Abstract
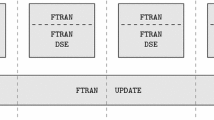
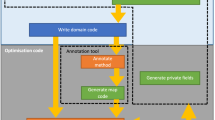
Based on the Greek term monolithos (stone consisting of one single block) Kallrath (Comput Chem Eng 33:1983–1993, 2009) introduced the term polylithic for modeling and solution approaches in which mixed integer or non-convex nonlinear optimization problems are solved by tailor-made methods involving several models and/or algorithmic components, in which the solution of one model is input to another one. This can be exploited to initialize certain variables, or to provide bounds on them (problem-specific preprocessing). Mathematical examples of polylithic approaches are decomposition techniques, or hybrid methods in which constructive heuristics and local search improvement methods are coupled with exact MIP algorithms. Tailor-made polylithic solution approaches with thousands or millions of solve statements are challenges on algebraic modeling languages. Local objects and procedural structures are almost necessary. Warm-start and hot-start techniques can be essential. The effort of developing complex tailor-made polylithic solutions is awarded by enabling us to solve real-world problems far beyond the limits of monolithic approaches and general purpose solvers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnhart C., Johnson E.L., Nemhauser G.L., Savelsberg M.W.P., Vance P.H.: Branch-and-price: column generation for solving huge integer programs. Oper. Res. 46(3), 316–329 (1998)
Beale E., Forrest J.: Global optimization using special ordered sets. Math. Progr. 10, 52–69 (1976)
Benders J.F.: Partitioning procedures for solving mixed-variables programming problems. Numerische Mathematik 4, 238–252 (1962)
Benoist T., Bourreau E.: Fast gloabl filtering for eternity II. Const. Progr. Lett. 3, 35–50 (2008)
Birge J.R., Louveaux F.V.: Introduction to Stochastic Programming, Operations Research and Financial Engineering. Springer, New York (2000)
Borisovsky P., Dolgui A., Eremeev A.: Genetic algorithms for supply management problem with lower-bounded demands. In: Dolgui, A., Morel, G., Pereira, C. (eds) Information Control Problems in Manufacturing 2006: A Proceedings volume from the 12th IFAC International Symposium, St Etienne, France, 17–19 May 2006, vol. 3, pp. 521–526. Elsevier, Dordrecht (2006)
Danna E., Rothberg E., Le Pape C.: Exploring relation induced neighborhoods to improve MIP solutions. Math. Progr. 102, 71–90 (2005)
Dantzig B., Wolfe P.: The decomposition algorithm for linear programming. Oper. Res. 8, 101–111 (1960)
de Farias I.R. Jr, Johnson E.L., Nemhauser G.L.: A generalized assignment problem with special ordered sets: a polyhedral approach. Math. Progr. Ser. A 89, 187–203 (2000)
de Farias I.R. Jr, Zhao M., Zhao H.: A special ordered set approach for optimizing a discontinuous separable piecewise linear function. Oper. Res. Lett. 36, 234–238 (2008)
Desrochers M., Desrosiers J., Solomon M.M.: A new optimization algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with time windows. Oper. Res. 40(2), 342–354 (1992)
Van Dinter, J., Rebennack, S., Kallrath, J., Denholm, P., Newman, A.: The Unit commitment model: a tight formulation for benders’ decomposition with a case study. Ann. Oper. Res. (2011, in press)
Fischetti M., Glover F.: The feasibility pump. Math. Progr. 104, 91–104 (2005)
Fischetti M., Lodi A.: Local branching. Math. Progr. 98, 23–47 (2003)
Floudas C.A.: Nonlinear and Mixed-Integer Optimization: Fundamentals and Applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1995)
Floudas C.A.: Deterministic Global Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2000)
Floudas C.A., Gounaris C.E.: A review of recent advances in global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 45, 3–38 (2009)
Gilmore P.C., Gomory R.E.: A linear programming approach to the cutting stock problem. Oper. Res. 9, 849–859 (1961)
Gilmore P.C., Gomory R.E.: A linear programming approach to the cutting stock problem, part II. Oper. Res. 11, 863–888 (1963)
Harjunkoski I., Jain V., Grossmann I.E.: Hybrid mixed-integer/constrained logic programming strategies for solving scheduling and combinatorial optimization problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 24, 337–343 (2000)
Horst, R., Pardalos, P.M. (eds): Handbook of Global Optimization. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1995)
Howitt, R., Msangi, S., Reynaud, A., Knapp, K.: Using polynomial approximations to solve stochastic dynamic programming problems: or a “betty crocker” approach to SDP. Technical report, Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics, University of California at Davis, Davis (2002)
Ignizio J.P.: Goal Programming and Extensions. Heath, Lexington (1976)
Jain V., Grossmann I.E.: Algorithms for hybrid MILP/CP models for a class of optimization problems. IFORMS J. Comput. 13, 258–276 (2001)
Johnson E.L., Kostreva M.M., Suhl U.H.: Solving 0-1 integer programming problems arising from large scale planning models. Oper. Res. 33, 803–819 (1985)
Kallrath J.: Mixed-integer nonlinear programming applications. In: Ciriani, T.A., Gliozzi, S., Johnson, E.L., Tadei, R. (eds) Operational Research in Industry, pp. 42–76. Macmillan, Houndmills (1999)
Kallrath J.: Modeling difficult optimization problems. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, pp. 2284–2297. Springer, New York (2008)
Kallrath J.: Combined strategic design and operative planning in the process industry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 33, 1983–1993 (2009)
Kallrath, J.: Solving difficult real world optimization problems: polylithic modeling and solution approaches with GAMS examples. Springer, Germany (2012, in press)
Kallrath J., Maindl T.I.: Real Optimization with SAP-APO. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Kalvelagen, E.: Branch-and-bound methods for an MINLP model with semi-continuous variables, discontinued on http://www.gams.com (2003)
Karuppiah R., Grossmann I.E.: A Lagrangean based branch-and-cut algorithm for global optimization of nonconvex mixed-integer nonlinear programs with decomposable structures. J. Glob. Optim. 41, 163–186 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10898-007-9203-8
Lin X., Floudas C.A., Kallrath J.: Global solution approaches for nonconvex MINLP problems in product portfolio optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 32, 417–431 (2005)
Lohmann, T.: Practical stochastic optimization using algebraic modeling systems. Master’s thesis, Technische Universität Braunschweig (2011)
Lübbecke M.E., Desrosiers J.: Selected topics in column generation. Oper. Res. 53(6), 1007–1023 (2005)
Maniezzo V., Stützle T., Voss S.: Hybridizing Metaheuristics and Mathematical Programming, Annals of Information Systems. Springer, Redwoord City (2010)
Maravelias C.T., Grossmann I.E.: A hybrid MILP/CP decomposition approach for the continuous time scheduling of multipurpose batch plants. Comput. Chem. Eng. 28, 1921–1949 (2004)
Misener R., Floudas C.A.: Piecewise-linear approximations of multidimensional functions. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 145, 120–147 (2010)
Muñoz, J., Gutierrez, G., Sanchis, A.: Evolutionary techniques in a constraint satisfaction problem: Puzzle Eternity II. In: Proceedings 2009 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 2985–2991 (2009)
Pochet Y., Wolsey L.A.: Production Planning by Mixed Integer Programming. Springer, New York (2006)
Rebennack S., Kallrath J., Pardalos P.M.: Column enumeration based decomposition techniques for a class of non-convex MINLP problems. J. Glob. Optim. 43, 277–297 (2009)
Rebennack S., Nahapetyan A., Pardalos P.M.: Bilinear modeling solution approach for fixed charged network flow problems. Optim. Lett. 3, 347–355 (2009)
Rebennack, S., Oswald, M., Theis, D.O., Seitz, H., Reinelt, G., Pardalos, P.M.: A branch and cut solver for the maximum stable set problem. J. Comb. Optim. doi:10.1007/s10878-008-9175-8 (2011)
Rebennack, S., Reinelt, G., Pardalos, P.M.: A tutorial on branch and cut algorithms for the maximum stable set problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. doi:10.1111/j.1475-3995.2011.00805.x (2011)
Roe B., Papageorgiou L.G., Shah N.: A hybrid MILP/CLP algorithm for multipurpose batch process scheduling. Comput. Chem. Eng. 29, 1277–1291 (2005)
Romero C.: Handbook of Critical Issues in Goal Programming. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1991)
Savelsbergh M.W.P.: Preprocessing and probing techniques for mixed integer programming problems. ORSA J. Comput. 6, 445–454 (1994)
Savelsbergh M.W.P.: Branch-and-price: integer programming with column generation. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, pp. 218–221. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
Schniederjans M.J.: Goal Programming: Methodology and Applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (1995)
Schrage L.: Optimization Modeling with LINGO. LINDO Systems, Inc., Chicago (2006)
Till J., Sand G., Engell S., Emmerich M., Schönemann L.: A new hybrid algorithm for solving two-stage stochastic problems by combining evolutionary and mathematical programming methods. In: Puigjaner, L., Espuña, A. (eds) Proceedings of European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering (ESCAPE)-15, pp. 187–192. Elsevier, Dordrecht (2005)
Timpe C.: Solving planning and scheduling problems with combined integer and constraint programming. OR Spectr. 24, 431–448 (2002)
Vielma J.P., Ahmed S., Nemhauser G.: Mixed-integer models for nonseparable piecewise-linear optimization: unifying framework and extensions. Oper. Res. 53, 303–315 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallrath, J. Polylithic modeling and solution approaches using algebraic modeling systems. Optim Lett 5, 453–466 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-011-0320-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-011-0320-4