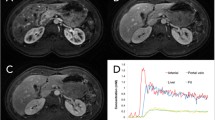
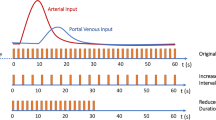
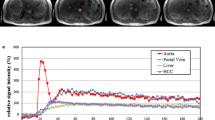
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the study was to compare two analytical methods—maximum slope (MS) and the dualinput single-compartment model (CM)—in computed tomography (CT) measurements of hepatic perfusion and to assess the effects of extrahepatic systemic factors.
Materials and methods
A total of 109 patients underwent hepatic CT perfusion. The scans were conducted at the hepatic hilum 7–77 s after administration of contrast material. Hepatic arterial perfusion (HAP) and portal perfusion (HPP) (ml/min/100 ml) and the arterial perfusion fraction (APF, %) were calculated with the two methods, followed by correlation assessment. Partial correlation analysis was used to assess the effects on hepatic perfusion values by various factors, including age, sex, risk of cardiovascular disease, compensation for respiratory misregistration, arrival time of contrast material at the abdominal aorta, transit time from abdominal aorta to hepatic parenchyma, and liver dysfunction.
Results
The mean HAPs, HPPs, and APFs were, respectively, 31.4, 104.2, and 23.9 for MS and 27.1, 141.3, and 22.1 for CM. HAP and APF showed significant (P < 0.0001) and moderate correlation (γ = 0.417 and 0.548) and HPP showed poor correlation (γ = 0.172) between the two methods. While MS showed weak correlations (γ = −0.39 to 0.34; P < 0.001 to <0.02) between multiple extrahepatic factors and perfusion values, CM showed weak correlation only between the patients’ sex and HAP (γ = 0.31, P = 0.001).
Conclusion
Hepatic perfusion values estimated by the two methods are not interchangeable. CM is less susceptible to extrahepatic systemic factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandharipande PV, Krinsky GA. Perfusion imaging of the liver: current challenges and future goals. Radiology 2005;234:661–673.
Cuenod CA, Fournier L, Balvay D, Miles KA. CT perfusion of the liver metastases and early detection of micrometastases. In: Cuenod CA, Miles KA, editors. Multidetector computed tomography in oncology: CT perfusion imaging. London: Informa Healthcare; 2007. p. 173–196.
Hashimoto K, Murakami T, Dono K, Hori M, Kim T, Kudo M. Assessment of the severity of liver disease and fibrotic change: the usefulness of hepatic CT perfusion imaging. Oncol Rep 2006;16:677–683.
Nakashige A, Horiguchi J, Tamura A, Asahara T, Shimamoto F, Ito K. Quantitative measurement of hepatic portal perfusion by multidetector row CT with compensation for respiratory misregistration. Br J Radiol 2004;77:728–734.
Ippolito D, Sironi S, Pozzi M, Antolini L, Invernizzi F, Ratti L, et al. Perfusion CT in cirrhotic patients with early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of tumor-related vascularization. Eur J Radiol 2010;73:148–152.
Yang HF, Du Y, Ni JX, Zhou XP, Li JD, Zhang Q, et al. Perfusion computed tomography evaluation of angiogenesis in liver cancer. Eur Radiol 2010;20:1424–1430. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1693-y
Schlemmer M, Sourbron SP, Schinwald N, Nikolaou K, Becker CR, Reiser MF, et al. Perfusion patterns of metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor lesions under specific molecular therapy. Eur J Radiol 2009 Aug 29 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.07.031
Pauls S, Gabelmann A, Heinz W, Fröhlich E, Juchems MS, Brambs HJ, et al. Liver perfusion with dynamic multidetector-row computed tomography as an objective method to evaluate the efficacy of chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Imaging 2009;33:289–294.
Qian LJ, Zhuang ZG, Cheng YF, Xia Q, Zhang JJ, Xu JR. Hemodynamic alterations in anterior segment of liver graft after right-lobe living-donor liver transplantation: computed tomography perfusion imaging findings. Abdom Imaging 2000 Aug 11 [Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.1007/s00261-009-9563-2
Zhuang ZG, Qian LJ, Wang BX, Zhou Y, Li QG, Xu JR, et al. Computed tomography perfusion in living donor liver transplantation: an initial study of normal hemodynamic changes in liver grafts. Clin Transplant 2009;23:692–699.
Weidekamm C, Cejna M, Kramer L, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Bader TR. Effects of TIPS on liver perfusion measured by dynamic CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:505–510.
Meijerink MR, van Waesberghe JH, van der Weide L, van den Tol P, Meijer S, Comans EF, et al. Early detection of local RFA site recurrence using total liver volume perfusion CT initial experience. Acad Radiol 2009;16:1215–1222.
Cuenod C, Leconte I, Siauve N, Resten A, Dromain C, Poulet B, et al. Early changes in liver perfusion caused by occult metastases in rats: detection with quantitative CT. Radiology 2001;218:556–561.
Funabasama S, Tsushima Y, Sanada S, Inoue K. Hepatic perfusion CT imaging analyzed by the dual-input one-compartment model. Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi 2003;59:1548–1554 (in Japanese).
Miles KA, Hayball MP, Dixon AK. Functional images of hepatic perfusion obtained with dynamic CT. Radiology 1993;188:405–411.
Materne R, Van Beers BE, Smith AM, Leconte I, Jamart J, Dehoux JP, et al. Non-invasive quantification of liver perfusion with dynamic computed tomography and a dual-input one-compartmental model. Clin Sci (Lond) 2000;99:517–525.
Miyazaki S, Murase K, Yoshikawa T, Morimoto S, Ohno Y, Sugimura K. A quantitative method for estimating hepatic blood flow using a dual-input single-compartment model. Br J Radiol 2008;81:790–800.
Miyazaki M, Tsushima Y, Miyazaki A, Paudyal B, Amanuma M, Endo K. Quantification of hepatic arterial and portal perfusion with dynamic computed tomography: comparison of maximum-slope and dual-input one-compartment model methods. Jpn J Radiol 2009;27:143–150.
Bae KT, Heiken JP, Brink JA. Aortic and hepatic contrast medium enhancement at CT. Part II. Effect of reduced cardiac output in a porcine model. Radiology 1998;207:657–662.
Wintermark M, Smith WS, Ko NU, Quist M, Schnyder P, Dillon WP. Dynamic perfusion CT: optimizing the temporal resolution and contrast volume for calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:720–729.
Van Beers BE, Leconte I, Materne R, Smith AM, Jamart J, Horsmans Y. Hepatic perfusion parameters in chronic liver disease: dynamic CT measurements correlated with disease severity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;176:667–673.
Meijerink MR, van Waesberghe JH, van der Weide L, van den Tol P, Meijer S, van Kuijk C. Total-liver-volume perfusion CT using 3-D image fusion to improve detection and characterization of liver metastases. Eur Radiol 2008;18:2345–2354.
Kandel S, Kloeters C, Meyer H, Hein P, Hilbig A, Rogalla P. Whole-organ perfusion of the pancreas using dynamic volume CT in patients with primary pancreas carcinoma: acquisition technique, post-processing and initial results. Eur Radiol 2009;19:2641–2646.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kanda, T., Yoshikawa, T., Ohno, Y. et al. Hepatic computed tomography perfusion: comparison of maximum slope and dual-input single-compartment methods. Jpn J Radiol 28, 714–719 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0497-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0497-y