Abstract
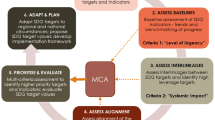
The recent adoption of the sustainable development goals (SDGs) confirms once again the growing importance of indicators in the context of ‘evidence-based decision making’. A sound indicator framework can turn the SDGs and their targets into a management tool to help countries develop implementation strategies, allocate resources and monitor progress. Indicator-based assessments will be a cornerstone of measuring progress on the SDGs through to 2030 at national, regional, global and thematic levels. Recent examples of indicator-based assessments and reports present useful case studies on emerging practice in the context of the SDGs, providing insights into the approaches and methods being adopted to measure and report on progress on the SDGs. In this context, this paper presents the recent experience of the United Nations in undertaking an indicator-based assessment for the Arab Sustainable Development Report (ASDR). The paper presents the innovative conceptual framework and approach used in the ASDR for benchmarking progress and analysing trends. The approach firstly takes a thematic ‘snapshot’ of progress and trends over two decades across 56 sustainable development indicators; a nested, integrated conceptual framework is then applied for a more in-depth exploration of interlinkages and dynamics among the SDGs. The approach emphasises the need to place human dignity and well-being at the core of the analysis; linkages to the natural resource base; the importance of peace, governance and institutions as crosscutting factors; and the role of the means of implementation for addressing gaps. This novel approach can be transferred and adapted to other regional contexts, and it is particularly relevant for developing regions where data gaps and the absence of targets present methodological challenges for any assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Inter-Agency and Expert Group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators 2016. Report of the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on Sustaianble Development Goal Indicators, E/CN.3/2016/2/Rev.1, New York. The total number of indicators in the original proposal was 241; however, this was later revised down to 230 indicators by removing duplicates.
Chapter 40, paragraph 40.4.
Several of the authors this paper were lead authors of the ASDR and were responsible for the assessment reviewed in this paper.
Several stakeholder meetings were held over the period 2013–2015 with regional governments, organisations and experts which discussed the SDGs and regional priorities as well as the proposed conceptual model for SDGs in the Arab region.
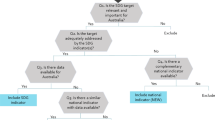
The gap analysis was undertaken towards the end of 2014 and as such data up until 2014 were collected for this analysis. Data for 2015 were subsequently collected as part of the indicator-based assessment as it became available.
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC): Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates; Least Developed Countries (LDCs): the Comoros, Djibouti, Mauritania, Somalia, the Sudan and Yemen; Maghreb: Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia; Mashreq: Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine and the Syrian Arab Republic.
Chapters 3, 4, 5 and 6 of the ASDR provide the outcome of the narrative reviews. Annex 1 to the ASDR provides additional information on the preparatory process for the report.
The region scored 3.5 out of 10 points on the Bertelsmann Stiftung Transformation Index, which was below the global average of 5.3.
Transparency International’s Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) studied the MENA region which includes most of the Arab countries.
References
Böhringer C, Jochem PE (2007) Measuring the immeasurable—a survey of sustainability indices. Ecol Econ 63:1–8
Dahl AL (2012) Achievements and gaps in indicators for sustainability. Ecol Ind 17:14–19
Dasgupta P, Duraiappah A, Managi S, Barbier E, Collins R, Fraumeni B, Gundimeda H, Liu G, Mumford K (2015) How to measure sustainable progress. Science 350:748
Eurostat (2014) Getting messages across using indicators: a handbook based on experience from assessing sustainable development indicators, Luxembourg
Geniaux G, Bellon S, Deverre C, Powell B (2006) Sustainable development indicator frameworks and initiatives
Geoghegan T (2013) Post-2015: framing a new approach to sustainable development, Policy Paper. Independent Research Forum on a Post-2015 Sustainable Development Agenda
Griggs D, Stafford-Smith M, Gaffney O, Rockström J, Öhman MC, Shyamsundar P, Steffen W, Glaser G, Kanie N, Noble I (2013) Policy: sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 495:305–307
Hulliger B, Lussmann P (2010) Assessment of Sustainable Development and Environmental Indicators, Technical report School of Business of the University of Applied Sciences Northwestern Switzerland, Olten
Inter-Agency and Expert Group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators, 2016. Report of the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators, E/CN.3/2016/2/Rev.1, New York
Le Blanc D (2015) Towards integration at last? The sustainable development goals as a network of targets. Sustain Dev 23:176–187
Managi S (2016) The wealth of nations and regions. Routledge
Mayer AL (2008) Strengths and weaknesses of common sustainability indices for multidimensional systems. Environ Int 34:277–291
Melamed C, Ladd P (2013) How to build sustainable development goals: integrating human development and environmental sustainability in a new global agenda, Research reports and studies
Mori K, Christodoulou A (2012) Review of sustainability indices and indicators: towards a new City Sustainability Index (CSI). Environ Impact Assess Rev 32:94–106
Nilsson M, Lucas P, Yoshida T (2013) Towards an integrated framework for SDGs: ultimate and enabling goals for the case of energy. Sustainability 5:4124–4151
Pinter L, Almassy D, Antonio E, Niestroy I, Olsen S, Pulawska G (2013) Sustainable development goals and indicators for a small planet
Raworth K (2012) A safe and just space for humanity: can we live within the doughnut, Oxfam Policy and practice: climate change and resilience, pp 1–26
Singh RK, Murty HR, Gupta SK, Dikshit AK (2009) An overview of sustainability assessment methodologies. Ecol Ind 9:189–212
Stiglitz JE, Sen A, Fitoussi J-P (2010) Report by the commission on the measurement of economic performance and social progress. Paris: Commission on the Measurement of Economic Performance and Social Progress
Sustainable Development Solutions Network (2013) An action agenda for sustainable development: report for the UN Secretary-General
Sustainable Development Solutions Network (2015) Indicators and a monitoring framework for the sustainable development goals, a report to the secretary-general of the United Nations by the Leadership Council of the Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York
United Nations (2012) League of Arab States, Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative. Sustainable Development Indicators for the Arab Region, Beirut
United Nations (2016) The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2016, New York
United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (1992) Agenda 21, Rio Declaration. United Nations, New York
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (2007) Indicators of sustainable development: guidelines and methodologies, Third Edition, New York
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (2014) Conference of European Statisticians Recommendations on Measuring Sustainable Development, Geneva
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, League of Arab States, 2013. The Arab Millennium Development Goals Report, Beirut
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, United Nations Environment Programme, 2015. Arab Sustainable Development Report, Beirut
United Nations Secretary-General, 2013. Initial input of the Secretary-General to the Open Working Group on SDGs
Young OR, Underdal A, Kanie N, Andresen S, Bernstein S, Biermann F, Gupta J, Haas PM, Iguchi M, Kok M, Levy M, Nilsson M, Pinter L, Stevens C (2014) Earth system challenges and a multi-layered approach for the sustainable development goals. United Nations University Institute for the Advanced Study of Sustainability
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia who led the development of the ASDR as well as the United Nations Environment Programme and the broad range of stakeholders and experts who contributed to the development of the ASDR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handled by Shunsuke Managi, Tohoku University, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, C., Nejdawi, R., El-Baba, J. et al. Indicator-based assessments of progress towards the sustainable development goals (SDGs): a case study from the Arab region. Sustain Sci 12, 975–989 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-017-0437-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-017-0437-1