Summary
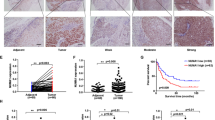
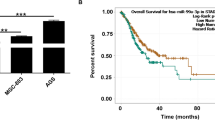
Anoikis is a form of apoptosis induced upon cell detachment from extracellular matrix. It has been determined that acquisition of resistance to anoikis is a critical step for tumor cell metastasis. MiR-21, the most prominent oncomiR, plays an important role in tumor progression. In this study, we revealed that up-regulation of miR-21 in human esophageal adenocarcinoma (EA) is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor survival rate. Because of the established anti-apoptosis effect of miR-21, it is tempting to speculate that miR-21 might contribute to tumor metastasis by regulating anoikis. qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that miR-21 expression in OE33/AR cells (subpopulation of human EA OE33 cells that acquired resistance to anoikis) was significantly increased. Also, transfection of miR-21 mimics provided OE33 cells resisting to anoikis. By luciferase assays, we verified that PDCD4 and PTEN were the functional targets of miR-21. In mouse model, via tail vein injection experiment, we showed that the metastasis formation of OE33 cells in vivo could be mediated by changing the miR-21 expression pattern. Taken together, our findings suggested that miR-21 was involved in the regulation of anoikis in human EA cells. Targeting miR-21 may provide a novel strategy to prevent metastasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013,1833(12):3481–3498
Malagobadan S, Nagoor NH. Evaluation of MicroRNAs Regulating Anoikis Pathways and Its Therapeutic Potential. Biomed Res Int, 2015,2015:716816.
Yang J, Zheng Z, Yan X, et al. Integration of autophagy and anoikis resistance in solid tumors. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2013,296(10):1501–1508
Pachmayr E, Treese C, Stein U. Underlying Mechanisms for Distant Metastasis—Molecular Biology. Visc Med, 2017,33(1):11–20
Slattum GM, Rosenblatt J. Tumour cell invasion: an emerging role for basal epithelial cell extrusion. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014,14(7):495–501
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2011,12(12):861–874
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ, et al. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol, 2012,13(6):e249–258
Gross N, Kropp J, Khatib H. MicroRNA Signaling in Embryo Development. Biology (Basel), 2017,6(3):34
Liu J, Zhu H, Yang X, et al. MicroRNA-21 is a novel promising target in cancer radiation therapy. Tumour Biol, 2014,35(5):3975–3979
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH, Pfeffer LM. The Role of miR-21 in Cancer. Drug Dev Res, 2015,76(6):270–277
Markou A, Zavridou M, Lianidou ES. miRNA-21 as a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl), 2016,7:19–27
Zhao J, Schnitzler GR, Iyer LK, et al. MicroRNAOffset RNA Alters Gene Expression and Cell Proliferation. PLoS One, 2016,11(6):e0156772
Zhu W, Xu B. MicroRNA-21 identified as predictor of cancer outcome: a meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2014,9(8):e103373
Wang W, Li J, Zhu W, et al. MicroRNA-21 and the clinical outcomes of various carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer, 2014,14:819
Schafer ZT, Grassian AR, Song L, et al. Antioxidant and oncogene rescue of metabolic defects caused by loss of matrix attachment. Nature, 2009,461(7260):109–113
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods, 2001,25(4):402–408
Yu SJ, Hu JY, Kuang XY, et al. MircroRNA-200a promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by targeting YAP1 in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2013,19(6):1389–1399
Wu MF, Yang J, Xiang T, et al. miR-21 targets Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2014,34(2):190–194
Feber A, Xi L, Luketich JD, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2008,135(2):255–260
Meng XR, Lu P, Mei JZ, et al. Expression analysis of miRNA and target mRNAs in esophageal cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2014,47(9):811–817
Winther M, Alsner J, Tramm T, et al. Evaluation of miR-21 and miR-375 as prognostic biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Acta Oncol, 2015,54(9):1582–1591
Pan X, Wang ZX, Wang R. MicroRNA-21: a novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther, 2010,10(12):1224–1232
Young MR, Santhanam AN, Yoshikawa N, et al. Have tumor suppressor PDCD4 and its counteragent oncogenic miR-21 gone rogue? Mol Interv, 2010,10(2):76–79
Wang G, Wang JJ, Tang HM, et al. Targeting strategies on miRNA-21 and PDCD4 for glioblastoma. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2015,580:64–74
Ming M, He YY. PTEN in DNA damage repair. Cancer Lett, 2012,319(2):125–129
Khalid A, Hussain T, Manzoor S, et al. PTEN: A potential prognostic marker in virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol, 2017,39(6):1010428317705754
Kumar A, Rajendran V, Sethumadhavan R, et al. AKT kinase pathway: a leading target in cancer research. Sci World J, 2013,2013:756134
Chen J, Xu T, Chen C. The critical roles of miR-21 in anti-cancer effects of curcumin. Ann Transl Med, 2015,3(21):330
Gaudelot K, Gibier JB, Pottier N, et al. Targeting miR-21 decreases expression of multi-drug resistant genes and promotes chemosensitivity of renal carcinoma. Tumour Biol, 2017,39(7):1010428317707372
He C, Dong X, Zhai B, et al. MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget, 2015,6(30):28867–28881
Yan LX, Wu QN, Zhang Y, et al. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res, 2011,13(1):R2
Sicard F, Gayral M, Lulka H, et al. Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther, 2013,21(5):986–994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81470818, No. 81472735 and No. 81472033).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, My., Wang, Lm., Liu, J. et al. MiR-21 Suppresses Anoikis through Targeting PDCD4 and PTEN in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. CURR MED SCI 38, 245–251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1872-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1872-7