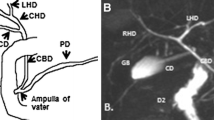
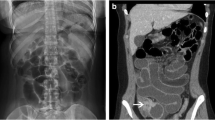
Abstract
Purpose
To describe MDCT findings in adult patients of midgut malrotation and to correlate the types of adult midgut malrotation with its complications.
Materials and methods
CT scans were performed on 14 adult patients with midgut malrotation. The images were reviewed retrospectively by one radiologist. Abnormal intestinal location, mesenteric vascular arrangement, extraintestinal anomalies and complications were evaluated and correlated with patterns of adult midgut malrotation.
Results
The 14 cases of adult midgut malrotation revealed the following CT findings: intestinal malposition (n = 14), abnormally oriented mesenteric vessels (n = 8), extraintestinal anomalies (n = 14). These cases were classified into six types: complete nonrotation (n = 3), nonrotated duodenum and partially rotated colon (n = 6), isolated nonrotation of the duodenum (n = 2), partial rotation of the duodenum and colon (n = 1), partially rotated duodenum (n = 1) and isolated colonic partial rotation (n = 1). Four of these patients had accompanying complications, including volvulus (n = 2), right paraduodenal hernia (n = 1) and gastroduodenal intussusception (n = 1), respectively.
Conclusion
Imaging features of adult midgut malrotation are characteristic. Adult midgut malrotation has various manifestations, and types of midgut malrotation may be closely related to their complications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gamblin TC, Stephens RE, Johnson RK, Rothwell M. Adult malrotation: a case report and review of the literature. Curr Surg. 2003;60(5):517–20.
Kanazawa T, Kasugai K, Miyata M, Miyashita M, Mizuno M, Nagase F, et al. Midgut malrotation in adulthood. Intern Med. 2000;39(8):626–31.
Applegate KE, Anderson JM, Klatte EC. Intestinal malrotation in children: a problem-solving approach to the upper gastrointestinal series. Radiographics. 2006;26:1485–500.
Zissin R, Rathaus V, Oscadchy A, Kots E, Gayer G, Shapiro-Feinberg M. Intestinal malrotation as an incidental finding on CT in adults. Abdom Imaging. 1999;24(6):550–5.
Pickhardt PJ, Bhalla S. Intestinal malrotation in adolescents and adults: spectrum of clinical and imaging features. AJR. 2002;179:1429–35.
Moldrem AW, Papaconstantinou H, Broker H, Megison S, Jeyarajah DR. Late presentation of intestinal malrotation: an argument for elective repair. World J Surg. 2008;32(7):1426–31.
Strouse PJ. Disorders of intestinal rotation and fixation. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34:837–51.
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI, Taylor GE. Radiographic patterns of intestinal malrotation in children. Radiographics. 1996;16:547–56.
Schey WL, Donaldson JS, Sty JR. Malrotation of bowel: variable patterns with different surgical considerations. Pediatr Surg. 1993;28:96–101.
Torres AM, Ziegler MM. Malrotation of the intestine. World J Surg. 1993;17:326–31.
Inoue Y, Nakamura H. Aplasia or hypoplasia of the pancreatic uncinate process: comparison in patients with and patients without intestinal nonrotation. Radiology. 1997;205(2):531–3.
Ditchfield MR, Hutson JM. Intestinal rotational abnormalities in polysplenia and asplenia syndromes. Pediatr Radiol. 1998;28:303–6.
Applegate KE, Goske MJ, Pierce G, Murphy D. Situs revisited: imaging of the heterotaxy syndrome. Radiographics. 1999;19:837–52.
Shimanuki Y, Aihara T, Takano H, Moritani T, Oguma E, Kuroki H, Shibata A, et al. Clockwise whirlpool sign at color Doppler US: an objective and definite sign of midgut volvulus. Radiology. 1996;199(1):261–4.
Okino Y, Kiyosue H, Mori H, Komatsu EJ, Matsumoto S, Yamada Y, et al. Root of the small-bowel mesentery: correlative anatomy and CT features of pathologic conditions. Radiographics. 2001;21:1475–90.
Selçuk D, Kantarci F, Oğüt G, Korman U. Radiological evaluation of internal abdominal hernias. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2005;16(2):57–64.
Martin LC, Merkle EM, Thompson WM. Review of internal hernias: radiographic and clinical findings. AJR. 2006;186:703–17.
Bartlett MK, Wang C, Williams WH. The surgical management of paraduodenal hernia. Ann Surg. 1968;2:249–54.
Hsieh TM, Sheen-Chen SM, Lin CC. Combination of adult intussusception and intestinal malrotation: an unusual presentation. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(11):3037–9.
Gardner-Thorpe J, Hardwick RH, Carroll NR, Gibbs P, Jamieson NV, et al. Adult duodenal intussusception associated with congenital malrotation. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(28):3892–4.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Chen, WH., Zhang, XF. et al. Adult midgut malrotation: multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) findings of 14 cases. Jpn J Radiol 31, 328–335 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0194-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0194-8