Abstract
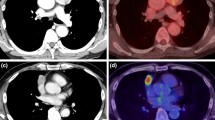
A 66-year-old man, who had undergone surgical resection of a primary noninvasive thymoma (type B1) in the right anterolateral mediastinum 6 years before, underwent follow-up computed tomography (CT) scanning. The CT scan revealed a few nodules located at the posterior portion of the right thoracic base and just behind the right upper anterior chest wall. Subsequent fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scans showed multiple foci with high [standard uptake value (SUV) 4.3] and low (SUV 2.6) FDG uptake in the right lower posterior area and right upper anterior area of the chest, respectively. The fusion image of the CT and FDG-PET scans demonstrated that the areas of the increased FDG uptake corresponded to those of the nodules on the CT scan. All of the nodules were successfully removed surgically, and the histological features of the nodules indicated that they were type B1 or types B1 plus B2. We regarded the nodule located just behind the right upper anterior chest wall as a type B1 thymoma, whereas those in the posterior area of the right thoracic base as combined thymomas of types B1 plus B2. Our limited experience suggests that the degree of FDG uptake is a reflection of the subtype according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. Furthermore, we showed the role of FDG-PET in the accurate assessment of recurrent thymoma and its therapeutic strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Nomori H Horinouchi S Kaseda (1988) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the malignant grade of thymoma by morphometric analysis Cancer 61 982–8 Occurrence Handle3338061 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7gvFeisA%3D%3D
A Masaoka Y Monden K Nakahara T Tanioka (1981) ArticleTitleFollow-up study of thymomas with special reference to their clinical stage Cancer 48 2485–92 Occurrence Handle7296496 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL38%2FkvVektg%3D%3D
J Rosai LH Sobin (1999) Histological typing of tumours of the thymus: international histological classification of the tumours EditionNumber2nd edition Springer New York
MS Park KY Chung KD Kim WI Yang JH Chung YS Kim et al. (2004) ArticleTitlePrognosis of thymic epithelial tumors according to the new World Health Organization histologic classification Ann Thorac Surg 78 992–8 Occurrence Handle15337034 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.03.097
J Han KS Lee CA Yi TS Kim YM Shim J Kim et al. (2003) ArticleTitleThymic epithelial tumors classified according to a newly established WHO scheme: CT and MRI findings Korean J Radiol 4 46–53 Occurrence Handle12679634 Occurrence Handle10.3348/kjr.2003.4.1.46
N Tomiyama NL MÜller SJ Ellis JR Cleverley M Okumura S Miyoshi et al. (2001) ArticleTitleInvasive and non-invasive thymoma: distinctive CT features J Comput Assist Tomogr 25 388–93 Occurrence Handle11351188 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ls1Sguw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004728-200105000-00010
N Tomiyama T Johkoh N Mihara O Honda T Kozuka M Koyama et al. (2002) ArticleTitleUsing the World Health Organization classification of thymic epithelial neoplasms to describe CT findings AJR Am J Roentgenol 179 881–6 Occurrence Handle12239030
YJ Jeong KS Lee J Kim YM Shim J Han OJ Kwon (2004) ArticleTitleDoes CT of thymic epithelial tumors enable us to differentiate histologic subtypes and predict prognosis? AJR Am J Roentgenol 183 283–9
KJ Jung KS Lee J Han J Kim TS Kim EA Kim (2001) ArticleTitleMalignant thymic epithelial tumors: CT—pathologic correlation AJR Am J Roentgenol 176 433–9 Occurrence Handle11159089 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3isVajsg%3D%3D
K Kubota S Yamada T Kondo K Yamada H Fukuda T Fujiwara et al. (1996) ArticleTitlePET imaging of primary mediastinal tumors Br J Cancer 73 882–6 Occurrence Handle8611400 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283hs1GisA%3D%3D
K Terauchi J Shimada D Kato M Nishimura K Ito M Yanada S Toda (2005) ArticleTitleLung metastasis of thymoma manifesting as myasthenia gravis 12 years after thymomectomy: report of a case Surg Today 35 309–12 Occurrence Handle15815848 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00595-004-2939-6
T Kirchner B Schalke J Buchwald M Ritter A Marx HK Muller-Hermelink (1992) ArticleTitleWell-differentiated thymic carcinoma: an organotypical low-grade carcinoma with relationship to cortical thymoma Am J Surg Pathol 16 1153–69 Occurrence Handle1463094 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s%2FpvVensw%3D%3D
E Ruffini M Mancuso A Oliaro (1997) ArticleTitleRecurrence of thymoma: analysis of clinicopathologic features, treatment and outcome J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 113 55–63 Occurrence Handle9011702 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7kvVynsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-5223(97)70399-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, H., Shimada, K., Isogami, K. et al. Recurrent thymoma: radiological (CT and FDG-PET) and histological (WHO criteria) features. Radiat Med 24, 292–296 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-005-1541-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-005-1541-1