Amico G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 62: 137–146; 2002.
Russo F. P.; Alison M. R.; Bigger B. W.; Amofah E.; Florou A.; Amin F.; Bou-Gharios G.; Jeffery R.; Iredale J. P.; Forbes S. J. The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 130: 1807–1821; 2006.
Rygiel K. A.; Robertson H.; Marshall H. L.; Pekalski M.; Zhao L.; Booth T. A.; Jones D. E.; Burt A. D.; Kirby J. A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition contributes to portal tract fibrogenesis during human chronic liver disease. Lab Invest 88: 112–123; 2008.
Sanchez A.; Alvarez A. M.; Benito M.; Fabregat I. Transforming growth factor beta modulates growth and differentiation of fetal hepatocytes in primary culture. J. Cell. Physiol. 165: 398–405; 1995.
Sicklick J. K.; Choi S. S.; Bustamante M.; McCall S. J.; Perez E. H.; Huang J.; Li Y. X.; Rojkind M.; Diehl A. M. Evidence for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in adult liver cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 291: G575–G583; 2006.
Thiery J. P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2: 442–454; 2002.
Valdes F.; Alvarez A. M.; Locascio A.; Vega S.; Herrera B.; Fernandez M.; Benito M.; Nieto M. A.; Fabregat I. The epithelial mesenchymal transition confers resistance to the apoptotic effects of transforming growth factor Beta in fetal rat hepatocytes. Mol. Cancer Res. 1: 68–78; 2002.
Willis B. C.; duBois R. M.; Borok Z. Epithelial origin of myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 3: 377–382; 2006.
Xu J.; Lamouille S.; Derynck R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 19: 156–172; 2009.
Zeisberg M.; Kalluri R. The role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis. J. Mol. Med. 82: 175–181; 2004.
Zeisberg M.; Yang C.; Martino M.; Duncan M. B.; Rieder F.; Tanjore H.; Kalluri R. Fibroblasts derive from hepatocytes in liver fibrosis via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 23337–23347; 2007.
Zhang M.; Zhang Z.; Pan H. Y.; Wang D. X.; Deng Z. T.; Ye X. L. TGF-beta1 induces human bronchial epithelial cell-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Lung 187: 187–194; 2009.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge Mr. Li Jian for assistance in confocal microscopic analysis. This work was supported by research grants from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China Y2110911, National 863 High Technology Research and Development Program of China 2005AA219010, 2006AA02A101, and 2006AA02A116, Major State Basic Development Program 2006CB701505 and 2007CB947701, The Chinese Academy of Sciences KSCX1-YWR-47 and KSCX1-05-02, R&D Infrastructure and Facility Development Program of Yunnan Province 2006PT08-2, Social Science and Technology Development Program of Yunnan Province 2007GH, National S&T Major Project 2009ZX09501- 028, National Key Technology R&D Program 2007BAI33B00, and Chinese National Science Foundation 30700159 and 30700425.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Shaohui Ji and Xihong Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure
Cell movement of the mLEPCs derived fibroblasts-like cells. Fibroblasts-like cells were observed under microscope in a condition controlled chamber for 12 h. The arrow head in (A–F) showed a representative cell with obvious movement. (GIF 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, S., Wang, X., Shu, J. et al. In vitro generation of myofibroblasts-like cells from liver epithelial progenitor cells of rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 47, 383–390 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-011-9401-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-011-9401-z