Abstract
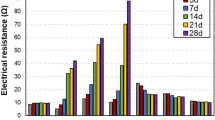
The influence of water content on the conductivity and piezoresistivity of cement-based material with carbon fiber (CF) and carbon black (CB) was investigated. The piezoresistivity of cement-based material with both CF and CB was compared with that of cement-based material with CF only, and the changes in electrical resistivity of cement-based material with both CF and CB under static and loading conditions in different drying and soaking time were studied. It is found that the piezoresistivity of cement-based material with both CF and CB has better repeatability and linearity than that of cement-based material with CF only. The conductivity and the sensitivity of piezoresistive cement-based material with both CF and CB are enhanced as the water content in piezoresistive cement-based material increases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P C Aitcin. Cements of Yesterday and Today Concrete of Tomorrow[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2000,30: 1 349–1 359
D D L Chung. Self-monitoring Structural Materials[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng.,1998,22: 57–78
E Hammond, T D Robson. Comparison of Electrical Properties of Various Cements and Concretes[J]. Eng., 1995, 166: 114–115
T C Hou, J P Lynch. Conductivity-based Strain Monitoring and Damage Characterization of Fiber Reinforced Cementitious Structural Components[C]. Proc of SPIE-Smart Structures and Materials 2005-Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems, San Diego, 2005
Z F Hou, Z Q Li, J J Wang. Influence of Aggregates on Properties of Carbon Fiber Electrically Conductive Concrete for Deicing or Snow Melting[J]. J. Wuhan University of Technology-Transport. Sci. Eng. Ed., 2005, 29(5): 704–706
Q Z Mao, P H Chen, B Y Zhao, et al. A Study on the Compression Sensibility and Mechanical Model of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement Smart Material [J]. Acta Mat. Compos. Sin., 1997, 10: 338–344
B G Han, X Yu, E Kwon. A Self-sensing Carbon Nanotube/Cement Composite for Traffic Monitoring[J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20: 445501
B G Han, J P Ou. Embedded Piezoresistive Cement-based Stress/Strain Sensor[J]. Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys., 2007, 138: 294–298
H G Xiao, H Li. Strain Sensing Property of Carbon Black Filled Cement-based Composites[C]. Proc 2th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, Shenzheng, 2005
B Chen, K R Wu, W Yao. Piezoresistivity in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement Based Composites[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, 20(6): 746–750
H Li, H G Xiao, J P Ou. Effect of Compressive Strain on Electrical Resistivity of Carbon Black-filled Cement-based Composites[J]. Cem. Concr. Compos., 2006, 28:824–828
S H Wen, D D L Chung. Carbon Fiber-reinforced Cement as a Strain-sensing Coating[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2001, 31: 665–667
L X Zheng, Z Q Li, X H Song. Corrosion Monitoring of Rebar by Compression Sensitivity of CFRC[J]. J. Exp. Mech., 2004, 19(2): 206–210
Z Q Shi, D D L Chung. Carbon Fiber-reinforced Concrete for Traffic Monitoring and Weighing in Motion[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 1999, 29: 435–439
B G Han, J P Ou. Smart Cement Paste Standard Stress/Strain Sensors and Self-sensory Concrete Members[C]. Proc 2th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, Shenzheng, 2005
B G Han, X C Guan, J P Ou. Electrode Design, Measuring Method and Data Acquisition System of Carbon Fiber Cement Paste Piezoresistive Sensors [J]. Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys., 2007,135: 360–369
Q Z Mao, B Y Zhao, D R Shen, et al. Study on the Compression Sensibility of Cement Matrix Carbon Fiber Composite[ J]. Acta Mat. Compos. Sin., 1996, 13(4): 8–11
B Chen, K R Wu, W Yao. Conductivity of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement-based Composites[J]. Cem. Concr. Compos., 2004, 26: 291–297
C F J Balta, R K Bayer, T A Ezquerra. Electrical Conductivity of Polyethylene-carbon-fiber Composites Mixed with Carbon Black[J]. J. Mater. Sci., 1998, 23(4): 1 411–1 415
P K Pramanik, D Khastgir, S K De, et al. Pressure-sensitive Electrically Conductive Nitrile Rubber Composites Filled with Particulate Carbon Black and Short Carbon Fiber [J]. J. Mater. Sci., 1990, 25(9): 3 848–3 853
M Q Sun, Z Q Li, Q P Liu. The Electromechanical Effect of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement[J]. Carbon, 2000,40:2 263–2 284
X C Guan, B G Han, M H Tang, et al. Temperature and Humidity Variation of Specific Resistance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement[C]. Proc of SPIE -Smart Structures and Materials 2005- Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems, San Diego, 2005
Y L Wang, X H Zhao. Positive and Negative Pressure Sensitivities of Carbon Fiber-reinforced Cement-matrix Composites and Their Mechanism[J]. Acta Mat. Compos. Sin., 2005, 22(4): 40–46
Z G Zhang. Functional Composite Materials [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 1–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50238040, 50538020), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 20060390803), and the High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2002AA335010)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, B., Zhang, L. & Ou, J. Influence of water content on conductivity and piezoresistivity of cement-based material with both carbon fiber and carbon black. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 25, 147–151 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-1147-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-1147-z