Summary
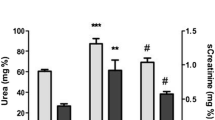
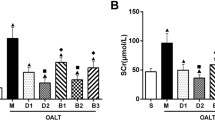
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of dexamethasone (DEX) on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into Sham group, IRI group and DEX group. The mice in IRI and DEX groups subjected to renal ischemia for 60 min, were treated with saline or DEX (4 mg/kg, i.p.) 60 min prior to I/R. After 24 h of reperfusion, the renal function, renal pathological changes, activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR), and the levels of iNOS and eNOS were detected. The results showed DEX significantly decreased the damage to renal function and pathological changes after renal IRI. Pre-treatment with DEX reduced ERK activation and down-regulated the level of iNOS, whereas up-regulated the level of eNOS after renal IRI. DEX could further promote the activation of GR. These findings indicated GR activation confers preconditioning-like protection against acute IRI partially by up-regulating the ratio of eNOS/iNOS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carl DE, Grossman C, Behnke M, et al. Effect of timing of dialysis on mortality in critically ill, septic patients with acute renal failure. Hemodial Int, 2010,14(1):11–17
Zarjou A, Agarwal A. Sepsis and acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011,22(6):999–1006
Leibowitz AB. Hypovolemia is not a common cause of acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med, 2010,38(6):1505–1506
Chronopoulos A, Rosner MH, Cruz DN, et al. Acute kidney injury in the elderly: a review. Contrib Nephrol, 2010,165:315–321
van den Akker EK, Manintveld OC. Protection against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by ischemic postconditioning. Transplantation, 2013,95(11):1299–1305
van der Vliet JA, Warle MC. The need to reduce cold ischemia time in kidney transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant, 2013,18(2):174–178
McQuarrie EP, Fellstrom BC, Holdaas H, et al. Cardiovascular disease in renal transplant recipients. J Ren Care, 2013,36(1):136–145
Yap SC, Lee HT. Adenosine and protection from acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2012,12(1):24–32
Kim JI, Jang HS, Park KM. Endotoxin-induced renal tolerance against ischemia and reperfusion injury is removed by iNOS, but not eNOS, gene-deletion. BMB Rep, 2012,43(9):629–634
Kalyanaraman B. Teaching the basics of redox biology to medical and graduate students: Oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol, 2012,1(1):244–257
Schneider R, Raff U, Vornberger N, et al. L-Arginine counteracts nitric oxide deficiency and improves the recovery phase of ischemic acute renal failure in rats. Kidney Int, 2003,64(1):216–225
Schramm L, La M, Heidbreder E, et al. L-arginine deficiency and supplementation in experimental acute renal failure and in human kidney transplantation. Kidney Int, 2002,61(4):1423–1432
Chen H, Xing B, Liu X, et al. Ozone oxidative preconditioning protects the rat kidney from reperfusion injury: the role of nitric oxide. J Surg Res, 2008,149(2):287–295
Urner M, Herrmann IK, Booy C, et al. Effect of hypoxia and dexamethasone on inflammation and ion transporter function in pulmonary cells. Clin Exp Immunol, 2012,169(2):119–128
Das A, Salloum FN, Xi L, et al. ERK phosphorylation mediates sildenafil-induced myocardial protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2009,296(5):H1236–H1243
Bladh LG, Johansson-Haque K, Rafter I, et al. Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling participates in repression of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activity by glucocorticoids. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009,1793(3):439–446
Kumar S, Allen DA, Kieswich JE, et al. Dexamethasone ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2009, 20(11):2412–2425
Rouillard C, Chiodo LA, Freeman AS. The effects of the phencyclidine analogs BTCP and TCP on nigrostriatal dopamine neuronal activity. Eur J Pharmacol, 1990,182(2):227–235
Zheng X, Feng B, Chen G, et al. Preventing renal ischemia-reperfusion injury using small interfering RNA by targeting complement 3 gene. Am J Transplant, 2006,6(9):2099–2108
Schwartz D, Mendonca M, Schwartz I, et al. Inhibition of constitutive nitric oxide synthase (NOS) by nitric oxide generated by inducible NOS after lipopolysaccharide administration provokes renal dysfunction in rats. J Clin Invest, 1997,100(2):439–448
Wessells H, Teal TH, Luttrell IP, et al. Effect of endothelial cell-based iNOS gene transfer on cavernosal eNOS expression and mouse erectile responses. Int J Impot Res, 2003,18(5):438–445
Sampaio AL, Dalli J, Brancaleone V, et al. Biphasic modulation of NOS expression, protein and nitrite products by hydroxocobalamin underlies its protective effect in endotoxemic shock: downstream regulation of COX-2, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and HMGB1 expression. Mediators Inflamm, 2013,3(1):791–804
Sanchez-Pozos K, Bobadilla NA. Is aldosterone a modulator of vascular tone. Rev Invest Clin, 2013,64(7):546–557
Kielstein A, Tsikas D, Galloway GP, et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)—a modulator of nociception in opiate tolerance and addiction? Nitric Oxide, 2007,17(2):55–59
Goligorsky MS, Brodsky SV, Noiri E. Nitric oxide in acute renal failure: NOS versus NOS. Kidney Int, 2002,61(3):855–861
Matsumoto T, Kuriwaka-Kido R, Kondo T, et al. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by interleukin-11 via AP-1 and Smad signaling. Endocr J, 2012, 59(2):91–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81170686, 81100498, 81100264, 81100485 and 81370798), and the Ministry of Education of China (No. 311028).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, Jh., Wang, L. et al. Glucocorticoid receptor agonist dexamethasone attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by up-regulating eNOS/iNOS. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 34, 516–520 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1308-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1308-y