Summary
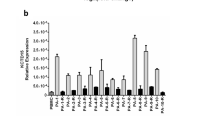
In order to investigate the expression and functional role of HERG1 K+ channels in leukemic cells and leukemic stem cells (LSCs), RT-PCR was used to detect the HERG1 K− channels expression in leukemic cells and LSCs. The functional role of HERG1 K+ channels in leukemic cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay, and cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed by flow cytometry. The results showed that herg mRNA was expressed in CD34+/CD38−, CD123− LSCs but not in circulating CD34+ cells. Herg mRNA was also up-regulated in leukemia cell lines K562 and HL60 as well as almost all the primary leukemic cells while not in normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNCs) and the expression of herg mRNA was not associated with the clinical and cytogenetic features of leukemia. In addition, leukemic cell proliferation was dramatically inhibited by HERG K+ channel special inhibitor E-4031. Moreover, E-4031 suppressed the cell growth by inducing a specific block at the G1/S transition phase of the cell cycle but had no effect on apoptosis in leukemic cells. The results suggested that HERG1 K+ channels could regulate leukemic cells proliferation and were necessary for leukemic cells to proceed with the cell cycle. HERG1 K+ channels may also have oncogenic potential and may be a biomarker for diagnosis of leukemia and a novel potential pharmacological target for leukemia therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair A, Hogge D E, Sutherland H J. Most acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo have the phenotype CD34(+)/CD1(-)/HLA-DR. Blood, 1998,92:4325–4335
Bonnet D, Dick J E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med, 1997,3:730–737
Curran M E, Splawski I, Timothy K W et al. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell, 1995,80(5):795–803
Jones E M, Roti E C, Wang J et al. Cardiac IKr channels minimally comprise hERG 1a and 1b subunits. J Biol Chem, 2004,279:44 690–44 694
Shi W, Wymore R S, Wang H S et al. Identification of two nervous system-specific members of the erg potassium channel gene family. J Neuroscience, 1997,17:9423–9432
Masi A, Becchetti A, Restano-Cassulini R et al. hERG1 channels are overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme and modulate VEGF secretion in glioblastoma cell lines. Br J Cancer, 2005,93:781–792
Cherubini A, Taddei G L, Crociani O et al. HERG potassium channels are more frequently expressed in human endometrial cancer as compared to non-cancerous endometrium. Br J Cancer, 2000,83:1722–1729
Lastraioli E, Guasti L, Crociani O et al. Hergl gene and HERG1 protein are overexpressed in colorectal cancers and regulate cell invasion of tumor cells. Cancer Res, 2004,64:606–611
Crociani O, Guasti L, Balzi M et al. Cell cycle-dependent expression of HERG1 and HERG1B isoforms in tumor cells. J Biol Chem, 2003,278:2947–2955
Bianchi L, Wible B, Arcangeli A et al. HERG encodes a K+ current highly conserved in tumors of different histogenesisa selective advantage for cancer cells? Cancer Res, 1998,58:815–822
Smith G A M, Tsui H W, Newell E W et al. Functional up-regulation of HERG K+ channels in neoplastic hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem, 2002,277:18 528–18 534
Pillozzsi S, Brizzi M F, Balzi M et al. HERG potassium channels are constitutively expressed in primary human acute myeloid leukemias and regulate cell proliferation of normal and leukemic hemopoietic progenitors. Leukemia, 2002,16(9):1791–1798
Jordan C T, Upchurch D, Szilvassy S J et al. The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia, 2000,14(10):1777–1784
Lemoli R M, Tafuri A, Fortuna A et al. Cycling status of CD34+ mobilized into peripheral blood of healthy donors by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood, 1997,89:1189–1196
Beeton C, Pennington M W, Wulff H et al. Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases. Mol Pharmacol, 2005,67:1369–1381
McClelland A, Kuhn L C, Ruddle F H. The human fransferrin receptor gene: genomic organization and the complete primary structure of the receptor deduced from a cDNA sequence. Cell, 1984,39:267–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LI Huiyu, female, born in 1960, Associate Professor
This project was supported by a grant from National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (No. 30225038).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, L., Guo, T. et al. Expression and fuactional role of HERG1, K+ channels in leukemic cells and leukemic stem cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 257–260 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0310-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0310-2