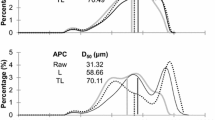
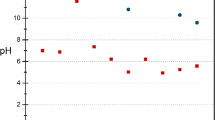
Abstract
The feasibility of high calcium fly ash (CFA)-based geopolymers to fix heavy metals were studied. The CFA-based geopolymers were prepared from CFA, flue gas desulfurization gypsum (FGDG), and water treatment residual (WTR). The static leaching showed that heavy metals concentrations from CFAbased geopolymers were lower than their maximum concentration limits according to the U.S. environmental protection law. And the encapsulated and fixed ratios of heavy metals by the CFA-based geopolymers were 96.02%–99.88%. The dynamic real-time leaching experiment showed that concentration of Pb (II) was less than 1.1 μg / L, Cr (VI) less than 3.25 mg / L, while Hg (II) less than 4.0 μg / L. Additionally, dynamic accumulated leaching concentrations were increased at the beginning of leaching process then kept stable. During the dynamic leaching process, heavy metals migrated and accumulated in an area near to the solid-solution interface. When small part of heavy metals in “the accumulated area” breached through the threshold value of physical encapsulation and chemical fixation they migrated into solution. The dynamic leaching ratios and effective diffusion coefficients of heavy metals from CFA-based geopolymer were very low and the long-term security of heavy metals in CFA-based geopolymer was safe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J W Shi, S H Chen, S M Wang, et al. Progress of Modification and Application of Coal Fly Ash in Water Treatment[J]. Chin. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. Process, 2008,27: 326–334
J M Wang, H Ban, X J Teng, et al. Impact of pH and Ammonia on the Leaching of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from Coal Fly Ash[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 64: 1 892–1 898
C Xia, X He, Y Li. Comparative Sorption Studies of Toxic Ocresol on Fly Ash and Impregnated Fly Ash[J]. Technol. Equip. Environ. Pollut. Control., 2000, 2: 82–86
American Coal Ash Association. Coal Combustion Product (CCP) Production & Use Survey Results (Revised) [DB/OL]. http://www.acaa-usa.org/associations/8003/files/2007_ACAA_CCP_Survey_Report_Form%2809-15-08%29.pdf. Site verified, January 20, 2009
P Bankowski, L Zou, R Hodges. Reduction of Metal Leaching in Brown Coal Fly Ash Using Geopolymers[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, B114: 59–67
S K Antiohos, S Tsimas. A Novel Way to Upgrade the Coarse Part of A High Calcium Fly Ash for Reuse into Cement Systems[J]. Waste Manage., 2007, 27: 675–683
X L Guo, H S Shi, W A Dick. Compressive Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Class C Fly Ash Geopolymer[J]. Cem. Concr. Compos., 2010, 32:142–147
X L Guo, H S Shi, L M Chen, et al. Alkali-Activated Complex Binders from Class C Fly Ash and Ca-Containing Admixtures[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 173: 480–486
United States Environmental Protection Agency Publication. Toxicity Characterisation Leaching Procedure (TCLP)[S]. EPA Method 1311, 1999
H A Van der Sloot. Developments in Evaluating Environmental Impact from Utilization of Bulk Inert Wastes Using Laboratory Leaching Tests and Field Verification[J]. Waste Manage., 1996, 16:65–81
C J Shi, R Spence. Designing of Cement-Based Formula for Solidification/Stabilization of Hazardous, Radioactive, and Mixed Wastes[J]. Environ. Sci. Techno., 2004, 34: 391–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.51208370, 51172164), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China(No.20110072120046)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Shi, H. & Xu, M. Static and dynamic leaching experiments of heavy metals from fly ash-based geopolymers. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 28, 938–943 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0797-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0797-z