Abstract
Background
The Glasgow prognostic score (GPS) is a patient-related measure to determine long-term outcomes in cancer patients. This study examined the impact of GPS on outcomes including postoperative complications after curative resection of gastric cancer.
Methods
The systemic inflammatory response was assessed by GPS, and the severity of postoperative complications was evaluated according to the Clavien–Dindo classification. Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan–Meier method and the log rank test. Multivariate analysis was performed to determine significant associations with complications by a logistic regression model and the independent prognostic values by Cox’s proportional hazards model.
Results
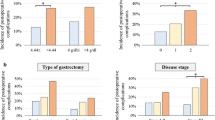
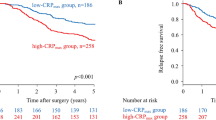
Study patients (n = 1017) were allocated as follows: 904 (88.9 %) to GPS 0, 92 (9.0 %) to GPS 1, and 21 (2.1 %) to GPS 2. One hundred sixty-three patients (16.0 %) had postoperative complications of ≥ grade 2. Multivariate logistic analysis identified gender, body mass index, tumor location, tumor depth, blood transfusion, and comorbidity as significantly correlated with postoperative complications. However, GPS was not associated with the incidence of complication. On the other hand, multivariate analysis for overall survival identified GPS as an independent prognostic factor.
Conclusions
GPS is a significant predictor of long-term survival in curable gastric cancer surgery but not of short-term outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelley JR, Duggan JM. Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol 2003;56:1-9.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2002;55:74-108.
Lochhead P, El-Omar EM. Gastric cancer. Br Med Bull 2008;85:87-100.
Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Oates J, Cunningham D. Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur J Cancer 1998;34:503-509.
Chau I, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Waters JS, Oates J, Ross PJ. Multivariate prognostic factor analysis in locally advanced and metastatic esophago-gastric cancer-pooled analysis from three multicenter, randomized, controlled trials using individual patient data. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:2395-2403.
Morgan DB, Hill GL, Burkinshaw L. The assessment of weight loss from a single measurement of body weight: the problems and limitations. Am J Clin Nutr 1980;33:2101-2105.
Rowland ML. Self-reported weight and height. Am J Clin Nutr 1990;52:1125-33.
Ando M, Ando Y, Hasegawa Y, Shimokata K, Minami H, Wakai K, Ohno Y, Sakai S. Prognostic value of performance status assessed by patients themselves, nurses, and oncologists in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 2001;85:1634-1639.
Copeland GP, Jones D, Walters M. POSSUM: a scoring system for surgical audit. Br J Surg 1991;78:355-360.
McMillan DC, Watson WS, O'Gorman P, Preston T, Scott HR, McArdle CS. Albumin concentrations are primarily determined by the body cell mass and the systemic inflammatory response in cancer patients with weight loss. Nutr Cancer 2001;39:210-213.
Lien YC, Hsieh CC, Wu YC, Hsu HS, Hsu WH, Wang LS, Huang MH, Huang BS. Preoperative serum albumin level is a prognostic indicator for adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:1041-1048.
Oñate-Ocaña LF, Aiello-Crocifoglio V, Gallardo-Rincón D, Herrera-Goepfert R, Brom-Valladares R, Carrillo JF, Cervera E, Mohar-Betancourt A. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2007;14:381-389.
Crumley AB, McMillan DC, McKernan M, McDonald AC, Stuart RC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with inoperable gastro-oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer 2006;94:637-641.
Crumley AB, Stuart RC, McKernan M, McMillan DC. Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer? World J Surg 2010;34:2393-2398.
O'Gorman P, McMillan DC, McArdle CS. Prognostic factors in advanced gastrointestinal cancer patients with weight loss. Nutr Cancer 2000;37:36-40.
Scott HR, McMillan DC, Forrest LM, Brown DJ, McArdle CS, Milroy R. The systemic inflammatory response, weight loss, performance status and survival in patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 2002;87:264-267.
Maltoni M, Caraceni A, Brunelli C, Broeckaert B, Christakis N, Eychmueller S, Glare P, Nabal M, Viganò A, Larkin P, De Conno F, Hanks G, Kaasa S; Steering Committee of the European Association for Palliative Care. Prognostic factors in advanced cancer patients: evidence-based clinical recommendations—a study by the Steering Committee of the European Association for Palliative Care. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:6240-6248. Review.
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dunlop DJ. Evaluation of cumulative prognostic scores based on the systemic inflammatory response in patients with inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 2003;89:1028-1030.
Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, Horie T, Kubota K. Inflammation-based prognostic score is a novel predictor of postoperative outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 2007;246:1047-1051.
Ramsey S, Lamb GW, Aitchison M, Graham J, McMillan DC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with metastatic renal cancer. Cancer 2007;109:205-212.
Deans DA, Tan BH, Wigmore SJ, Ross JA, de Beaux AC, Paterson-Brown S, Fearon KC. The influence of systemic inflammation, dietary intake and stage of disease on rate of weight loss in patients with gastro-oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer 2009;100:63-69.
Gockel I, Dirksen K, Messow CM, Junginger T. Significance of preoperative C-reactive protein as a parameter of the perioperative course and long-term prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:3746-3750.
Dutta S, Al-Mrabt NM, Fullarton GM, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. A comparison of POSSUM and GPS models in the prediction of post-operative outcome in patients undergoing oesophago-gastric cancer resection. Ann Surg Oncol 2011;18:2808-2817.
McMillan DC, Crozier JF, Canna K, Angerson WJ, McArdle CS. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) in patients undergoing resection for colon and rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 2007;22:881-886.
McMillan DC. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009;12:223-226.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 2004;240:205-213.
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, Vauthey JN, Dindo D, Schulick RD, de Santibañes E, Pekolj J, Slankamenac K, Bassi C, Graf R, Vonlanthen R, Padbury R, Cameron JL, Makuuchi M. The Clavien–Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg 2009;250:187-196.
Lerut T, Moons J, Coosemans W, Van Raemdonck D, De Leyn P, Decaluwé H, Decker G, Nafteux P. Postoperative complications after transthoracic esophagectomy for cancer of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction are correlated with early cancer recurrence: role of systematic grading of complications using the modified Clavien classification. Ann Surg 2009;250:798-807.
Roxburgh CS, McMillan DC. Role of systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol 2010;6:149-163.
Richards CH, Leitch EF, Horgan PG, Anderson JH, McKee RF, McMillan DC. The relationship between patient physiology, the systemic inflammatory response and survival in patients undergoing curative resection of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2010;103:1356-1361.
Nozoe T, Iguchi T, Egashira A, Adachi E, Matsukuma A, Ezaki T. Significance of modified Glasgow prognostic score as a useful indicator for prognosis of patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg 2011;201:186-191.
Moyes LH, Leitch EF, McKee RF, Anderson JH, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. Preoperative systemic inflammation predicts postoperative infectious complications in patients undergoing curative resection for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2009;100:1236-1239.
Al-Shaiba R, McMillan DC, Angerson WJ, Leen E, McArdle CS, Horgan P. The relationship between hypoalbuminaemia, tumour volume and the systemic inflammatory response in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer 2004;91:205-207.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Shogo Nomura, a biostatistician, M.Sc. (Research Center for Innovative Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital East, Chiba, Japan), for providing advice on our statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, T., Hiki, N., Nunobe, S. et al. Significance of the Inflammation-Based Glasgow Prognostic Score for Short- and Long-Term Outcomes After Curative Resection of Gastric Cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 16, 2037–2044 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2036-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2036-x