Abstract
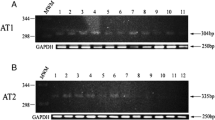
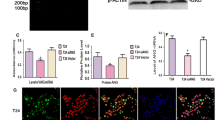
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a crucial pro-angiogenic component in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA), and its high expression levels have been correlated with poor prognosis and early postoperative recurrence. We have recently shown that high levels of angiotensin II (AngII) type 1 receptor (AT1R) correlate and colocalize with VEGF in invasive PDA and that AngII induces VEGF expression in PDA cell lines. In this study, we explored the signaling mechanisms involved in the AngII-mediated VEGF induction and correlated AT1R and VEGF expression in noninvasive precursor lesions. An AT1R antagonist significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited the AngII-mediated induction of VEGF messenger RNA and protein in all PDA cell lines. AngII-VEGF induction was inhibited by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein, suggesting a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling mechanism. AngII activated the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), but not p38 or c-Jun NH2-terminal MAP kinases. Inhibition of ERK1/2 activation reduced the AngII-induced VEGF synthesis. Immunohistochemical analysis of precursor lesions showed increased expression of AT1R in most ductal cells undergoing metaplasia. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms showed more intense AT1R staining when compared to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, which showed heterogeneous immunoreactivity. VEGF followed the same distribution pattern of AT1R in both lesions. AT1R expression in the premalignant pancreatic lesions suggests its involvement in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Our mechanistic findings provide the first insight into an AngII-initiated signaling pathway that regulates PDA angiogenesis. An AT1R-mediated VEGF induction suggests the possibility of AT1R blockade as a novel therapeutic strategy to control angiogenesis in PDA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Koniaris L, Kaushal S, Abrams RA, Sauter PK, Coleman J, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas-616 patients: results, outcomes, and prognostic indicators. J Gastrointest Surg 2000;4:567–579.
Korc M. Pathways for aberrant angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 2003;7:2–8.
Seo Y, Baba H, Fukuda T, Takashima M, Sugimachi K. High expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with liver metastasis and a poor prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2000;88:2239–2245.
Gupta VK, Jaskowiak NT, Beckett MA, Mauceri HJ, Grunstein J, Johnson RS, Calvin DA, Nodzenski E, Pejovic M, Kufe DW, Posner MC, Weichselbaum RR. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances endothelial cell survival and tumor radioresistance. Cancer J 2002;8:47–54.
Harmey JH, Bouchier-Hayes D. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a survival factor for tumour cells: implications for anti-angiogenic therapy. Bioessays 2002;24:280–283.
Hotz HG, Reber HA, Hotz B, Sanghavi PC, Yu T, Foitzik T, Buhr HJ, Hines OJ. Angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 reduces human pancreatic cancer growth. J Gastrointest Surg 2001;5:131–138.
De Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger TH. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2000;52:415–472.
Kim S, Iwao H. Stress and vascular responses: mitogen-activated protein kinases and activator protein-1 as promising therapeutic targets of vascular remodeling. J Pharmacol Sci 2003;9:177–181.
Zhang A, Ding G, Huang S, Wu Y, Pan X, Guan X, Chen R, Yang T. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mediation of angiotensin II-induced proliferation of human mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2005;88:F1118–F1124.
Amaya K, Ohta T, Kitagawa H, Kayahara M, Takamura H, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Shimizu K, Miwa K. Angiotensin II activates MAP kinase and NF-kappaB through angiotensin II type I receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 2004;4:849–856.
Schmidt D, Textor B, Pein OT, Licht AH, Andrecht S, Sator-Schmitt M, Fusenig NE, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M. Critical role for NF-kappaB-induced JunB in VEGF regulation and tumor angiogenesis. EMBO J 2007;26:710–719.
Takahasi K, Bardhan S, Kambayashi Y, Shirai H, Inagami T. Protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition by angiotensin II in rat pheochromocytoma cells through type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;198:60–66.
Bottari SP, King IN, Reichlin S, Dahlstroem I, Lydon N, de Gasparo M. The AT2 receptor stimulates protein tyrosine phosphatase activity and mediates inhibition of particulate guanylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;183:206–211.
Tahmasebi M, Puddefoot JR, Inwang ER, Vinson GP. The tissue renin-angiotensin system in human pancreas. J Endocrinol 1999;161:317–322.
Leung PS, Chappell MC. A local pancreatic renin–angiotensin system: endocrine and exocrine roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2003;35:838–846.
Campbell DJ, Habener J. Angiotensinogen gene is expressed and differentially regulated in multiple tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest 1986;78:31–39.
Campbell DJ. Circulating and tissue angiotensin systems. J Clin Invest 1987;79:1–6.
Arafat HA, Gong Q, Chipitsyna G, Rizvi A, Saa CT, Yeo CJ. Antihypertensives as novel antineoplastics: angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 2007;20:996–1005.
Kobari M, Hisano H, Matsuno S, Sato T, Kan M, Tachibana T. Establishment of six human pancreatic cancer cell lines and their sensitivities to anti-tumor drugs. Tohoku J Exp Med 1986;150:231–248.
Gould KL, Hunter T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces multisite phosphorylation of pp60c-src and increases its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Molec Cell Biol 1988;8:3345–3356.
Menard J, Clauser E, Bouhnik J, Corvol P. Angiotensinogen: biochemical aspects. In Robertson JIS, Nichollas MS, eds. The renin angiotensin system. London: Gower Medical Publishing, 1993, pp 8.1–8.10.
Kim S, Iwao H. Stress and vascular responses: mitogen-activated protein kinases and activator protein-1 as promising therapeutic targets of vascular remodeling. J Pharmacol Sci 2003;9:177–181.
Zhang A, Ding G, Huang S, Wu Y, Pan X, Guan X, Chen R, Yang T. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mediation of angiotensin II-induced proliferation of human mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2005;88:F1118–F1124.
Itakura J, Ishiwata T, Shen B, Kornmann M, Korc M. Concomitant over-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 2000;85:27–34.
Itakura J, Ishiwata T, Friess H, Fujii H, Matsumoto Y, Buchler MW, Korc M. Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic cancer correlates with local disease progression. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:1309–1316.
Buchler P, Reber HA, Buchler MW, Friess H, Hines OJ. EGF-RII influences the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 2002;23:738–749.
Nickenig G, Sachinidis A, Michaelsen F, Bohm M, Seewald S, Vetter H. Upregulation of vascular angiotensin II receptor gene expression by low-density lipoprotein in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation 1997;95:473–478.
Chipitsyna G, Gong Q, Gray CF, Haroon Y, Kamer E, Arafat HA. Induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by angiotensin II in the pancreatic islets and beta-cells. Endocrinology 2007;148:2198–2208.
Duff JL, Marrero MB, Paxton WG, Schieffer B, Bernstein KE, Berk BC. Angiotensin II signal transduction and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res 1995;30:511–517.
Hirano M, Osada S, Aoki T, Hirai S, Hosaka M, Inoue J, Ohno S. MEK kinase is involved in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and degradation of IkappaB-alpha. J Biol Chem 1996;271:13234–13238.
Crews CM, Alessandrini A, Erikson RL. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science 1992;258:478–780.
Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ. How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem 1995;270:14843–14846.
Duff JL, Berk BC, Corson MA. Angiotensin II stimulates the pp44 and pp42 mitogen-activated protein kinases in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;188:257–264.
Hruban RH, Wilentz RE, Maitra A. Identification and analysis of precursors to invasive pancreatic cancer. Methods Mol Med 2005;103:1–13.
Tokunaga T, Abe Y, Tsuchida T, Hatanaka H, Oshika Y, Tomisawa M, Yoshimura M, Ohnishi Y, Kijima H, Yamazaki H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura M. Ribozyme mediated cleavage of cell-associated isoform of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits liver metastasis of a pancreatic cancer cell line. Int J Oncol 2002;21:1027–1032.
Won SM, Park YH, Kim HJ, Park KM, Lee WJ. Catechins inhibit angiotensin II–induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via mitogen–activated protein kinase pathway. Exp Mol Med 2006;38:525–534.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the American Cancer Society (Research Scholar Grant), and by an institutional grant from the Kimmel Cancer Center, Thomas Jefferson University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anandanadesan, R., Gong, Q., Chipitsyna, G. et al. Angiotensin II Induces Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Through an Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor and ERK1/2 Signaling. J Gastrointest Surg 12, 57–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0403-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0403-9