Abstract
Background
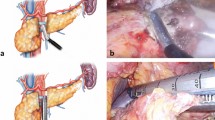
Pancreatic fistula is a significant problem for patients undergoing distal pancreatectomy with fistula rates up to 61%. Fistulas lead to substantial morbidity. The study objective was to compare radiofrequency dissector closure with traditional stump closure for distal pancreatectomy.
Methods
Sixty-two patients underwent distal pancreatectomy at our institution between 2002 and 2011. Thirty-three patients had traditional stump closure compared with 29 patients who had radiofrequency closure. Fistula rates, operative times, and blood loss were compared. The control patients underwent open operation in 20 (60%) cases and laparoscopic operation in the remaining 13 (40%). Of the patients that underwent radiofrequency closure, 10 (35%) underwent open operation, and the remaining 19 (65%) patients underwent laparoscopic operation.
Results
Fistula occurred in 12 of 33 (36%) patients with traditional stump closure compared to 3 of 29 (10%) patients with radiofrequency closure (p < 0.02). Operative time (307 vs. 231 min [p < 0.002]) and blood loss (364–200 mL [p < 0.02]) were decreased in the radiofrequency closure group. Length of stay decreased from 7.8 to 6.6 days; however, this was not statistically significant.
Conclusions
The use of radiofrequency dissector in distal pancreatectomy is effective with low rates of fistula formation. Radiofrequency closure should be studied further in prospective trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleeff J, Diener MK, Z’graggen K, Hinz U, Wagner M, Bachmann J, Zehetner J, Muller MW, Friess H, Buchler MW. Distal pancreatectomy: risk factors for surgical failure in 302 consecutive cases. Annals of Surgery 2007;245:573–582.
Kooby DA, Hawkins WG, Schmidt CM, Weber SM, Bentrem DJ, Gillespie TW, Sellers JB, Merchant NB, Scoggins CR, Martin RCG, Kim HJ, Ahmad S, Cho CS, Parikh AA, Chu CK, Hamilton NA, Doyle CJ, Pinchot S, Hayman A, McClaine R, Nakeeb A, Staley CA, McMaaters KM, Lillemoe KD. A multicenter analysis of distal pancreatectomy for adenocarcinoma: is laparoscopic resection appropriate? J Am Coll Surg 2010;210:779–787.
DiNorcia J, Schrope BA, Lee MK, Reavey PL, Rosen SJ, Lee JA, Chabot JA, Allendorf JD. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy offers short hospital stays with fewer complications. J Gastrointest Surg 2010;14:1804–12.
Birkmeyer JD, Siewers AE, Finlayson EV, Stukel TA, Lucas FL, Batista I, Welch HG, Wennberg DE. Hospital volume and surgical mortality in the United States. NEJM 2002;346:1128–37
Cameron JL, Pitt HA, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, Kaufman HS, Colemanet J. One hundred and forty-five consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies without mortality. Ann Surg 1993;217:430–5.
Balzano G, Zerbi A, Cristallo M, DiCarlo V. The unsolved problem of fistula after left pancreatectomy: the benefit of cautious drain management. J Gastrointest Surg 2005;837–842.
Knaebel HP, Diener MK, Wente MN, Buchler MW, Seiler CM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of technique for closure of the pancreatic remnant after distal pancreatectomy. Br J Surg 2005;92:539–546.
Geller AD, Tsung A, Maheshwari V, Rutstein KA, Fung JJ, March JW. Hepatic resection in 170 patients using saline-cooled radiofrequency coagulation. HBP 2005;7:208–213.
Truty MJ, Sawyer MD, Que FG. Decreasing pancreatic leak after distal pancreatectomy: saline-coupled radiofrequency ablation in a porcine model. J Gastrointest Surg 2007;1:998–1007.
Kitagawa H, Ohta T, Tani T, Tajima H, Nakagawara H, Ohnishi I, Takamura H, Kayahara M. Nonclosure technique with saline-coupled bipolar electrocautery in management of the cut surface after distal pancreatectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2008;15:377–383.
Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, Neoptolemos J, Sarr M, Traverso W, Buchler M. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery 2005;138:8–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blansfield, J.A., Rapp, M.M., Chokshi, R.J. et al. Novel Method of Stump Closure for Distal Pancreatectomy with a 75% Reduction in Pancreatic Fistula Rate. J Gastrointest Surg 16, 524–528 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1794-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1794-1