Abstract
Background
Esophageal dysmotility is a common finding in patients being evaluated for antireflux surgery, although its implication remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate outcomes of patients with esophageal dysmotility after fundoplication.
Methods
A retrospective review of a prospective quality-database was performed. All patients who underwent laparoscopic Nissen (NF) or Toupet (TF) fundoplication were included. Esophageal dysmotility was defined using the Chicago Classification v4.0 and conventional metrics, creating three sub-groups: ineffective esophageal motility (IEM), distal/diffuse esophageal spasm (DES), and hypercontractile esophagus (HE). Quality of life (QOL) outcomes were measured by the Reflux Severity Index (RSI), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Health Related Quality of Life (GERD-HRQL), and Dysphagia Scores.
Results
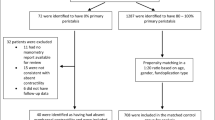
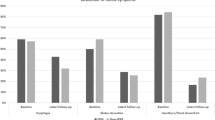
Of 487 patients included, 99 (20.3%) had esophageal dysmotility (49 IEM, 40 DES, 10 HE). While a majority in the dysmotility group (81.8%) underwent TF, most patients in the normal group (76.5%) underwent NF (p < 0.001). On multivariable analysis controlling for sex, age, BMI, hiatal hernia, and surgery type, the normal group had higher Dysphagia Scores at 3 weeks (2.2 ± 0.9 vs. 1.7 ± 0.8, p < 0.001), but not at 6-month, 1-year, 2-year, or 5-year follow-up. There were no differences between normal and dysmotility groups in terms of RSI or GERD-HRQL scores at any time point. Patients with different sub-types of esophageal dysmotility had similar QOL outcomes at all time points.
Conclusion
Patients with esophageal dysmotility had similar outcomes compared to those with normal motility after fundoplication, suggesting the tailored approach favoring partial fundoplication for patients with dysmotility as part of an appropriate treatment algorithm.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Worrell SG, Greene CL, DeMeester TR (2014) The State of Surgical Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease after Five Decades. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 219:819–830 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.05.018
Shaw JM, Bornman PC, Callanan MD, Beckingham IJ, Metz DC (2010) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic Nissen and laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a prospective, randomized trial. Surg Endosc 24:924–932 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0700-3
Dallemagne B, Weerts J, Markiewicz S, Dewandre J-M, Wahlen C, Monami B, Jehaes C (2006) Clinical results of laparoscopic fundoplication at ten years after surgery. Surg Endosc 20:159–165 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0174-x
Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, Ro G, Ross K, Sandhu K, Katkhouda N, Hagen JA, Lipham JC (2017) Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 21:441–445 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-016-3320-y
Chrysos E, Tsiaoussis J, Zoras OJ, Athanasakis E, Mantides A, Katsamouris A, Xynos E (2003) Laparoscopic surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease patients with impaired esophageal peristalsis: total or partial fundoplication? Journal of the American College of Surgeons 197:8–15 . https://doi.org/10.1016/S1072-7515(03)00151-0
Armijo PR, Hennings D, Leon M, Pratap A, Wheeler A, Oleynikov D (2019) Surgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Severe Esophageal Dysmotility. J Gastrointest Surg 23:36–42 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-018-3968-6
Martinucci I, de Bortoli N, Giacchino M, Bodini G, Marabotto E, Marchi S, Savarino V, Savarino E (2014) Esophageal motility abnormalities in gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 5:86–96 . https://doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v5.i2.86
Strate U, Emmermann A, Fibbe C, Layer P, Zornig C (2008) Laparoscopic fundoplication: Nissen versus Toupet two-year outcome of a prospective randomized study of 200 patients regarding preoperative esophageal motility. Surg Endosc 22:21–30 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9546-8
Hunter JG, Swanstrom L, Waring JP (1996) Dysphagia after laparoscopic antireflux surgery. The impact of operative technique. Ann Surg 224:51–57
Lund RJ, Wetcher GJ, Raiser F, Glaser K, Perdikis G, Gadenstätter M, Katada N, Filipi CJ, Hinder RA (1997) Laparoscopic toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease with poor esophageal body motility. J Gastrointest Surg 1:301–308 . https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(97)80049-2
Xiao Y, Kahrilas PJ, Kwasny MJ, Roman S, Lin Z, Nicodème F, Lu C, Pandolfino JE (2012) High Resolution Manometry Correlates of Ineffective Esophageal Motility. Am J Gastroenterol 107:1647–1654 . https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.286
Novitsky YW, Wong J, Kercher KW, Litwin DEM, Swanstrom LL, Heniford BT (2007) Severely disordered esophageal peristalsis is not a contraindication to laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 21:950–954 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-006-9126-3
Heider TR, Behrns KE, Koruda MJ, Shaheen NJ, Lucktong TA, Bradshaw B, Farrell TM (2003) Fundoplication improves disordered esophageal motility. J Gastrointest Surg 7:159–163 . https://doi.org/10.1016/s1091-255x(02)00145-2
Pizza F, Rossetti G, Rosetti G, Del Genio G, Maffettone V, Brusciano L, Del Genio A (2008) Influence of esophageal motility on the outcome of laparoscopic total fundoplication. Dis Esophagus 21:78–85 . https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00756.x
Ravi N, Al-Sarraf N, Moran T, O’Riordan J, Rowley S, Byrne PJ, Reynolds JV (2005) Acid normalization and improved esophageal motility after Nissen fundoplication: equivalent outcomes in patients with normal and ineffective esophageal motility. The American Journal of Surgery 190:445–450 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.05.040
Z Tian B Wang C Shan W Zhang D Jiang M Qiu (2015) A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials to Compare Long-Term Outcomes of Nissen and Toupet Fundoplication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease PLoS One 10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127627
Fibbe C, Layer P, Keller J, Strate U, Emmermann A, Zornig C (2001) Esophageal Motility in Reflux Disease Before and After Fundoplication: A Prospective, Randomized, Clinical, and Manometric Study. Gastroenterology 121:5–14 . https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2001.25486
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2002) Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Symptom Index (RSI). Journal of Voice 16:274–277 . https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-1997(02)00097-8
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality of life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183:217–224
Velanovich V (2007) The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus 20:130–134 . https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00658.x
Gunter RL, Shada AL, Funk LM, Wang X, Greenberg JA, Lidor AO (2017) Long-Term Quality of Life Outcomes Following Nissen Versus Toupet Fundoplication in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Journal of Laparoendoscopic & Advanced Surgical Techniques 27:931–936 . https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2017.0232
Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Pugh M, Winters D, Hobbs N, Tarazi M, Panda N, Dalmia S, Mansour M, Malik S (2018) Impact of Toupet Versus Nissen Fundoplication on Dysphagia in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Associated Preoperative Esophageal Dysmotility: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surg Innov 25:636–644 . https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350618799549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no personal or financial conflict of interests related to this work to disclose. Drs Linn, Haggerty, and Ujiki receive payment for lectures from Gore. Dr Haggerty is a paid consultant to Medtronic. Dr Ujiki is a scientific board member for Boston Scientific, is a paid consultant for Olympus and Cook, and receives payment for lectures from Medtronic and Erbe. Drs Wong, Su, Attaar, Hedberg, and Kristine Kuchta have no financial support to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This manuscript was presented at the 2nd Annual Illinois Surgical Conference by the Illinois Chapter of the American College of Surgeons on Saturday, April 24, 2021.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, H.J., Vierra, M., Hedberg, M. et al. A Tailored Approach to Laparoscopic Fundoplication: Outcomes in Patients with Esophageal Dysmotility. J Gastrointest Surg 26, 2426–2433 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-022-05452-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-022-05452-4