Abstract
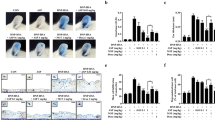
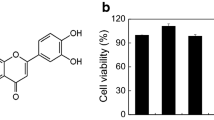
To explore effects of Forsythia koreana methanol extract (FKME) on mast cell-mediated allergic and inflammatory properties, the effect of FKME was evaluated on compound 48/80-induced systemic anaphylaxis, ear swelling, and anti-dinitrophenyl (DNP) immunoglobulin E (IgE)-induced passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA). In addition, the effect of FKME was investigated on the histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMCs) stimulated by compound 48/80, which promotes histamine release. The human mast cell line HMC-1 was stimulated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate plus calcium ionophore A23187. Activated HMC-1 can produce several proinflammatory and chemotactic cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8. Cytokine levels in the culture supernatant were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Cytotoxicity by FKME was determined by a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. FKME inhibited compound 48/80-induced systemic anaphylactic shock and ear swelling in mice. When 1 g/kg FKME was pretreated or posttreated with mice, compound 48/80-induced mice morality was 50 and 66.7%, respectively. One gram per kilogram of FKME pretreatment inhibited ear-swelling responses derived from compound 48/80 by 29.75%. A PCA reaction was inhibited by 17.9%. In an in vitro model, FKME (1 mg/ml) inhibited histamine release from the RPMCs by 13.8% and TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 production from HMC-1 cells by 71.16% (P < 0.001), 86.72% (P < 0.001), and 44.6%, respectively. However, FKME had no cytotoxic effects on cell viability. In conclusion, FKME inhibited not only systemic anaphylaxis and ear swelling induced by compound 48/80 but also inhibited a PCA reaction induced by anti-DNP IgE in vivo. Treatment with FKME showed significant inhibitory effects on histamine, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 release from mast cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfonso, A.; Cabado, A. G.; Vieytes, M. R.; Botana, L. M. Functional compartments in rat mast cells for cAMP and calcium on histamine release. Cell. Signal. 2:343–350; 2000.
Alonzi, T.; Fattori, E.; Lazzaro, D.; Costa, P.; Probert, L.; Kollias, G. Interleukin 6 is required for the development of collagen-induced arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 187:461–468; 1998.
Artuc, M.; Hermes, B.; Steckelings, U. M.; Grutzkau, A.; Henz, B. M. Mast cells and their mediators in cutaneous wound healing-active participants or innocent bystanders? Exp. Dermatol. 8:1–16; 1999.
Boe, A.; Baiocchi, M.; Carbonatto, M.; Papoian, R.; Serlupi-Crescenzi, O. Interleukin 6 knock-out mice are resistant to antigen-induced experimental arthritis. Cytokine 11:1057–1064; 1999.
Bradding, P.; Holgate, S. T. Immunopathology and human mast cell cytokines. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 31:119–133; 1999.
Broide, D. H.; Lotz, M.; Cuomo, A. J.; Coburn, D. A.; Federman, E. C.; Wasserman, S. I. Cytokines in symptomatic asthma airways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 89 (5):958–67; 1992.
Bronner, C.; Wiggins, C.; Monte, D.; Marki, F.; Capron, A.; Landry, Y.; Franson, R. C. Compound 48/80 is a potent inhibitor of phospholipase C and a dual modulator of phospholiphase A2 from human platelet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 920:301–305; 1987.
Camusi, G.; Albano, E.; Tetta, C.; Bussolino, F. The molecular action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur. J. Biochem. 202:3–14; 1991.
Chadi, A.; Fraundorfer, P. F.; Beaven, M. A. Compound 48/80 activates mast cell phospholipase D via heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292:122–130; 2000.
Feldmann, M.; Brennan, F. M.; Maini, R. N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:297–440; 1996.
Gosset, P.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Wallaert, B.; Vannimenus, C.; Joseph, M.; Tonnel, A. B.; Capron, A. Increased secretion by tumor necrosis factor-a and interleukin 6 by alveolar macrophages consecutive to the development of the late asthmatic reaction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 88:561–571; 1991.
Hashimoto, S.; Gon, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Takeshita, I.; MacHino, T.; Horie, T. Intracellular glutathione regulates tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced p38 MAP kinase activation and RANTES production by human bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 31:144–151; 2001.
Hoeck, J.; Woisetschlager, M. STAT6 mediates eotaxin-1 expression in IL-4 or TNF-alpha-induced fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 166:4507–4515; 2001.
Hosoda, M.; Yamaya, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamada, N.; Kamanaka, M.; Sekizawa, K.; Butterfield, J. H.; Watanabe, T.; Nishimura, H.; Sasaki, H. Effects of rhinovirus infection on histamine and cytokine production by cell lines from human mast cells and basophils. J. Immunol. 169 (3):1482–1491; 2002.
Jeong, H. J., Koo, H. N., Myung, N. I., Shin, M. K., Kim, J. W., Kim, D.K., Kim, K. S., Kim, H. M., Lee, Y. M. Inhibitory effects of mast cell-mediated allergic reactions by cell cultured Siberian Ginseng. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 23(1):107–117; 2001.
Jippo-Kanemoto, T.; Kasugai, T.; Yamatodani, A.; Ushio, H.; Mochizuki, T.; Tohya, K.; Kimura, M.; Nishimura, M.; Kitamura, Y. Supernormal histamine release and normal cytotoxic activity of beige (Chediak–Higashi syndrome) rat mast cells with giant granules. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 100:99–106; 1993.
Kim, H. M.; Yi, J. M.; Lim, K. S. Magnoliae flos inhibits mast cell-dependent immediate-type allergic reactions. Pharmacol. Res. 39:107–111; 1999
Kim, M. S.; Lim, W. K.; Cha, J. G.; An, N. H.; Yoo, S. J.; Park, J. H.; Kim, H. M.; Lee, Y. M. The activation of PI 3-K and PKC zeta in PMA-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 171:79–85; 2001.
Kim, M. S.; Na, H. J.; Han, S. W.; Jin, J. S.; Song, U. Y.; Lee, E. J.; Song, B. K.; Hong, S. H.; Kim, H. M. Forsythia fructus inhibits the mast-cell-mediated allergic inflammatory reactions. Inflammation 27 (3):129–135; 2003.
Kim, N. Y.; Kang, T. H.; Song, E. K.; Pae, H. O.; Chung, H. T.; Kim, Y. C. Inhibitory effects of butanol fraction of the aqueous extract of Forsythia koreana on the nitric oxide production by murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 73 (1–2):323–327; 2000.
Tkaczyk, C.; Okayama, Y.; Metcalfe, D. D.; Gilfillan, A. M. Fcgamma receptors on mast cells: activatory and inhibitory regulation of mediator release. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 133(3):305–315; 2004
Krishnaswamy, G.; Kelley, J.; Johnson, D.; Youngberg, G.; Stone, W.; Huang, S. K.; Bieber, J.; Chi, D. S. The human mast cell; Functions in physiology and disease. Front. Biosci. 6:1109–1127; 2001.
Metcalfe, D. D.; Baram, D.; Mekori, Y. A. Mast cells. Physiol. Rev. 77:1033–1079; 1999.
Mousli, M.C.; Bronner, C.; Landry, Y.; Bockaert, J.; Rouot, B. Direct activation of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) by substance P and compound 48/80. FEBS Lett. 25:260–262; 1990a.
Mousli, M.C.; Bronner, C.; Bockaert, J.; Rouot, B.; Landry, Y. Interaction of substance P, compound 48/80 and mastoparan with α-subunit C-terminal of G protein. Immunol. Lett. 25:355–358; 1990b.
Murrant, T.; Bihari, D. Anaphylaxis and anaphylactoid reactions. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 54:322–328; 2000.
Moon, P. D.; Na, H. J.; Kim, H. M. Action of enzyme food, Green Life Enzyme of systemic and local anaphylaxis. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 3:46–50; 2003.
Na, H. J., Jeong, H. J., Bae, H., Kim, Y. B., Park, S. T., Yun, Y. G., Kim, H. M. Tongkyutang inhibits mast cell-dependent allergic reactions and inflammatory cytokines secretion. Clin. Chim. Acta. 7;319(1):35–41; 2002.
Pearce, F. L. Mast cells; Function, differentiation and activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1:630–636; 1989.
Petersen, L. J.; Mosbech, H.; Skov, P. S. Allergen-induced histamine release in intact human skin in vivo assessed by skin microdialysis technique: characterization of factors influencing histamine releasability. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 97:672–679; 1996.
Royer, B.; Varadaradjalou, S.; Saas, P.; Gabiot, A. C.; Kantelip, B.; Feger, F. Guillosson, J. J.; Kantelip, J. P.; Arock, M. Autocrine regulation of cord blood-derived human mast cell activation by IL-10. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108:80–86; 2001a.
Royer, B.; Varadaradjalou, S.; Saas, P.; Guillosson, J. J.; Kantelip, J. P.; Arock, M. Inhibition of IgE-induced activation of human mast cells by IL-10. Clin. Exp. Allergy 31:694–704; 2001b.
Sato, E.; Nelson, D.; Koyama, S.; Hoyt, J. C.; Robbins, A. Inflammatory cytokines modulate eotaxin release by human lung fibroblast cell line. Exp. Lung Res. 27:173–183; 2001.
Shin, B. K.; Lee, E. H.; Kim, H. M. Suppression of l-histidine decarboxylase mRNA expression by methyleugenol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 232:188–191; 1997.
Shin, H. Y.; Lee, E. H.; Kim, C. Y.; Shin, T. Y.; Kim, S. S.; Song, Y. S.; Lee, K. N.; Hong, S. H.; Kim, H. M. Anti-inflammatory activity of Korean folk medicine purple bamboo salt. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 25(3):377–384; 2003.
Shin, T. Y.; Lee, J. K. Effect of Phlomis umbrosa root on mast cell-dependent immediate-type allergic reactions by anal therapy. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 25:73–85; 2003.
Shore, P. A.; Burkhalter, A.; Cohn, V. H. A method for fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 127:182–186; 1959.
Shute, J. K.; Vrugt, B.; Lindley, I. J.; Holgate, S. T.; Bron, A.; Aalbers, R.; Djukanovic, R. Free and complexed interleukin-8 in blood and bronchial mucosa in asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care. Med. 155:1877–1883; 1997.
Stassen, M.; Muller, C.; Arnold, M.; Hultner, L.; Klein-Hessling, S.; Neudorfl, C.; Reineke, T.; Serfling, E.; Schmitt, E. IL-9 and IL-13 production by activated mast cells is strongly enhanced in the presence of lipopolysaccharide: NF-kappa B is decisively involved in the expression of IL-9. J. Immunol. 166:4391–4398; 2001.
Tasaka, K.; Mio, M.; Okamoto, M. Intracellular calcium release induced by histamine releasers and its inhibition by some antiallergic drugs. Ann. Allergy 56:464–469; 1986.
Warbrick, E. V.; Thomas, A. L.; Williams, C. M. The effects of cyclosporin A, dexamethasone and other immunomodulatory drugs on induced expression of IL-3, IL-4 and IL-8 mRNA in a human mast cell line. Toxicology 116(1–3):211–218; 1997.
Williams, C. M.; Coleman, J. W. Induced expression of mRNA for IL-5, IL-6, TNF-alpha, MIP-2 and IFN-gamma in immunologically activated rat peritoneal mast cells: inhibition by dexamethasone and cyclosporin A. Immunology 86(2):244–249; 1995.
Yurt, R. W.; Leid, R. W.; Austen, K. F. Native heparin from rat peritoneal mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 252:518–521; 1977.
Zhu, Y. P. Chinese material medica: Chemistry, Pharmacology and Applications. Harwood Academic Publishers 176–180; 1998.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by VestibuloCochlear Research Center of Wonkwang University (R13-2002-055-01003-0), and a grant of the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, South Korea (01-PJ2-PG4-J201PT01-0006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: J. Denry Sato
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, IY., Moon, PD., Koo, HN. et al. Observations of Forsythia koreana methanol extract on mast cell-mediated allergic reactions in experimental models. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 43, 215–221 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-007-9040-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-007-9040-6