Summary
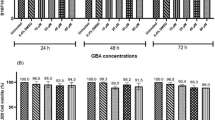
The inhibitory effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on the invasion of human malignant melanoma cell line A375 and the possible molecular mechanisms of this effect were investiaged. A375 cells were pretreated with 20 μg/mL EGCG for 24, 48 and 72 h respectively and the E-cadherin expression was detected by Western blot analysis. A375 cells were also pretreated with different concentrations of EGCG (1, 5, 10 and 20 μg/mL) for 72 h and the expression of E-cadherin was measured by RT-PCR. The adhesion and invasion of A375 cells were tested by cell-matrigel adhesion assay and matrigel invasion assay respectively. The results showed that EGCG could significantly up-regulate the expression of E-cadherin time-and concentration-dependently (both P<0.05). Statistical analysis showed that A375 cells invasion was inhibited by EGCG and correlated with the up-regulation of E-cadherin expression. It was suggested that EGCG strongly inhibited invasion of A375 cells, and the inhibition mechanism was possibly associated with the up-regulation of E-cadherin expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gassmann P, Enns A, Haier J. Role of tumor cell and adhesion and migration in organ-specific metastasis formation. Onkologie, 2004,27(6):577–582
Hirohashi S. Inactivation of the E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancers. Am J Pathol, 1998,153:333–339
Hanahan D, Weinberg R A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 2000,100:57–70
Hirohashi S, Kanai Y. Cell adhesion system and human cancer Morphogenesis. Cancer Sci, 2003,94:575–581
Yang F, Oz H S, Barve S et al. The green tea polyphenol [-]-epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks nuclear factor-κB activation by inhibiting κB kinase activity in the intestinal epithelial cell line IEC-6. Mol Pharmacol, 2001,60:528–534
Liu J D, Chen S H, Lin C L et al. Inhibition of melanoma growth and metastasis by combination with [-]-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and dacarbazine in mice. J Cell Biochem, 2001,83:631–642
Jung Y D, Ellis L M. Inhibition of tumour invasion and angiogenesis by epigallicatechin gallate, a major component of green tea. Int J Exp Pathol, 2001,82:309–316
Oshiro T, Koyama S, Suqiyama S et al. Interaction of POB-1, a down-stream molecule of small G protein ra1, with PAG2, a paxillin-binding protein, is involved in cell migration. J Biol Chem, 2002,277(10):38 618–38 626
Liotta L A. Tumor invasion and metastasis: role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res, 1986,46:1–7
Wei D Z, Yang J Y, Liu J W et al. Inhibition of liver cancer cell proliferation and migration by combination with [-]-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ascorbic acid. J Chemotherapy, 2003,15:591–595
Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A. Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol, 2004,48:365–375
Graff J R, Gabrielson E, Fujii H et al. Methylation patterns of the E-cadherin 5’CpG island are unstable and reflect the dynamic, heterogeneous loss of E-cadherin expression during metastatic progression. J Biol Chem, 2000,275:2727–2732
Miura Y, Shiomi H, Sakai F et al. Assay system for screening food components that have anti-proliferative and anti-invasion activity to rat ascites hepatoma cells: in vitro and exvivo effects of green tea extract. Cytotechnology, 1999,31:127–133
Zhang G Y, Miura Y, Yagasaki K. Effects of green, oolong and blank teas and related components on the proliferation and invasion of liver cancer cells in culture. Cytotechnology, 1999,31:37–44
Hidvegi M, Raso E, Tomoskozi-Farkas R et al. Effect of avemar and avemar+vitamin C on tumor growth and metastasis in experimental animals. Anticancer Res, 1998,18:2353–2358
Miwa N, Yamazaki H. Potentiated susceptibility of ascites tumor to acyl derivatives of ascorbate caused by balanced hydrophobicity in the molecule. Exp Cell Biol, 1986,54:245–249
Fang M Z, Wang Y, Ai N et al. Tea polyphenol(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res, 2003,63:7563–7670
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Lin, Y., Liu, H. et al. Inhibition of invasion and up-regulation of E-cadherin expression in human malignant melanoma cell line A375 by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 356–359 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0330-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0330-3