Summary
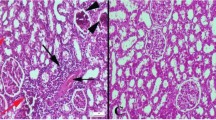
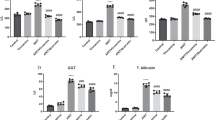
In order to investigate whether Yinchenhao decoction (YCHD) attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis in the bile duct ligation (BDL) model via recovering and restoring the self-regulation and balance of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), 33 specific-pathogen-free (SPF) male Sprague-Dawley rats with common BDL and scission were randomly divided into five groups as follows: G1, the sham group (n=4); G2, BDL 7-day group (n=5); G3, BDL+YCHD 430 mg/mL (n=8); G4, BDL+losartan 0.65 mg/mL (ARB group, n=8); G5, model group (BDL without any treatment, n=8). YCHD and losartan (10 mL·kg−1·day−1) were given by gastric gavage for 16 days following BDL in G3 and G4 groups, respectively. The effect of YCHD on liver fibrosis and the detailed molecular mechanisms were assessed by liver function including total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), indirect bilirubin (IDBIL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Histological changes were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Masson trichrome staining. Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression level of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) components including angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R), ACE2, angiotensin II (AngII) as well as transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1). The experimental data were analyzed by principle component analytical method of pattern recognition. The results showed that biochemically, serum TBIL, DBIL, IDBIL, ALT and AST levels were markedly increased following BDL as compared with the sham group (P<0.05). Serum TBIL, IDBIL and DBIL levels in G3 group were dramatically decreased as compared with G5 and G4 groups (P<0.05). Serum AST level in G3 was significantly lowered than in G5 group (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference in ALT among G3, G4 and G5 groups (P>0.05). Histologically, livers in G3 group showed less hepatocytes necrosis, less bile duct hyperplasia and less collagen formation than in G4 and G5 groups. The protein expression levels of ACE2, ACE, AngII, AT1R and TGFβ1 in G2, G3 and G4 groups were significantly higher than in sham group (P<0.05), and lower than in G5 group (P<0.05). However, the differences among G2, G3 and G4 groups were not significant (P>0.05). ACE2 protein expression in G3 group was significantly higher than in G2 group (P<0.05) and there was no significant difference in comparison with G4 group (P>0.05). Moreover, the protein expression of TGFβ1 in G3 group was significantly lower than in G5 and G4 groups (P<0.05). Our findings suggest that the antifibrotic effects of YCHD may be associated with the decreased classical RAS pathway components and TGFβ1 downexpression so as to recover and rebuild self-regulation of the RAS by elevating the protein expression of ACE2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munshi MK, Uddin MN, Glaser SS, et al. The role of the renin-angiotensin system in liver fibrosis. Exp Biol Med, 2011,236(5):557–566
Zhu R, Yang L, Shen L, et al. ANGII-AT1 receptor pathway involves in the antifibrosis mechanism of β-elemene. J Huazhong Univ Sci Techol Med Sci, 2009,29(2):177–181
Yang L, Zhu R, Zhu QJ, et al. Influence of β-elemene on the secretion of angiotensin II and expression of AT1R in hepatic stellate cells. Front Med China, 2009,3(1):36–40
Warner FJ, Lubel JS, McCaughan GW, et al. Liver fibrosis: a balance of ACEs? Clin Sci, 2007,113(3):109–118
Liu C, Sun MY, Wang L, et al. Effects of Yinchenhao Tang and related decoctions on DMN-induced cirrhosis/fibrosis in rats. Chin Med (Chinese), 2008,3:1
Kountouras J, Billing BH, Scheuer PJ. Prolonged bile duct A: new experimental model for cirrhosis in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol, 1984,65(3):305–311
Fyhrquist F, Saijonmaa O. Renin-angiotensin system revisited. Intern Med, 2008,264(3):224–236
Bataller R, Schwabe RF, Choi YH, et al. NADPH oxidase signal transduces angiotensin II in hepatic stellate cells and is critical in hepatic fibrosis. Clin Invest, 2003,112(9):1383–1394
Bataller R, Gäbele E, Parsons CJ, et al. Systemic infusion of angiotensin II exacerbates liver fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats. Hepatology, 2005,41(5):1046–1055
Kanno K, Tazuma S, Chayama K. AT1A-deficient mice show less severe progression of liver fibrosis induced by CCl4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003,308(1):177–183
Osterreicher CH, Taura K, De Minicis S, et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 inhibits liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology, 2009,50(3):929–938
Pereira RM, dos Santos RAS, Teixeira MM, et al. The renin-angiotensin system in a rat model of hepatic fibrosis: evidence for a protective role of angiotensin(1–7). Hepatology, 2007,46(4):674–681
Cao HX, Sui H, Jiang GX, et al. Comparative study on the protective effects of Yinchenhao decoction against liver injury induced by alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate and carbon tetrachloride. Chin J Integr Med (Chinese), 2009,15(3):204–209
Komiyama T, Tsukui M, Oshio H. Studies of ‘Inchinko’. I. Capillarisin, a new choleretic substance. Yakugaku Zasshi, 1976,96(7):841–854
Guo MZ, Li XS, Xu HR, et al. Rhein inhibits liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2002,23(8):739–744
Paizis G, Tikellis C, Cooper ME, et al. Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2. Gut, 2005,54(12):1790–1796
Huang, Q, Xie Q, Shi CC, et al. Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in CCL4 induced rat liver fibrosis. Int J Mol Med, 2009,23(6):717–723
Herath CB, Warner FJ, Lubel JS, et al. Upregulation of hepatic angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and angiotensin-(1–7) levels in experimental biliary fibrosis. J Hepatol, 2007,47(3):387–395
Paizis G, Mark E, Cooper JM, et al. Up-regulation of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the bile duct-ligated rat liver. Gastroenterology, 2002,123(5):1667–1676
Zhang W, Miao JF, Li PF, et al. Up-regulation of components of the renin-angiotensin system in liver fibrosis in the rat induced by CCL4. Res Vet Sci, 2013,95(1):54–58
Yi ET, Liu RX, Wen Y, et al. Telmisartan attenuates hepatic fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2012,33(12):1518–1524
Azoulay L, Assimes TL, Yin H, et al. Long-term use of angiotensin receptor blockers and the risk of cancer. PLoS One, 2012,7(12):50893
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81102692), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China (No. JX6B09), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (No. 2015QN203).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Zhou, Pq., Xie, Jw. et al. Effects of Yinchenhao decoction on self-regulation of renin-angiotensin system by targeting angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in bile duct-ligated rat liver. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 35, 519–524 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1463-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1463-9