Abstract
Introduction
In this study, we assess the effectiveness of a conservative therapeutic treatment of acute corrosive poisonings in adults, and we define therapeutic protocols based on clinical and endoscopic criteria.
Methods
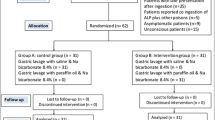
We analyzed clinical records of patients with acute corrosive poisonings who were hospitalized and treated at the Toxicology Clinic at the University of Skopje, Republic of Macedonia, during a 5-year period (2006–2010). A total of 481 patients’ records with cases of acute corrosive poisonings were analyzed. There were 317 female (65.9 %) and 164 male (34.1 %) patients. The purpose of the therapy in the cases of acute corrosive poisonings is to prevent perforation as well as progressive fibrosis and stenosis of the esophagus and stomach. Therapeutic approach mainly consists of proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, antibiotics, and intensive hyperalimentation. There are different opinions regarding conservative treatment of acute corrosive poisonings in adults.
Conclusion
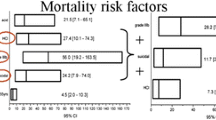
Based on our study of corrosive poisonings of adults, we propose a list of optimal treatment recommendations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gen Tohda, Choichi Sugawa, Christopher Gayer, et al. Clinical evaluation and management of caustic injury in the upper gastrointestinal tract in 95 adult patients in an urban medical center. Surg Endosc 2008; 22:1119–1125
Carmen Cabral, Mirce´a Chirica, Ce´cile de Chaisemartin, et al. Caustic injuries of the upper digestive tract: a population observational study. Surg Endosc 2012; 26:214–221
N. Ananthakrishnan, G. Parthasarathy, Vikram Kate. Chronic Corrosive Injuries of the Stomach—A Single Unit Experience of 109 Patients Over Thirty Years. World J Surg 2010; 34:758–764
Andon Chibishev, Zanina Pereska, Vesna Chibisheva et al. Corrosive Poisonings in Adults . Mat Soc Med 2012; 24 : 125–130
Sarfati E, Gossot D, Assens P, et al. Management of caustic ingestion in adults. Br J Surg 1987; 74:146–148
Hao-Tsai Cheng, Chi-Liang Cheng, Cheng-Hui Lin et al. Caustic ingestion in adults: The role of endoscopic classification in predicting outcome. BMC Gastroenterology 2008; 8:31
Munoz-Bonerand N, Gornet JM. Diagnostic and therapeutic management of digestive caustic burns. J Chirug (Paris) 2002;139 : 72–6
Zargar SA, Kuchhar R, Mehta S, et al. The role of fibroptic endoscopy in the management of corrosive ingestion and modified endoscopic classification of burns. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:165–169.
Fulton JA, Hoffman RS. Steroids in second degree caustic burns of the esophagus: a systematic pooled analysis of fifty years of human data: 1956–2006. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2007; 45:402–8.
Katzka A David MD. Caustic Injury to the Esophagus . Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology 2001; 4:59–6
Christesen HB. Diagnostic and treatment of caustic ingestion. Ugeskr Laeger 1994;158 : 4125–4126.
Mihalache C, Mihalache S. Clinical aspects of the post-caustic esophageal stenosis on 116 cases . Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2006; 110 :377–80
Zerbib P, Voisin B, Truant S, et al. The conservative management of severe caustic gastric injuries. Ann Surg. 2011; 253:684–8.
Zhou J-H, Jiang Y-G, Wang R-W et al. Management of corrosive esophageal burns in 149 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005; 130: 449–55.
Ramasamy K, Gumaste V V. Corrosive ingestion in adults. J Clin Gastroenterol 2003; 37: 119–24.
Cox A J III, Eisenbeis J F. Ingestion of caustic hair relaxer: is endoscopy necessary? Laryngoscope 1997; 107: 897–902.
Celik B, Nadir A, Sahin E, Kaptanoglu M. Is esophagoscopy necessary for corrosive ingestion in adults? Dis Esophagus. 2009; 22 : 638–41
Kikendal JW. Caustic ingestion injuries. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1991; 20 : 847–857
Zagar SA, Kochhar R, Nagar B, et al. Ingestion of corrosive acid. Gastroenterology. 1989; 97:702–707.
Triadafilopulos George. Caustic esophageal injury in adults, up to date, June 2006, Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/caustic-esophageal-injury-in-adults
Mamede RC, De Mello Filho FV . Treatment of caustic ingestion: an analysis of 239 cases. Dis Esophagus 2002; 15 :210–3.
Peclova D. Navratil. Do corticosteroids prevent oesophageal stricture after corrosive ingestion. Toxicol Rev.2005; 24 : 125–9
Kardon E. Caustic ingestion, com [homepage on the Internet]. Emergency Medicine Toxicology. [updated 2010 may; cited June 2010]. Available from: emedicine.medscape.com
Carlos Arevalo-Silva, Ron Eliashar, Jay Wohlgelernter et al. Ingestion of Caustic Substances:A 15-Year Experience. Laryngoscope 2006; 116:1422–1426
Abakumov M M, Pinchuk TP, ll’iashenko LG.Is antisecretory therapy of patients with chemical burn of the esophagus mandatory. Khirurgiia (Mosk) 2007; 1:20–4.
Antisecretory therapy for prevention of stenoses of bougienage after-burn of esophageal strictures. Allakhverdian AS, Mazurin VS, Morozov SV et al. Gastroenterol. 2003; 4:36–9, 114
Chibishev A. Post-corrosive late complications in esophagus and stomach--role of the esophageal rest. Med Arh2010 .;64:320–3.
Chibishev A, Simonovska-Veljanovska N, Pereska Z. Artificial Nutrition in Therapeutic Approach of Acute Caustic Poisonings . Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 2010; 3:180–187.
DI Constanco. New therapeutic approaches to corrosive burns. Gut 1982; 21:370–375
Zwischenberger, Joseph B. Clare Savage, and Akhil Bidan. Surgical Aspects of Esophageal Disease Perforation and Caustic Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med2002; 165:1037–40
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that they had no conflict of interest during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chibishev, A., Pereska, Z., Simonovska, N. et al. Conservative Therapeutic Approach to Corrosive Poisonings in Adults. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 1044–1049 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2190-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2190-9