Abstract
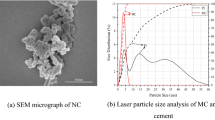
Leaching is one of the major factors that alter the mechanical properties of cement-based composites. This study is aimed to investigate the effect of leaching on the properties of cement-based composites. Specimens with two water/cementitious ratios and two mineral admixtures were tested. An electrical potential was applied to accelerate the leaching process. Compressive strength test, scanning electronic microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis were conducted. Test results demonstrated that the calcium leaching reduced compressive strengths of concrete specimens, and such effect was prominent on the specimens without mineral admixtures. The leaching resistance increased with a decrease in water/cementitious ratio and an increase in amount of mineral admixtures. The mineral admixtures would reduce the amount of calcium hydroxide and refine the pore structure through pozzolanic reactions. A fair relationship was found between the calcium leaching and the compressive strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F M Heukamp, F J Ulm, J T Germaine. Poroplastic Properties of Calcium-leached Cement-based Materials[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2003, 33(8): 1 155–1 173
H Saito, A Deguchi. Leaching Tests on Different Mortars Using Accelerated Electrochemical Method[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2000, 30(11): 1 815–1 825
B W Lu, J D Lu, W H Huang. Leaching Behavior of Concrete Barrier of Low-level Radwaste Disposal Site[J]. Monthly Journal of Taipower’s Engineering, 2007, 710: 11–22
V Matte, M Moranville. Durability of Reactive Powder Composites: Influence of Silica Fume on the Leaching Properties of Very Low Water/binder Pastes[J]. Cem. Concr. Comp., 1999, 21(1): 1–9
U R Berner. Evolution of Pore Water Chemistry During Degradation of Cement in A Radioactive Waste Repository Environment[J]. Waste Management, 1992, 12(2–3): 201–219
D Kuhl, C Meschke. A Comparison of Coupled Chemomechanical Damage Models of Concrete Using Phenomenological Chemistry and Reaction Kinetics[C]. First MIT Conference on Computational Fluid and Solid Mechanics, 2001: 1 278–1 280
H Saito, S Nakane. Comparison Between Diffusion Test and Electrochemical Acceleration Test for Leaching Degradation of Cement Hydration Products[J]. ACI Mat. J., 1999, 96(2): 208–212
F Agostini, Z Lafhaj, F Skoczylas, et al. Experimental Study of Accelerated Leaching on Hollow Cylinders of Mortar[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2007, 37(1): 71–78
N Burlion, D Bernard, D Chen. X-ray Microtomography: Application to Microstructure Analysis of A Cementitious Material During Leaching Process[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2006, 36(2): 346–357
J Hou, D D L Chung. Effect of Admixtures in Concrete on the Corrosion Resistance of Steel Reinforced Concrete[J]. Corros. Sci., 2000, 42(9): 1 489–1 507
R Mejia, S Delvasto, C Gutierrez, et al. Chloride Diffusion Measured by A Modified Permeability Test in Normal and Blended Cements[J]. Adv. Cem. Res., 2003, 15(3): 113–118
L Franke, K Sisomphon. A New Chemical Method for Analyzing Free Calcium Hydroxide Content in Cementing Material[J]. Cem. Con. Res., 2004, 34(7): 1 161–1 165
B W Jo, C H Kim, G H Tae, et al. Characteristics of Cement Mortar with Nano-SiO2 Particles[J]. Constr. Build. Mat., 2007, 21(6): 1 351–1 355
C Carde, R Francois. Modelling the Loss of Strength and Porosity Increase Due to the Leaching of Cement Paste[J]. Cem. Concr. Comp., 1999, 21(3): 181–188
J S Ryu, N Otsuki, H Minagawa. Long-term Forecast of Ca Leaching from Mortar and Associated Degeneration[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2002, 32(10): 1 539–1 544
C Alonso, M Castellote, I Llorente, et al. Ground Water Leaching Resistance of High and Ultra High Performance Concretes in Relation to the Testing Convection Regime[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2006, 36(9): 1 583–1 594
C Hall. Water Sorptivity of Mortar and Concretes: A Review[J]. Mag. Concr. Res., 1989, 41(147): 51–61
B E Jazairi, J M Lllston. The Hydration of Cement Paste Using the Semi-Isothermal Method of Derivative Thermogravity[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 1980, 10: 361–366
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, W., Cheng, A., Huang, R. et al. Effect of calcium leaching on the properties of cement-based composites. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 990–997 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0350-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0350-x