Summary
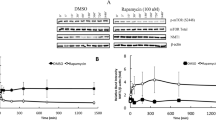
The activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in endometrial carcinoma cells Ishikawa and HEC-1A was investigated. The expression of mTOR was detected by confocal fluorescence microscopy in Ishikawa and HEC-1A cells. The mRNA levels of PTEN and mTOR, the downstream substrate S6K1 and 4E-BP1 protein were assayed by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. The expression of PTEN in Ishikawa cells was deficient, but intact in HEC-1A cells respectively (P<0.01). There was mTOR expression in both Ishikawa and HEC-1A cells and the phosporylated substrate levels in Ishikawa cells were higher than those in HEC-1A cells (P<0.05). mTOR signaling pathway is activated in two endometrial carcinoma cell strains and the status of activation is related with PTEN expression of the cells. The activation level of mTOR is higher in PTEN-deficient endometrial carcinoma cells than that in PTEN-intact endometrial carcinoma cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janus A, Robak T, Smolewski P. The mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) kinase pathway: its role in tumourigenesis and targeted anti-tumour therapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2005,10:479–498
Xu G, Zhang W, Bertram P et al. Pharmacogenomic profiling of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in common human tumor. Int J Oncol, 2004,24(4):901–908
Sahin F, Kannangai R, Adegbola O et al. mTOR and P70 S6 kinase expression in primary liver neoplasms. Clin Cancer Res, 2004,10:8421–8425
Ito D, Fujimoto K, Mori T et al. In vivo antitumor effect of the mTOR inhibitor CCI2779 and gemcitabine in xenograft models of human pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer, 2006,118:2337–2343
Altomare D A, You H, Xiao G H et al. Human and mouse mesotheliomas exhibit elevated activity, which can be targeted pharmacologically to inhibit tumor cell growth. Oncogene, 2005,24(40):6080–6089
Tolcher A. Novel therapeutic molecular targets for prostate cancer: the mTOR signaling pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor. J Urol, 2004,171(2 Pt 2):41–44
Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J et al. The rapamycin anolog CCI-779 is a potent inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2005,331:295–302
Atkins M B, Hidalgo M, Stadler W M et al. Randomized phase II study of multiple does levels of CCI-779, a novel mammalian target of rapamycin kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced refractory renal cell carcinomas. J Clin Oncol, 2004,22:909–918
Cantley L C, Neel B G. New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA, 1999,96(8):4240–4245
Bakiewicz A, Gozdzik J, Sporny S. Pten gene expression in the endometrial mucosa. Ginekol Pol, 2006,77(4):323–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xiao, L., Yang, Y. et al. The expression of mammalian target of rapamycin in Ishikawa and HEC-1A cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 340–342 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0325-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0325-0