Abstract
Background
A small proportion of patients evaluated with manometry prior to a fundoplication have a high-pressure lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This paper examines the outcome of laparoscopic fundoplication for these patients.
Material and Methods
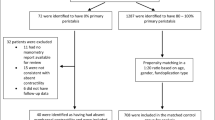
Between October 1991 and December 2006, 1,886 patients underwent primary laparoscopic fundoplication. Those with a high-pressure LES on preoperative manometry (LESP ≥30 mm Hg at end expiration) were identified from a prospective database. Long-term outcomes were determined using analogue symptom scores (0–10) for heartburn, dysphagia, and patient satisfaction and compared to those of a matched control group.
Results
Thirty patients (1.6%), nine men and 21 women, median age 51 years, had a hypertensive LES (mean, 36 mmHg; range, 30–55). Median follow-up after fundoplication was 99 (12–182) months. These patients had similar mean symptom scores to 30 matched controls for heartburn (2.3 vs. 2.2, P = 0.541), dysphagia (2.7 vs. 3.1, P = 0.539), and satisfaction (7.4 vs. 7.6, P = 0.546). Five patients required revision for dysphagia compared to no control patients (P = 0.005). These patients had a higher preoperative dysphagia score (6.6 vs. 3.1, P = 0.036).
Conclusion
Laparoscopic fundoplication can be performed with good long-term results for patients with reflux and a hypertensive LES. However, those with preoperative dysphagia have a higher failure rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Code CF, Schlegel JF, Kelly ML, Olsen AM, Ellis FHG. Hypertensive gastroesophageal sphincter. Proc Mayo Clin 1960;35:391–399.
Spechler SJ, Castell DO. Classification of oesophageal motility abnormalities. Gut 2001;49:145–151. doi:10.1136/gut.49.1.145.
Tambankar AP, Almogy G, Arain M, Portale G, Hagen JA, Peters JH, et al. Surgical management of hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter with dysphagia or chest pain. J Gastrointest Surg 2003;7:990–996. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2003.09.003.
Katada N, Hinder RA, Lund RJ, Perdikis J, Stalzer RA, McGinn TR. The hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Surg 1996;172(5):439–442. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(96)00219-X.
Varga G, Kiraly A, Cseke L, Kalmar K, Horvath OP. Effect of fundoplication on hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter associated with gastroesophageal reflux. J Gastrointest Surg 2008;12:304–307. doi:10.1007/s11605-007-0397-3.
Waterman DC, Dalton CB, Ott DJ, Castell JA, Bradley LA, Castell DO, et al. Hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter: what does it mean? J Clin Gastroenterol 1989;11(2):139–146. doi:10.1097/00004836-198904000-00006.
Jamieson GG, Maddern GJ. Long esophageal myotomy through the diaphragmatic hiatus in the treatment of hypertensive lower esophagus associated with gastroesophageal reflux. In Siewert JR, Holscher AH, eds. Diseases of the esophagus. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 1988, pp 918–20.
Katzka DA, Sidhu M, Castell DO. Hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter: an apparent paradox that is not unusual. Am J Gastroenterol 1995;90:280–284.
Gockel I, Lord RV, Bremner CG, Hamrah P, Demeester TR. The hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter: a motility disorder with manometric features of outflow obstruction. J Gastrointest Surg 2003;7(5):692–700. doi:10.1016/S1091-255X(03)00043-X.
Maddern G. The reproducibility of oesophageal manometry. Dis Esoph 1991;4:95–99.
Jamieson GG, Watson DI, Britten-Jones R, Mitchell PC, Anvari M. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg 1994;220(2):137–145. doi:10.1097/00000658-199408000-00004.
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Pike GK, Davies N, Richardson M, Devitt PG. Prospective randomized double-blind trial between laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and anterior partial fundoplication. Br J Surg 1999;86(1):123–130. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.00969.x.
Krysztopik RJ, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Watson DI. A further modification of fundoplication. 90 degrees anterior fundoplication. Surg Endosc 2002;16(10):1446–1451. doi:10.1007/s00464-002-8801-2.
Barreca M, Oelschlager BK, Pellegrini CA. Outcomes of laparoscopic fundoplication in patients with the ‘hypercontractile esophagus’. Arch Surg 2002;137:724–729. doi:10.1001/archsurg.137.6.724.
Blom D, Peters JH, Demeester TR, Crookes PF, Hagen JA, Demeester SR, et al. Physiologic mechanism and preoperative prediction of new onset dysphagia after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2002;6(1):22–27. doi:10.1016/S1091-255X(01)00051-8.
Kelly JJ, Watson DI, Chin KF, Devitt PG, Game PA, Jamieson GG. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: clinical outcomes at 10 years. J Am Coll Surg 2007;205(4):570–575. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.05.024.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the invaluable assistance of Carolyn Lally, Janet Pinno, Lorelle Smith, and Nicky Ascott in obtaining follow-up data and maintaining the laparoscopic fundoplication database. We would also like to thank surgeons Peter G. Devitt and Philip A. Game from the Royal Adelaide Hospital and David I Watson and Justin Bessell from Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, for contributing patients to the database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamb, P.J., Myers, J.C., Thompson, S.K. et al. Laparoscopic Fundoplication in Patients with a Hypertensive Lower Esophageal Sphincter. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 61–65 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0688-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0688-3