Abstract
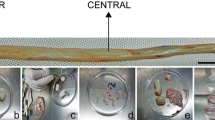
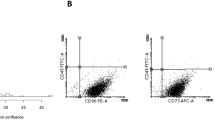
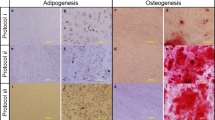
The Wharton’s Jelly (WJ) of the umbilical cord (UC) is an excellent source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with a range of potential therapeutic applications. The present study was conducted to demonstrate the efficiency of the protocols used by Biogenea-Cellgenea Ltd. for isolation and expansion of WJ MSCs from donors across Greece. Umbilical cord samples were collected from 599 females following childbirth and processed for WJ MSC isolation. Stem cells were expanded using DMEM-based media and cell counts and overall viability figures derived using Trypan blue exclusion. To investigate the application of isolation and expansion protocols on samples received 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 d after their collection, ten fresh samples were processed at these time intervals and evaluated. The cellular yield of most WJ samples was 1.1–5.0 × 106 cells at 21–30 d after processing. As culture time increased, cell counts decreased. Statistical analysis of mean cell counts showed a significant reduction after 21 d. Finally, we demonstrate for the first time that it is possible to obtain satisfactory cell numbers from samples processed 1, 2, 3, 4 and even 5 d after collection. We have derived favourable data on the protocols used at Biogenea-Cellgenea Ltd. to isolate and culture MSCs from the WJ. Protocol choice is crucial when handling large numbers of samples on a daily basis and should be made to ensure the best possible outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakhshi T.; Zabriskie R. C.; Bodie S.; Kidd S.; Ramin S.; Paganessi L. A.; Gregory S. A.; Funq H. C.; Christopherson K. W. 2nd Mesenchymal stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly of umbilical cord segments provide stromal support for the maintenance of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells during long-term ex vivo culture. Transfusion 48: 2638–2644; 2008.
Banfi A.; Muraglia A.; Dozin B.; Mastrogiacomo M.; Cancedda R.; Quarto R. Proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells: implications for their use in cell therapy. Exp. Hematol. 28: 707–715; 2000.
Baxter M. A.; Wynn R. F.; Jowitt S. N.; Wraith J. E.; Fairbairn L. J.; Bellantuono I. Study of telomere length reveals rapid aging of human marrow stromal cells following in vitro expansion. Stem Cells 22: 675–682; 2004.
Friedman R.; Betancur M.; Boissel L.; Tuncer H.; Cetrulo C.; Klingemann H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: adjuvants for human cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant 13: 1477–1486; 2007.
Kan I.; Melamed E.; Offen D. Integral therapeutic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Curr. Drug Targets 6: 31–41; 2005.
Kim J. W.; Kim S. Y.; Park S. Y.; Kim Y. M.; Kim J. M.; Lee M. H.; Ryu H. M. Mesenchymal progenitor cells in the human umbilical cord. Ann. Hematol. 83: 733–738; 2004.
La Rocca G.; Anzalone R.; Corrao S.; Magno F.; Loria T.; Lo Iacono M.; Di Stefano A.; Giannuzzi P.; Marasà L.; Cappello F.; Zummo G.; Farina F. Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 131: 267–282; 2009.
Ma L.; Feng X. Y.; Cui B. L.; Law F.; Jiang X. W.; Yang L. Y.; Xie Q. D.; Huang T. H. Human umbilical cord Wharton’s Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells. Chin. Med. J. 118: 1987–1993; 2005.
McElreavey K. D.; Irvine A. I.; Ennis K. T.; McLean W. H. Isolation, culture and characterization of fibroblast-like cells from the Wharton’s jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 19: 29S; 1991.
Pereira W. C.; Khushnooma I.; Madkaikar M.; Ghosh K. Reproducible methodology for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord and its potential for cardiomyocyte generation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2: 394–399; 2008.
Romanov Y. A.; Svintsitskaya V. A.; Smirnov V. N. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells 21: 105–110; 2003.
Seshareddy K.; Troyer D.; Weiss M. L. Method to isolate mesenchymal-like cells from Wharton’s Jelly of umbilical cord. Methods Cell Biol. 86: 101–119; 2008.
Wang H. S.; Hung S. C.; Peng S. T.; Huang C. C.; Wei H. M.; Guo Y. J.; Fu Y. S.; Lai M. C.; Chen C. C. Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton’s jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells 22: 1330–1337; 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: J. Denry Sato
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petsa, A., Gargani, S., Felesakis, A. et al. Effectiveness of protocol for the isolation of Wharton’s Jelly stem cells in large-scale applications. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 45, 573–576 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-009-9227-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-009-9227-0