Summary
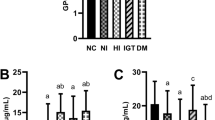
The P85 regulatory subunit protein and gene expression and P110 catalylic subunit activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K) were investigated in adipose tissue of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in order to explore the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance (IR) of GDM. Samples from patients with GDM (n=50), and controls (n=50) were collected. Fasting insulin (FIN) was determined by radioimmunoassay. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) was measured by oxidase assay. Western blot technique was used to detect the levels of PI-3K P85 subunit in adipose tissues of patients with GDM. The mRNA expression of PI-3K P85 subunit was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method in the adipose tissue. PI-3K activity was examined by immunoprecipitation, thin-layer chromatography and gamma scintillation counting. The results were analyzed statistically. It was found that the levels of FPG, FIN and HOMA-IR in GDM group were significantly higher than those in control group (all P<0.01). There was no significant difference in the protein and gene expression of PI-3K P85 subunit between GDM group and control group (P>0.05). PI-3K activity was significantly decreased to 82.89% in GDM group as compared with control group (P<0.01) and negatively correlated with HOMA-IR (r=−0.75, P<0.01). It was concluded that PI-3K in GDM patients may be involved in the insulin signaling pathway, resulting in IR of GDM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zawiejska A, Wender Ozegowska E, Brazert J, et al. Components of metabolic syndrome and their impact on fetal growth in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2008,59(S4):5–18
Voldner N, Qvigstad E, Froslie KF, et al. Increased risk of macrosomia among overweight women with high gestational rise in fasting glucose. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2010,23(1):74–81
Le J. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 6th eds. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2004,179–182
Goodyear LJ, Giorgino F, Sherman LA, et al. Insulin receptor phosphorylation, insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphoralytion, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity are decreased in intact skeletal muscle strips from obese subjects. J Clin Invest, 1995,95(5):2195–2204
Folli F, Saad Mario JA, Backer JM, et al. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and associated with insulin receptor substrate 1 in liver and muscle of the intact rat. J Bio Chem, 1992,267(31):22 171–22 177
Das S, Behera MK, Misra S, et al. Beta-cell function and insulin resistance in pregnancy and their relation to fetal development. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 2010,8(1):25–32
Qvigstad E, Voldner N, Godang K, et al. Overweight is associated with impaired beta-cell function during pregnancy: a longitudinal study of 553 normal pregnancies. Eur J Endocrinol, 2010,162(1):67–73
Keely EJ, Malcolm JC, Hadjiyannakis S, et al. Prevalence of metabolic markers of insulin resistance in offspring of gestational diabetes pregnancies. Pediatr Diabetes, 2008, 9(1):53–59
Endo S, Maeda K, Suto M, et al. Differences in insulin sensitivity in pregnant women with overweight and gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2006, 22(6):343–349
Mamabolo RL, Alberts M, Levitt NS, et al. Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the effect of weight on measures of insulin secretion and insulin resistance in third-trimester pregnant rural women residing in the Central Region of Limpopo Province, South Africa. Diabet Med, 2007,24(3):233–239
Scioscia M, Gumaa K, Selvaggi LE, et al. Increased inositol phosphoglycan P-type in the second trimester in pregnant women with type 2 and gestational diabetes mellitus. J Perinat Med, 2009,37(5):469–471
Vela Huerta MM, San Vicente Santoscoy EU, Guizar Mendoza JM, et al. Leptin, insulin, and glucose serum levels in large-for-gestational-age infants of diabetic and non-diabetic mothers. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab, 2008, 21(1):17–22
Kleiblova P, Dostalova I, Bartlova M, et al. Expression of adipokines and estrogen receptors in adipose tissue and placenta of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2010,314(1):150–156
Catalano PM, Drago NM, Amini SB. Longitudinal changes in pancreatic beta-cell function and metabolic clearance rate of insulin in pregnant women with normal and abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care, 1998, 21(3):403–408
Buchanan TA, Xiang AH. Gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest, 2005,115(3):485–491
Barros RP, Morani A, Moriscot A, et al. Insulin resistance of pregnancy involves estrogen-induced repression of muscle GLUT4. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2008,295(1–2): 24–31
Glueck CJ, Goldenberg N, Sieve L, et al. An observational study of reduction of insulin resistance and prevention of development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with metformin and diet. Metabolism, 2008,57(7):954–960
Smirnakis KV, Martinez A, Blatman KH, et al. Early pregnancy insulin resistance and subsequent gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 2005,28(5):1207–1208
Kuzmicki M, Telejko B, Szamatowicz J, et al. High resistin and interleukin-6 levels are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2009,25(4): 258–263
Carr DB, Utzschneider KM, Hull RL, et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus increases the risk of cardiovascular disease in women with a family history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 2006,29(9):2078–2083
Colomiere M, Permezel M, Riley C, et al. Defective insulin signaling in placenta from pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol, 2009, 160(4):567–578
Retnakaran R, Qi Y, Connelly PW, et al. Low adiponectin concentration during pregnancy predicts postpartum insulin resistance, beta cell dysfunction and fasting glycaemia. Diabetologia, 2010,539(2):268–276
Anai M, Ono H, Funaki M. Different subcellular distribution and regulation of expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-3 from those of IRS-1 and IRS-2. J Biol Chem, 1998,273(45):29 686–29 692
Udelhoven M, Pasieka M, Leeser U, et al. Neuronal insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) expression is regulated by ZBP89 and SP1 binding to the IRS2 promoter. J Endocrinol, 2010,204(2):199–208
Rung J, Cauchi S, Albrechtsen A, et al. Genetic variant near IRS1 is associated with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. Nat Genet, 2009,41(10): 1110–1115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the Doctoral Fund of Shandong Province in China (No. 2006BS03053).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Y., Liu, W., Cui, Q. et al. Analysis of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation in the adipose tissue of gestational diabetes mellitus patients and insulin resistance. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 30, 505–508 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0458-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0458-9