Abstract
Purpose
To assess brain-core temperature of end-stage liver disease patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) using a temperature measurement technique based on the apparent diffusion coefficient of the cerebrospinal fluid in the lateral ventricles.
Materials and methods
The study group was composed of 19 patients with a model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score of 23.7 who underwent MR imaging before and after OLT. MR imaging studies were performed with a 1.5T MR scanner. Brain-core temperature (T: °C) was calculated using the following equation from the apparent diffusion coefficient (D) of the cerebrospinal fluid in the lateral ventricles: \(T = {{2256.74} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{2256.74} {\ln \left( {4.39221/D} \right)}}} \right. \kern-0pt} {\ln \left( {4.39221/D} \right)}}{-}273.15\) measured with a DWI sequence (b value 1000 s/mm2). We compared brain-core temperature of all patients before and after OLT.
Results
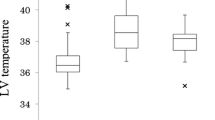
Brain-core temperature measurements were successfully taken in all patients before and after OLT. The measured brain-core temperature mean ± standard deviation was 38.67 ± 1.76 °C before OLT and 38.60 ± 0.99 °C after OLT, showing no significant difference (P = 0.643).
Conclusions
Brain-core temperature was stable in patients undergoing OLT. DWI thermometry may provide a supplementary brain biomarker to confirm that cerebral blood flow and metabolism are stable in patients undergoing OLT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASL:
-
Arterial spin labeling
- CBF:
-
Cerebral blood flow
- CMRO2 :
-
Cerebral metabolic rate for oxygen
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- FSE:
-
Fast-spin-echo
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- LV:
-
Lateral ventricles
- MELD:
-
Model for end-stage liver disease
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OTL:
-
Orthotopic liver transplantation
- PWI:
-
Perfusion-weighted imaging
References
Madoff DC, Wallace MJ, Ahrar K, Saxon RR. TIPS-related hepatic encephalopathy: management options with novel endovascular techniques. Radiographics. 2004;24:21–36.
Ardizzone G, Arrigo A, Schellino MM, et al. Neurological complications of liver cirrhosis and orthotopic liver transplant. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:789–92.
Ardizzone G, Arrigo A, Panaro F, et al. Modifications of cerebral vascular resistance and autoregulation after graft reperfusion during human orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2004;36:1473–8.
Herynek V, Wagnerová D, Hejlová I, et al. Changes in the brain during long-term follow-up after liver transplantation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35(6):1332–7.
Naegele T, Grodd W, Viebahn R, et al. MR imaging and (1)H spectroscopy of brain metabolites in hepatic encephalopathy: time-course of renormalization after liver transplantation. Radiology. 2000;216:683–91.
Mcilvoy L. Comparison of brain temperature to core temperature: a review of the literature. J Neurosci Nurs. 2004;36:23–31.
Sumida K, Sato N, Ota M, et al. Intraventricular temperature measured by diffusion-weighted imaging compared with brain parenchymal temperature measured by MRS in vivo. NMR Biomed. 2016;29:890–5.
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464–70.
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE. Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time–dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys. 1965;42:288–92.
Mills R. Self-diffusion in normal and heavy water in the range 1-45.deg. J Phys Chem. 1973;77:685–8.
Kozak LR, Bango M, Szabo M, Rudas G, Vidnyanszky Z, Nagy Z. Using diffusion MRI for measuring the temperature of cerebrospinal fluid within the lateral ventricles. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:237–43.
Sakai K, Yamada K, Sugimoto N. Calculation methods for ventricular diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry: phantom and volunteer studies. NMR Biomed. 2012;25:340–6.
Sakai K, Yamada K, Sugimoto N. Automated temperature calculation method for DWI-thermometry: the usefulness of LV probability map on healthy subjects. In: Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2013, pp 499–502.
Aggarwal S, Obrist W, Yonas H, et al. Cerebral hemodynamic and metabolic profiles in fulminant hepatic failure: relationship to outcome. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:1353–60.
Zivković SA. Neurologic complications after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol. 2013;5:409–16.
Zivković SA, Abdel-Hamid H. Neurologic manifestations of transplant complications. Neurol Clin. 2010;28:235–51.
Strauss G, Hansen BA, Kirkegaard P, Rasmussen A, Hjortrup A, Larsen FS. Liver function, cerebral blood flow autoregulation, and hepatic encephalopathy in fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology. 1997;25:837–9.
Pere P, Höckerstedt K, Isoniemi H, Lindgren L. Cerebral blood flow and oxygenation in liver transplantation for acute or chronic hepatic disease without venovenous bypass. Liver Transpl. 2000;6:471–9.
Philips BJ, Armstrong IR, Pollock A, Lee A. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in patients with chronic liver disease undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1998;27:369–76.
Larsen FS, Ejlersen E, Strauss G, et al. Cerebrovascular metabolic autoregulation is impaired during liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1999;68:1472–6.
Skak C, Rasmussen A, Kirkegaard P, Secher NH. Cerebral oxygen saturation and blood flow during liver transplantation. Anesth Analg. 1997;84:730–3.
Strauss G, Hansen BA, Kirkegaard P, Rasmussen A, Hjortrup A, Larsen FS. Liver function, cerebral blood flow autoregulation, and hepatic encephalopathy in fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology. 1997;25:837–9.
Ardizzone G, Arrigo A, Panaro F, et al. Cerebral hemodynamic and metabolic changes in patients with fulminant hepatic failure during liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2004;36:3060–4.
Bertolizio G, Mason L, Bissonnette B. Brain temperature: heat production, elimination and clinical relevance. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011;21:347–58.
Kuriyama N, Yamada K, Sakai K, et al. Ventricular temperatures in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) measured with DWI-based MR thermometry. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2015;14:305–12.
Yamada K, Sakai K, Akazawa K, et al. Moyamoya patients exhibit higher brain temperatures than normal controls. NeuroReport. 2010;21:851–5.
Sumida K, Sato N, Ota M, et al. Intraventricular cerebrospinal fluid temperature analysis using MR diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry in Parkinson’s disease patients, multiple system atrophy patients, and healthy subjects. Brain Behav. 2015;5:e00340.
Ota M, Sato N, Sakai K, et al. Altered coupling of regional cerebral blood flow and brain temperature in schizophrenia compared with bipolar disorder and healthy subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34:1868–72.
Sparacia G, Sakai K, Yamada K, et al. Assessment of brain core temperature using MR DWI-thermometry in Alzheimer disease patients compared to healthy subjects. Jpn J Radiol. 2017;35:168–71.
Tazoe J, Yamada K, Sakai K, Akazawa K, Mineura K. Brain core temperature of patients with mild traumatic brain injury as assessed by DWI-thermometry. Neuroradiology. 2014;56:809–15.
Sai A, Shimono T, Sakai K, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry in multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;40:649–54.
Tsukamoto T, Shimono T, Sai A, et al. Assessment of brain temperatures during different phases of the menstrual cycle using diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry. Jpn J Radiol. 2016;34:277–83.
Sakai K, Yamada K, Mori S, Sugimoto N, Nishimura T. Age-dependent brain temperature decline assessed by diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry. NMR Biomed. 2011;24:1063–7.
Hasan KM, Moeller FG, Narayana PA. DTI-based segmentation and quantification of human brain lateral ventricular CSF volumetry and mean diffusivity: validation, age, gender effects and biophysical implications. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32:405–12.
Fleischer CC, Wu J, Qiu D, et al. The brain thermal response as a potential neuroimaging biomarker of cerebrovascular impairment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38:2044–51.
Wang H, Wang B, Normoyle KP, et al. Brain temperature and its fundamental properties: a review for clinical neuroscientists. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:307.
Sukstanskii AL, Yablonskiy DA. An analytical model of temperature regulation in human head. J Therm Biol. 2004;29:583–7.
Long LL, Li XR, Huang ZK, Jiang YM, Fu SX, Zheng W. Relationship between changes in brain MRI and (1)H-MRS, severity of chronic liver damage, and recovery after liver transplantation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009;234:1075–85.
Schulz GJ, Coelho JC, Matias JE, Campos AC, Schulz DD, Bertoldi GA. Cerebral magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with hepatic encephalopathy: analysis before and after liver transplantation. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 1992;2009(55):35–9.
Thomas MA, Huda A, Guze B, et al. Cerebral 1H MR spectroscopy and neuropsychologic status of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1123–30.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Warren Blumberg, science editor at ISMETT, for his help in revising the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics standards
Our retrospective cohort study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Research Review Board (IRRB) of our institution, and informed consent form was waived; however, informed written consent to the MR was obtained from all patients. We declare that all human studies have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Sparacia, G., Cannella, R., Lo Re, V. et al. Brain-core temperature of patients before and after orthotopic liver transplantation assessed by DWI thermometry. Jpn J Radiol 36, 324–330 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-0729-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-0729-0