Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effectiveness of two orthogonal topograms on radiation dose and image quality (IQ) associated with topogram-based automatic tube voltage selection (ATVS) for lung CT scanning.
Methods
Thirty-seven patients were enrolled in this study. At baseline, only an anteroposterior topogram was obtained and at follow-up, both anteroposterior and lateral topograms were performed. ATVS was turned on during all scans. Objective and subjective IQ evaluations were performed and compared; tube voltage and radiation dose of each scan were noted and analyzed.
Results
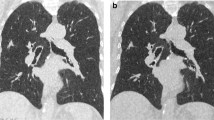
A significant difference was observed regarding the objective parameters between baseline and follow-up only in image noise and signal–noise ratio (SNR) in the upper one-third of the image (image noise: 7.49 ± 1.08 vs. 9.10 ± 1.13, p < 0.001; SNR: 4.08 ± 0.87 vs. 3.37 ± 0.63, p < 0.001). No differences were found between baseline and follow-up in the subjective assessment of IQ. The radiation dose was significantly lower at follow-up than that at baseline (2.73 ± 0.83 mSv vs. 3.55 ± 1.24 mSv, respectively; p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Using two orthogonal topograms associated with ATVS could significantly reduce the total radiation dose for lung CT scanning, while subjective IQ was maintained.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalra MK, Maher MM, Toth TL, Schmidt B, Westerman BL, Morgan HT, et al. Techniques and applications of automatic tube current modulation for CT. Radiology. 2004;233(3):649–57.
McCollough CH, Bruesewitz MR, Kofler JM Jr. CT dose reduction and dose management tools: overview of available options. Radiographics. 2006;26(2):503–12.
Raman SP, Johnson PT, Deshmukh S, Mahesh M, Grant KL, Fishman EK. CT dose reduction applications: available tools on the latest generation of CT scanners. J Am Coll Radiol. 2013;10(1):37–41.
Soderberg M, Gunnarsson M. The effect of different adaptation strengths on image quality and radiation dose using Siemens Care Dose 4D. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2010;139(1–3):173–9.
Frellesen C, Stock W, Kerl JM, Lehnert T, Wichmann JL, Nau C, et al. Topogram-based automated selection of the tube potential and current in thoraco-abdominal trauma CT—a comparison to fixed kV with mAs modulation alone. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(7):1725–34.
Mangold S, Wichmann JL, Schoepf UJ, Poole ZB, Canstein C, Varga-Szemes A, et al. Automated tube voltage selection for radiation dose and contrast medium reduction at coronary CT angiography using 3(rd) generation dual-source CT. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(10):3608–16.
O’Daniel JC, Stevens DM, Cody DD. Reducing radiation exposure from survey CT scans. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185(2):509–15.
Strauss KJ, Goske MJ, Kaste SC, Bulas D, Frush DP, Butler P, et al. Image gently: ten steps you can take to optimize image quality and lower CT dose for pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(4):868–73.
Singh S, Petrovic D, Jamnik E, Aran S, Pourjabbar S, Kave ML, et al. Effect of localizer radiograph on radiation dose associated with automatic exposure control: human cadaver and patient study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014;38(2):293–8.
Feng R, Tong J, Liu X, Zhao Y, Zhang L. High-pitch coronary CT angiography at 70 kVp adopting a protocol of low injection speed and low volume of contrast medium. Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(5):763–72.
Zhang LJ, Qi L, Wang J, Tang CX, Zhou CS, Ji XM, et al. Feasibility of prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch coronary CT angiography with 30 mL iodinated contrast agent at 70 kVp: initial experience. Eur Radiol. 2014;24:1537–46.
Bongartz G, Golding SJ, Jurik AG, et al. European guidelines for multislice computed tomography: appendix c funded by the European Commission. Contract number FIGM-CT2000-20078-CT-TIP. 2013. http://www.msct.eu/CT_Quality_Criteria.htm. Accessed 7 Sept 2016.
AAPM Task Group 204. Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in pediatric and adult body CT examinations, 2011. http://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/rpt_204.pdf. Accessed 7 Sept 2016.
Christner JA, Braun NN, Jacobsen MC, Carter RE, Kofler JM, McCollough CH. Size-specific dose estimates for adult patients at CT of the torso. Radiology. 2012;265:841–7.
Mangold S, De Cecco CN, Schoepf UJ, Kuhlman TS, Varga-Szemes A, Caruso D, et al. CT angiography for planning transcatheter aortic valve replacement using automated tube voltage selection: image quality and radiation exposure. Eur J Radiol. 2017;86:276–83.
Mangold S, De Cecco CN, Wichmann JL, Canstein C, Varga-Szemes A, Caruso D, et al. Effect of automated tube voltage selection, integrated circuit detector and advanced iterative reconstruction on radiation dose and image quality of 3rd generation dual-source aortic CT angiography: an intra-individual comparison. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(5):972–8.
Park C, Gruber-Rouh T, Leithner D, Zierden A, Albrecht MH, Wichmann JL, et al. Single-source chest-abdomen-pelvis cancer staging on a third generation dual-source CT system: comparison of automated tube potential selection to second generation dual-source CT. Cancer Imaging. 2016;16(1):33.
Zhang LJ, Qi L, Wang J, Tang CX, Zhou CS, Ji XM, et al. Feasibility of prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch coronary CT angiography with 30 mL iodinated contrast agent at 70 kVp: initial experience. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(7):1537–46.
Achenbach S, Marwan M, Ropers D, Schepis T, Pflederer T, Anders K, et al. Coronary computed tomography angiography with a consistent dose below 1 mSv using prospectively electrocardiogram-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(3):340–6.
Ghoshhajra BB, Engel LC, Major GP, Verdini D, Sidhu M, Karolyi M, et al. Direct chest area measurement: a potential anthropometric replacement for BMI to inform cardiac CT dose parameters? J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2011;5(4):240–6.
Li JL, Huang MP, Liang CH, Zhao ZJ, Liu H, Cui YH, et al. Individualized radiation dose control in 256-slice CT coronary angiography (CTCA) in retrospective ECG-triggered helical scans: using a measure of body size to adjust tube current selection. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(11):3146–53.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
This study was approved by the Ethic Committee of the First Hospital of China Medical University, and all patients provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhang, M., Zhang, L. et al. Radiation dose reduction using two orthogonal topograms associated with automatic tube voltage selection for lung CT scanning as compared with a single anteroposterior topogram. Jpn J Radiol 37, 292–300 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-00809-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-00809-9