Abstract
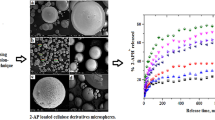
A kind of slow release drug-loaded microspheres were prepared with gelatin, chitosan and montmorillonite(MMT) by an emulsification/chemical cross-linking method using glutaraldehyde as crosslinking agent and acyclovir as model drug. The microspheres were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), respectively. The morphology, drug content, encapsulation efficiency and drug-release behavior were investigated with different MMT contents. The experimental results indicated that intercalated microspheres could be prepared, the morphology of microspheres was markedly affected by MMT. The glomeration performance of uncross-linked microspheres was improved because of the physical cross-linking of MMT. Drug content and encapsulation efficiency were decreased when increased the content of MMT, but burst release and the drug release were signifi cantly decreased with the addition of MMT. Effective physical cross-linking could be formed when added MMT, and MMT could reduce the content of toxic chemical cross-linking agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel Z S, Yamamoto M, Ueda H, et al. Biodegradable Gelatin Microparticles as Delivery Systems for the Controlled Release of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2[J]. Acta Biomater., 2008, 4(5): 1 126–1 138
Dong Z F, Wang, Q, Du Y. Alginate/Gelatin Blend Films and Their Properties for Drug Controlled Release[J]. J. Membrane Sci., 2006, 280(1–2): 37–44
Zhou X F, Liu B, Yu X H, et al. Controlled Release of PEI/DNA Complexes from Mannose-bearing Chitosan Microspheres as a Potent Delivery System to Enhance Immune Response to HBV DNA Vaccine[J]. J. Control Release, 2007, 121(3): 200–207
Zhang Y Z, Venugopal J, Huang Z M, et al. Cross-linking of the Electrospun Gelatine Nanofibers Polymer[J]. Polymer, 2006, 47(8): 2 911–2 917
Lin M, Meng S, Zhong W, et al. Novel Drug-loaded Gelatin Films and Their Sustained-release Performance[J]. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2009, 90B(2): 939–944
Liang H C, Chang W H, Lin K J, et al. Genipin-crosslinked Gelatin Microspheres as a Drug Carrier for Intramuscular Administration: In vitro and in vivo studies[J]. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2003, 65A(2): 271–282
Sinha V R, Singla A K, Wadhawan, S et al. Chitosan Microspheres as a Potential Carrier for Drugs[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2004, 274(1–2): 1–33
Zhao X L, Li K X, Zhao X F, et al. Study on Colon-specifi c 5-Fu pH-enzyme Di-dependent Chitosan Microspheres[J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2008, 56(7): 963–968
Weerakody R, Fagan P, Kosaraju S L, et al. Chitosan Microspheres for Encapsulation of α-lipoic Acid[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2008, 357(1–2): 213–218
Kang M L, Cho C S, Yoo H S. Application of Chitosan Microspheres for Nasal Delivery of Vaccines[J]. Biotechnol. Adv., 2009, 27(6): 857–865
Chen Y F, Lin X F, Park H, et al. Study of Artemisinin Nanocapsules as Anticancer Drug Delivery Systems[J]. Nanomed., 2009, 5(3): 316–322
Yao K D, Xu M X, Yin Y J, et al. pH-sensitive Chitosan/ Gelatin Hybrid-polymer Network Microspheres for Delivery of Cimetidine[J]. Polym. Int., 1995, 39: 333–337
Esposito E, Cortesi R, Nastruzzi C. Preparation Parameters and Thermal Treatment on Chemico-physical and Biopharmaceutical Properties[J]. Biomaterials, 1996, 17(20): 2 009–2 020
Joshi G V, Kevadiya B D, Patel H A, et al. Montmorillonite as a Drug Delivery System: Intercalation and in Vitro Release of Timolol Maleate[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2009, 374(1–2): 53–57
Lin F H, Lee Y H, Jian C H, et al. A Study of Purified Montmorillonite Intercalated with 5-Fluorouracil as Drug Carrier[J], Biomaterials, 2002, 23(9): 1 981–1 987
Zheng J P, Luan L, Wang H Y, et al. Study on Ibuprofen/Montmorillonite Intercalation Composites as Drug Release System[J]. Appl. Clay Sci., 2007, 36(4): 297–301
Vergin H, Kikuta C, Mascher H, et al. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Different Formulations of Acyclovir[J]. Drug Res., 1995, 45(1): 508–519
Meadows K C, Dressman J B. Mechanism of Acyclovir Uptake in Rat Jejunum[J]. Pharm. Res., 1990, 7(3): 299–303
Tao Y Y, Lu Y F, Sun Y J, et al. Development of Mucoadhesive Microspheres of Acyclovir with Enhanced Bioavailability[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2009, 378(1–2): 30–36
Lewis L D, Fowle A S, Bittiner S B, et al. Human Gastrointestinal Absorption of Acyclovir from Tablet Duodenal Infusion and Sipped Solution[J]. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 1986, 21(4): 459–462
Stulzer H K, Lacerda L, Tagliari M P, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Cross-linked Malonylchitosan Microspheres for Controlled Release of Acyclovir[J]. Carbohyd. Polym., 2008, 73(3): 490–497
Rokhade A P, Patil S A, Aminabhavi T M. Synthesis and Characterization of Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Network Microspheres of Acrylamide Grafted Dextran and Chitosan for Controlled Release of Acyclovir[J]. Carbohyd. Polym., 2007, 67(4): 605–613
Zheng J P, Wang H Y, Zhuang H, et al. Intercalation of Amido Cationic Drug with Montmorillonite[J]. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater.Sci.Ed., 2007, 22(2): 250–252
Zheng J P, Li P, Ma Y L, et al. Gelatin/Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanocomposite. I. Preparation and Properties[J]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 86: 1189–1194
Chang Y H, Xiao L, Tang Q. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Thermosensitive Hydrogel Based on Chitosan and Gelatin Blends[J]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2009, 131(1): 400–407
Engstrom J D, Simpson D T, Lai E S, et al. Morphology of Protein Particles Produced by Spray Freezing of Concentrated Solutions[J]. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 2007, 65(2): 149–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J., Shan, J., Fan, Z. et al. Preparation and properties of gelatin-chitosan/montmorillonite drug-loaded microspheres. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 628–633 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0281-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0281-6