Summary
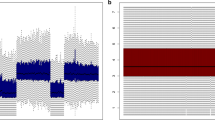
To determine whether the microRNAs (miRNAs) contained in cancer-derived microvesicles (MVs) mirror those of the parental tumor cells, we compared the miRNA expression profiles of MVs derived from their parental hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. The presence and levels of 888 miRNAs from SMMC-7721 cells and MVs were detected by Agilent miRNA microarray analysis. Four selected miRNAs were verified by real time qRT-PCR. Furthermore, the genes of the miRNAs were bioinformatically identified to explore potential roles of the miRNAs in HCC microenvironment. Our results showed that miRNAs expression profiles of MVs derived from HCC were significantly changed. Of all the miRNAs tested, 148 miRNAs were co-expressed in MVs and SMMC-7721 cells, only 121 and 15 miRNAs were detected in MVs and SMMC-7721 cells, respectively. Among the 148 co-expressing miRNAs, 48 miRNAs had the similar expression level and 6 of them were supposed to be oncogenic or suppressive miRNAs. According to the target prediction by Quantile Algorithm method, these miRNAs may regulate 3831 genes which were closely related to cell cycle, apoptosis and oncogenesis, and 78 were known tumor suppressors or oncogenes. Gene ontology (GO) analysis indicated that 3831 genes were mainly associated with nucleic acid binding, cell death, cell adhesion. MVs containing miRNAs, released into the HCC microenvironment, bear the characteristic miRNAs of the original cells and might participate in cancer progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature, 2005,435(7043): 834–838
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression pattern in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene, 2006,25(17):2537–2545
Huang YS, Dai Y, Yu XF, et al. Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissue without vial hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008,23(1):87–94
Lin M, Chen W, Huang J, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in human colorectal cancers with liver metastases. Oncol Rep, 2011,25(3):739–747
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol, 2007,9(6):654–659
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumor growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol, 2008,10(12):1470–1476
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, et al. Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS One, 2008,3(11):e3694
Michael A, Bajracharya SD, Yuen PS, et al. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis, 2010,16(1):34–38
Wysoczynski M, Ratajczak MZ. Lung cancer secreted microvesicles: underappreciated modulators of microenvironment in expanding tumors. Int J Cancer, 2009,125(7): 1595–1603
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD, et al. Oncomirs: the potential role of non-coding microRNAs in understanding cancer. Bioinformation, 2008,2(8):330–334
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, et al. Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. Embo J, 2007,26(15): 3699–3708
Wong QW, Lung RW, Law PT, et al. MicroRNA-223 is commonly repressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and potentiates expression of Stathmin1. Gastroenterology, 2008,135(1):257–269
van Niel G, Porto-Carreiro I, Simoes S, et al. Exosomes: a common pathway for a specialized function. J Biochem, 2006,140(1):13–21
Schorey JS, Bhatnagar S. Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic, 2008,9(6): 871–881
Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen X, et al. Secreted monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell, 2010,39(1):133–144
Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, et al. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: a mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology, 2011,54(4):1237–1248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81170462).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, W., Sun, Lp., Chen, Xm. et al. Comparison of microRNA expression profiles in HCC-derived microvesicles and the parental cells and evaluation of their roles in HCC. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 346–352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1122-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1122-y