Abstract
Introduction
Aggressive management of hepatic neuroendocrine (NE) metastases improves symptoms and prolongs survival. Because of the rarity of these tumors, however, the best method for hepatic artery embolization has not been established. We hypothesized that in patients with hepatic NE metastases, hepatic artery chemoembolization (HACE) would result in better symptom improvement and survival compared to bland embolization (HAE).
Methods
Retrospective review identified all patients with NE hepatic metastases managed by HACE or HAE at three institutions from January 1996 through December 2007.
Results
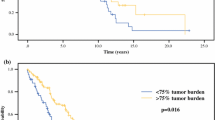
We identified 100 patients managed by HACE (n = 49) or HAE (n = 51) that were similar with respect to age, gender, and primary tumor type. The percentage of patients experiencing morbidity, 30-day mortality, and symptom improvement were similar between the two groups (HACE vs. HAE: 2.4% vs. 6.6%; 0.8% vs. 1.8%; and 88% vs. 83%, respectively.) No differences in the median overall survival were observed between HACE and HAE from the time of the first embolization procedure (25.5 vs. 25.7 months, p = 0.79). Multivariate analysis revealed that resection of the primary tumor predicted survival (73.8 vs. 19.4 months, p < 0.04).
Conclusions
These data suggest that morbidity, mortality, symptom improvement, and overall survival are similar in patients with hepatic neuroendocrine metastases managed by chemo- or bland hepatic artery embolization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Hardacre J, Uzar A, Cameron J, Choti M. Isolated liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: does resection prolong survival? J Am Coll Surg 1998;187:88–93. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(98)00099-4.
Touzios JG, Kiely JM, Pitt SC, Rilling WS, Quebbeman EJ, Wilson SD et al. Neuroendocrine hepatic meastases: does aggressive management improve survival? Ann Surg 2005;241:776–785. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000161981.58631.ab.
Musunuru S, Chen H, Rajpal S, Stephani N, McDermott JC, Holen K et al. Metastatic neuroendocrine hepatic tumors: resection improves survival. Arch Surg 2006;141:1000–1004. doi:10.1001/archsurg.141.10.1000.
Yoa KA, Talamonti MS, Nemeck A, Angelos P, Chrisman H, Skarda J et al. Indications and results of liver resection and hepatic chemoembolization for metastastic gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 2001;130:677–685. doi:10.1067/msy.2001.117377.
Woodside KJ, Townsend CM Jr, Evers MB. Current management of gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:742–756. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2004.04.010.
Schupak KD, Wallner KE. The role of radiation therapy in the treatment of locally unresectable or metastatic carcinoid tumors. Int J Radiol Oncol Biol Phys 1991;20:489–495.
Townsend CM Jr, Thompson JC. The clinical use of gastrointestinal hormones for alimentary tract disease. Adv Surg 1996;29:79–92.
Que FG, Nagorney DM, Batts KP et al. Hepatic resection for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am J Surg 1995;169:36–42. doi:10.1016/S0002–9610(99)80107-X.
O’Toole D, Maire F, Ruszniewski P. Ablative therapies for liver metastases of digestive endocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer 2003;10:463–468. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0100463.
Le Treut YP, Delpero JR, Dousset B et al. Results of liver transplantation in the treatment of metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: a 31-case French multicentric report. Ann Surg 1997;225:355–364. doi:10.1097/00000658-199704000-00003.
Gupta S, Johnson MM, Murthy R, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Madhoff DC et al. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: variables affecting response rate and survival. Cancer 2005;104:1590–1602. doi:10.1002/cncr.21389.
Ruutiainen AT, Soulen MC, Tuite CM, Clark TWI, Mandschein JI, Stavropoulos SW et al. Chemoembolization and bland embolization of neuroendocrine tumor metastases to the liver. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007;18:847–855. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2007.04.018.
Lunderquist A, Ericsson M, Nobin A, Sandén G. Gelfoam powder embolization of the hepatic artery in liver metastases of carcinoid tumors. Radiologe 1982;22:65–70.
Mårtensson H, Nobin A, Bengmark S, Lunderquist A, Owman T, Sandén G. Embolization of the liver in the management of metastatic carcinoid tumors. J Surg Oncol 1984;27:152–158. doi:10.1002/jso.2930270305.
Stöckman F, Von Romatowski HJ, Reimold WV, Schuster R, Cruetzfeldt W. Hepatic artery embolization for the treatment of endocrine gastrointestinal tumors with liver metastases. Z Gastroenterol 1984;22:652–660.
Odurny A, Birsch SJ. Hepatic arterial embolisation in patients with metastatic carcinoid tumours. Clin Radiol 1985;36:597–602. doi:10.1016/S0009-9260(85)80241-5.
Eriksson BK, Larsson EG, Skogseid BM, Löfberg Am, Lörelius LE, Oberg KE. Liver embolizations of patients with malignant neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumors. Cancer 1998;83:2293–2301. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19981201)83:11<2293::AID-CNCR8>3.0.CO;2-E.
Brown KT, Koh BY, Brody LA, Getrajdman GI, Susman J, Fong Y et al. Particle embolization of hepatic neuroendocrine metastases for control of pain and hormonal symptoms. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1999;10:397–403.
Chamberlain RS, Canes D, Brown KT, Saltz L, Jarnagin W, Fong Y et al. Hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: does intervention alter outcomes? J Am Coll 2000;190:432–435. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00222-2.
Schell SR, Camp ER, Caridi JG, Hawkins IF Jr. Hepatic artery embolization for control of symptoms, octreotide requirements, and tumor progression in metastatic carcinoid tumors. J Gastrointest Surg 2002;6:664–670. doi:10.1016/S1091-255X(02)00044-6.
Strosberg JR, Choi J, Cantor AB, Kvols LK. Selective hepatic artery embolization for treatment of patients with metastatic carcinoid and pancreatic endocrine tumors. Cancer Control 2006;13:72–78.
Osborne DA, Zervos EE, Strosberg J, Boe BA, Malafa M, Rosemurgy AS et al. Improved outcome with cytoreduction versus embolization for symptomatic hepatic metastases of carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 2006;13:572–581. doi:10.1245/ASO.2006.03.071.
Granberg D, Eriksson LG, Welin S, Kindmark H, Janson ET, Skogseid B et al. Liver embolization with trisacryl gelatin microshperes (embosphere) in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Acta Radiol 2007;48:180–185. doi:10.1080/02841850601080440.
Stokes KR, Stuart K, Clouse ME. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for metastatic endocrine tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1993;4:341–345.
Therasse E, Breittmayer F, Roche A, DeBaere T, Indushekar S, Ducreux M et al. Transcatheter chemoembolization of progressive carcinoid liver metastases. Radiology 1993;189:541–7.
Clouse ME, Perry L, Stuart K, Stokes KR. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Digestion 1994;199(55):92–97.
Drougas JG, Anthony LB, Blair TK, Lopez RR, Wright JK Jr, Chapman WC et al. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for management of patients with advanced metastatic carcinoid tumors. Am J Surg 1998;175:408–412. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(98)00042-7.
Dominguez S, Denys A, Madiera I, Hammel P, Vilgrain V, Menu Y et al. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with streptozocin in patients with metastatic digestive endocrine tumors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000;12:151–157.
Gupta S, Yao JC, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Morello FA, Madoff DC et al. Hepatic arterial embolizationand chemoembolization for treatment of patients with metastatic carcinoid tumors: the M.D. Anderson experience. Cancer J 2003;9:261–267. doi:10.1097/00130404-200307000-00008.
Ho AS, Picus J, Darcy MD, Tan B, Gould JE, Pilgram TK et al. Long-term outcome after chemoembolization and embolization of hepatic metastatic lesions from neuroendocrine tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;188:1201–1207. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.0933.
Moertel CG, Johnson CM, McKusick MA, Martin JK Jr, Nagorney DM, Kvols LK et al. The management of patients with advanced carcinoid tumors and islet cell carcinomas. Ann Intern Med 1994;120:302–309.
McDermott EW, Guduric B, Brennan MF. Prognostic variables in patients with gastrointestinal carcinoid tumours. Br J Surg 1994;81:1007–1009. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800810725.
Shabani KO, Souba WW, Finkelstein DM, Stark PC, Elgadi KM, Tenabe KK et al. Prognosis and survival in patients with gastrointestinal tract carcinoid tumors. Ann Surg 1999;229:815–823. doi:10.1097/00000658-199906000-00008.
Caprotti R, Angelini C, Mussi C et al. Gastrointestinal carinoids. Prognosis and survival. Minerva Chir 2003;58:523–532.
Woodside KJ, Townsend CM Jr, Evers MB. Current management of gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:742–756. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2004.04.010.
Andreyev HJ, Scott-Mackie P, Cunningham D, Nicolson V, Norman AR, Badve SS et al. Phase II study of continuous infusion fluorouracil and interferon alpha-2b in the palliation of malignant neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:1486–1492.
Ducreux MP, Boige V, Leboulleux S et al. A phase II study irinotecan with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with pretreated gastroenteropancreatic well-differentiated endocrine carcinomas. Oncology 2006;70:134–140. doi:10.1159/000093004.
Kouvaraki MA, Anjani JA, Hoff P, Wolff R, Evans DB, Lozano R et al. Fuorouracil, doxorubicin, and streptozosin in the treatment of patients with locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic endocrine carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:4762–4771. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.04.024.
Bajetta E, Catena L, Procopio G, De Dosso S, Bichisao E, Ferrari L et al. Are capecitabine and oxaliplatin (XELOX) suitable treatment for progressing low-grade and high-grade neuroendocrine tumours? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2007;59:637–642. doi:10.1007/s00280-006-0306-6.
Durán I, Salazar R, Casanovas O, Arruzubi V, Vilar E, Siu LL et al. New drug development in digestive neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Oncol 2007;18:1307–1313. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm009.
Modlin IM, Oberg K, Chung DC, Jensen RT, de Herder WW, Thakker RV et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Lancet Oncol 2008;9:61–72. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70410-2.
Pinchot SN, Pitt SC, Sippel RS, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Chen H. Novel target for the treatment and palliation of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2008;9:576–582.
Chu QD, Hill HC, Douglass HO Jr, Driscoll D, Smith JL, Nava HR et al. Predictive factors associated with long-term survival in patients with neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas. Ann Surg Oncol 2002;9:855–862. doi:10.1007/BF02557521.
Sarmiento JM, Heywood G, Rubin J et al. Surgical treatment of neuroendocrine metastases to the liver: a plea for resction to increase survival. J Am Coll Surg 2003;197:29–37. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(03)00230-8.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the American College of Surgeons Resident Research Scholarship and National Institutes of Health Grant T32 CA009614 Physician Scientist Training in Cancer Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant Support American College of Surgeons Resident Research Scholarship, National Institutes of Health Grant T32 CA009614 Physician Scientist Training in Cancer Medicine.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitt, S.C., Knuth, J., Keily, J.M. et al. Hepatic Neuroendocrine Metastases: Chemo- or Bland Embolization?. J Gastrointest Surg 12, 1951–1960 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0640-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0640-6