Abstract
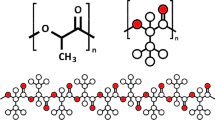
A new thermal ring-opening polymerization technique for 1, 1, 3, 3-tetra-ph enyl-1, 3-disilacyclobutane (TPDC) based on the use of metal nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation was investigated. This method facilitates the synthesis of polydiphenysilylenemethyle (PDPhSM) thin film, which is difficult to make by conventional methods because of its insolubility and high melting point. TPDC was first evaporated on silicon substrates and then exposed to metal nanoparticles deposition by pulsed laser ablation prior to heat treatment. The TPDC films with metal nanoparticles were heated in an electric furnace in air atmosphere to induce ring-opening polymerization of TPDC. The film thicknesses before and after polymerization were measured by a stylus profilometer. Since the polymerization process competes with re-evaporation of TPDC during the heating, the thickness ratio of the polymer to the monomer was defined as the polymerization efficiency, which depends greatly on the technology conditions. Therefore, a well trained radial base function neural network model was constructed to approach the complex nonlinear relationship. Moreover, a particle swarm algorithm was firstly introduced to search for an optimum technology directly from RBF neural network model. This ensures that the fabrication of thin film with appropriate properties using pulsed laser ablation requires no in-depth understanding of the entire behavior of the technology conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Rossignol, Y Nakata, H Nagai, et al. Fabrication of Poly(diphenylsilylenemethyle ne) and Poly(diphenylsiloxane) Thin Films Using Fine Metal Particles[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 1998,34(7):1317–1326
M Suzuki, Y Nakata, H Nagai, et al. Poly (diarylsilmethylene) s.2. Thermal and Mechanical Properties[J]. J.Polym.Sci. -Part B: Polym. Phys., 1996, 34(7): 131–1326
L Patrone, D Nelson, V I Safarov, S Giorgio, et al. Photoluminescence of Silicon Nanoclusters with Reduced Size Dispersion Produced by Laser Ablation[J]. J. Appl. Phys., 2000,87(8): 3593–4041
R G Song, M Yamaguchi, Q Nishimura, et al. Investigation of Metal Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation and Their Catalytic Activity[J]. Applied. Surface. Science, 2007, 253(4): 3093–3097
W M YANG, J YU, L Y HE, et al. Crystallization and Electrical Properties of(Ba0.4Pb0.3)Sr0.3TiO3 Thin Film by Pulsed Laser Deposition[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2007, 22(4):634–637
R G Song, M Yamaguchi, Q Nishimura, et al. Effect of Laser-ablated Copper Nanoparticles on Polymerization of 1,1,3,3-trtrapheny 1,1,3-disilacyclobutane[J]. Applied Physics A:Materials Science & Processing, 2004,78(6):867–875
Z F ZHOU, S M WANG. Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Preparation of Nanosized ZrO2 Powders by Evaporative Decomposition of Solutions[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2008,23(3):309–311
R G Song, Q Z Zhang. Heat Treatment Technique for 7175 Aluminum Alloy by an Artificial Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithm[J]. Jounal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 117(2): 84–88
S J Issam. Modeling Capability of the Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Topredict the Effect of the Hot Deformation Parameters on Thestrength of Al-base Metal Matrix Composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2003, 63(2): 63–67
J L Zhou, C D Zheng, L Yong, et al. PSO-based Neural Network Optimization and Its Utilization in a Boring Machine[ J]. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 178(5): 19–23
I T Cristian. The Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm: Convergence Analysis and Parameter Selection[J]. Information Processing Letters, 2003, 85(6): 317–325
Z Zhang, K Friedrich, K Velten. Prediction on Tribological Properties of Short Fibre Composites Using Artificial Neural Networks[J]. Wear, 2002, 252(7): 668–675
D S Broomhead, D Lowe. Multivariate Functional Interpolation and Adaptive Networks[J]. Complex System, 1988, 2(3): 321–355
B P Jong, K S Lee J R Shin,et al. A Particle Swarm Optimization for Economic Dispatch with Nonsmooth Cost Functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2005, 20(1): 34–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No.R405031), Jiaxing Science Planning Project(2009 2007), and the Education Department of Zhejiang Province (No.20051441)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, P., Song, R., Chai, G. et al. Optimization of laser ablation technology for PDPhSM matrix nanocomposite thin film by artificial neural networks-particle swarm algorithm. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 25, 188–193 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-2188-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-2188-z