Summary
This study investigated the expression profiles of IL-10 gene in three human hepatoma cell lines including Huh7, HepG2, and HepG2 transfected with a plasmid containing hepatitis B virus (HBV) named HepG2.2.15. RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that IL-10 message RNA was absent in HepG2 and Huh7 cells, whereas it was present in HepG2.2.15 cells, which was consistent with ELISA result. Furthermore, except for lamivudine other antiviral treatments did not significantly decrease the HBV DNA level in HepG2.2.15 cells, while they had different effects on the expression of IL-10 protein, although stimulation by LPS had no significant effect. In addition, except for poly(I:C), the other treatments decreased the expression of IL-10 protein to different degrees, but had no significant effects on the expression of NF-κB and MyD88. Meanwhile, all treatments we used had effect on the expression of STAT1. In conclusion, IL-10 was expressed in HepG2.2.15 cells and STAT1 pathway might be involved in the regulation of IL-10 expression in HepG2.2.15 cells, but it was not the sole pathway, the exact mechanism warrants further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavanaugh VJ, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Interleukin-12 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J Virol, 1997,71(4),3236–3243
Kimura K, Kakimi K, Wieland S, et al. Interleukin-18 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in the livers of transgenic mice. J Virol, 2002,76(21):10702–10707
Suri D, Schilling R, Lopes AR, et al. Non-cytolytic inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in human hepatocytes. J Hepatol, 2001,35(6):790–797
Wu JF, Wu TC, Chen CH, et al. Serum levels of interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 predict early, spontaneous hepatitis B virus e antigen seroconversion. Gastroenterology, 2010,138(1):165–72.e1–e3
Bai F, Town T, Qian F et al. IL-10 signaling blockade controls murine West Nile virus infection. PLoS Pathog, 2009,5(10):e1000610
Blackburn SD, Wherry EJ. IL-10, T cell exhaustion and viral persistence. Trends Microbiol, 2007,5(4):143–146
Brooks DG, Trifilo MJ, Edelmann KH et al. Interleukin-10 determines viral clearance or persistence in vivo. Nat Med, 2006,12(11):1301–1309
Maris CH, Chappell CP, Jacob J. Interleukin-10 plays an early role in generating virus-specific T cell anergy. BMC Immunol, 2007,8:8
Mosser DM, Zhang X. Interleukin-10: new perspectives on an old cytokine. Immunol Rev, 2008,226:205–218
Saraiva M, O’Garra A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010,10(3):170–181
Louis H, Van Laethem JL, Wu W, et al. Interleukin-10 controls neutrophilic infiltration, hepatocyte proliferation, and liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Hepatology, 1998,28(6):1607–1615
Thompson K, Maltby J, Fallowfield J’ et al. Interleukin-10 expression and function in experimental murine liver inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology, 1998,28(6):1597–1606
Tsukamoto H. Is interleukin-10 antifibrogenic in chronic liver injury? Hepatology, 1998,28(6):1707–1709
Warren A, Le Couteur DG, Fraser R, et al. T lymphocytes interact with hepatocytes through fenestrations in murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatology, 2006,44(5): 1182–1190
Herkel J, Jagemann B, Wiegard C, et al. MHC class II-expressing hepatocytes function as antigen-presenting cells and activate specific CD4 T lymphocyutes. Hepatology, 2003,37(5):1079–1085
Muhlbauer M, Fleck M, Schutz C, et al. PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-alpha and -gamma and mediates T cell apoptosis. J Hepatol, 2006,45(4):520–528
Wiegard C, Wolint P, Frenzel C, et al. Defective T helper response of hepatocyte-stimulated CD4 T cells impairs antiviral CD8 response and viral clearance. Gastroentero logy, 2007,133(6):2010–2018
Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R, et al. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol, 2007,8(3): 239–245
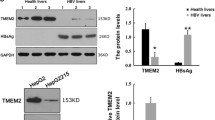
Sells MA, Chen ML, Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1987, 84(4):1005–1009
Preiss S, Thompson A, Chen X, et al. Characterization of the innate immune signalling pathways in hepatocyte cell lines. J Viral Hepat, 2008,15(12):888–900
Liu J, Yang Y, Hu B, et al. Development of HBsAgbinding aptamers that bind HepG2.2.15 cells via HBV surface antigen. Virol Sin, 2010,25(1):27–35
Chen Y, Wu W, Li LJ, et al. Comparison of the results for three automated immunoassay systems in determining serum HBV markers. Clin Chim Acta, 2006,372(1–2): 129–133
Lei YC, Hao YH, Zhang ZM, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by APOBEC3G in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol, 2006,12(28):4492–4497
Aman MJ, Tretter T, Eisenbeis I, et al. Interferon-alpha stimulates production of interleukin-10 in activated CD4+ T cells and monocytes. Blood, 1996,87(11):4731–4736
Ozenci V, Kouwenhoven M, Huang YM, et al. Multiple sclerosis is associated with an imbalance between tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)- and IL-10-secreting blood cells that is corrected by interferon-beta (IFN-beta) treatment. Clin Exp Immunol, 2000,120(1):147–153
Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Lotzerich M, Schaefer A, et al. IFN-alpha induces the human IL-10 gene by recruiting both IFN regulatory factor 1 and Stat3. J Immunol, 2003, 171(1):285–290
Mori N, Prager D. Activation of the interleukin-10 gene in the human T lymphoma line HuT 78: identification and characterization of NF-kappa B binding sites in the regulatory region of the interleukin-10 gene. Eur J Haematol, 1997,59(3):162–170
Bondeson J, Browne KA, Brennan FM, et al. Selective regulation of cytokine induction by adenoviral gene transfer of IkappaBalpha into human macrophages: lipopolysaccharide-induced, but not zymosan-induced, proinflammatory cy-tokines are inhibited, but IL-10 is nuclear factor-kappaB independent. J Immunol, 1999, 162(5):2939–2945
Batten M, Kljavin NM, Li J, et al. Cutting edge: IL-27 is a potent inducer of IL-10 but not FoxP3 in murine T cells. J Immunol, 2008, 180(5):2752–2756
Kalliolias GD, Ivashkiv LB. IL-27 activates human monocytes via STAT1 and suppresses IL-10 production but the inflammatory functions of IL-27 are abrogated by TLRs and p38. J Immunol, 2008,180(9):6325–6333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the National Major Science and Technology Special Project for Infectious Diseases of China (No. 2008ZX10002-011).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Hao, Y., Ding, H. et al. Interleukin-10 is expressed in HepG2.2.15 cells and regulated by STAT1 pathway. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 625–631 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0572-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0572-3